Abstract
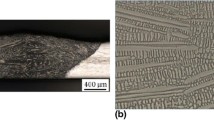
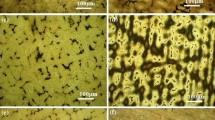
This study examined the effects of a variety of metallurgical factors on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of superaustenitic stainless steel welds. First, the effects of the sigma (σ)-phase on the corrosion behavior were studied by means of a three-dimensional-atom probe. Cr and Mo depletion areas formed around the σ-phases which are precipitated in the interdendritic area were clearly observed. Second, the effects of oxide inclusion on the pitting corrosion of the steel welds were analyzed. The utilization of high resolution transmission electron microscope clearly demonstrated that the thickness and Cr content of the passive film formed on the steel surface decreased significantly with decreasing distance to the oxide inclusion, resulting in a deterioration of the corrosion resistance. Third, the effects of alloying elements, Cu and Al, were evaluated using an electrochemical polarization technique. This confirmed that Cu has a detrimental effect on the resistance to localized corrosion of the steel. The addition of Al up to 0.25 wt% had no significant effects on corrosion resistance in a chloride environment despite the presence of an Al-based oxide layer (Al2O3) on the outermost surface.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.T. Kim, S.Y. Kim, I.S. Lee, Y.S. Park, M.C. Shin, and Y.S. Kim: Effects of shielding gases on the microstructure and localized corrosion of tube-to-tube sheet welds of super austenitic stainless steel for seawater cooled condenser. Corros. Sci. 53, 2611 (2011).
G. Mori and D. Bauernfeind: Pitting and crevice corrosion of superaustenitic stainless steels. Mater. Corros. 55, 164 (2004).
T.G. Gooch: Corrosion behavior of welded stainless steel. Weld. J. 75, 135s (1996).
ASM International: Corrosion of Weldments (ASM International, Materials Park, 2006).
S.W. Banovic, J.N. Dupoint, and A.R. Marder: Dilution and microsegregation in dissimilar metal welds between super austenitic stainless steel and nickel base alloys. Sci. Technol. Weld. Joining 7, 374 (2002).
S.K. Nam, S.J. Park, H.S. Na, and C.Y. Kang: Effect of welding thermal cycle on microstructure and pitting corrosion property of multi-pass weldment of super duplex stainless steel. J. Weld. Joining 28, 18 (2010).
P. Paulraj and R. Garg: Effect of intermetallic phases on corrosion behavior and mechanical properties of duplex stainless steel and super-duplex stainless steel. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 9, 87 (2015).
S.H. Jang, S.T. Kim, I.S. Lee, and Y.S. Park: Effect of shielding gas composition on phase transformation and mechanism of pitting corrosion of hyper duplex stainless steel welds. Mater. Trans. 52, 1228 (2011).
P. Marcus and I. Olefjord: A round robin on combined electrochemical and AES/ESCA characterization of the passive films on Fe Cr and Fe Cr Mo alloys. Corros. Sci. 28, 589 (1998).
R. Qvarfort: Some observations regarding the influence of molybdenum on the pitting corrosion resistance of stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 40, 215 (1998).
J.O. Nilsson and A. Wilson: Influence of isothermal phase transformations on toughness and pitting corrosion of super duplex stainless steel SAF 2507. Mater. Sci. Technol. 9, 545 (1993).
M.E. Wilms, V.J. Gadgil, J.M. Krougman, and F.P. Ijsseling: The effect of σ-phase precipitation at 800 °C on the corrosion resistance in sea-water of a high alloyed duplex stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 36, 871 (1994).
K. Ravindranath and S.N. Malhotra: The influence of aging on the intergranular corrosion of 22 chromium-5 nickel duplex stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 37, 121 (1995).
K. Ravindranath and S.N. Malhotra: Influence of aging on intergranular corrosion of a 25% chromium-5% nickel duplex stainless steel. Corrosion 50, 318 (1994).
G.S. Frankel: Pitting corrosion of metals. J. Electrochem. Soc. 145, 2186 (1998).
H.Y. Ha, C.J. Park, and H.S. Kwon: Effect of non-metallic inclusions on the initiation of pitting corrosion in 11% Cr ferritic stainless steel examined by micro-droplet cell. Corros. Sci. 49, 1266 (2007).
G. Eklund: Initiation of pitting at sulfide inclusions in stainless steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 121, 467 (1974).
G. Wranglen: Pitting and sulphide inclusions in steel. Corros. Sci. 14, 331 (1974).
E.G. Webb, T. Suter, and R.C. Alkire: Microelectrochemical measurements of the dissolution of single MnS inclusions, and the prediction of the critical conditions for pit initiation on stainless steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 148(5), B186 (2001).
D.E. Williams and Y.Y. Zhu: Explanation for initiation of pitting corrosion of stainless steels at sulfide inclusions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 147(5), 1763 (2000).
Z. Szklarska-Smialowska: Influence of sulfide inclusions on the pitting corrosion of Steels. Corrosion 28, 388 (1972).
A. Yamamoto, T. Ashiura, and E. Kamisaka: Mechanism of improvement on corrosion resistance by copper addition to ferritic stainless steels. Boshoku Gijutsu 35, 448 (1986).
S.T. Kim and Y.S. Park: Effect of copper addition on corrosion behavior of high performance austenitic stainless steel in highly concentrated sulfuric acid solution. Corrosion 63, 114 (2007).
S.H. Jeon, S.T. Kim, I.S. Lee, J.H. Park, K.T. Kim, J.S. Kim, and Y.S. Park: Effects of copper addition on the formation of inclusions and the resistance to pitting corrosion of high performance duplex stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 53, 1408 (2011).
A. Pardo, M.C. Merino, M. Carboneras, A.E. Coy, and R. Arrabal: Pitting corrosion behavior of austenitic stainless steels with Cu and Sn additions. Corros. Sci. 49, 510 (2007).
M. Gurram, K. Adepu, R.R. Pinninti, and M.R. Gankidi: Effect of copper and aluminium addition on mechanical properties and corrosion behavior of AISI 430 ferritic stainless steel gas tungsten arc welds. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2, 238 (2013).
X. Zhang, L. Fan, Y. Xu, J. Li, X. Xiao, and L. Jiang: Effect of aluminum on microstructure, mechanical properties and pitting corrosion resistance of ultra-pure 429 ferritic stainless steels. Mater. Des. 65, 682 (2015).
S.J. Kim and S.G. Hong: A study on pitting initiation mechanism of super-austenitic stainless steel weld in chloride environment. J. Mater. Res. 31, 3345 (2016).
ASTM G48: Standard Test Methods for Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steels and Related Alloys by Use of Ferric Chloride Solution (ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 2011).
S.J. Kim and S.G. Hong: Evaluation of localized corrosion resistance and clarification of the corrosion mechanism of super austenitic stainless steel weld. POSCO Technol. Rep. 20(1), 1–8 (2015).
D.A. Porter and K.E. Easterling: Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloys (Chapman & Hall, London, UK, 1997).
I. Kaprálik: Thermal expansion of spinels MgCr2O4, MgAl2O4 and MgFe2O4. Chem. Zvesti 23, 665 (1969).
H.S. Khatak and B. Raj: Corrosion of Austenitic Stainless Steels, Mechanism, Mitigation and Monitoring (Alpha Science International, Oxford, UK, 2002).
O. Smuk, P. Nenonen, H. Hänninen, and J. Liimatainen: Microstructures of a powder metallurgy-hot-isostatically pressed super duplex stainless steel forming in industrial heat treatments. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 35A, 2103 (2004).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This paper was supported by Sunchon National University Research Fund in 2016.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.J., Hong, S.G. & Oh, Ms. Effect of metallurgical factors on the pitting corrosion behavior of super austenitic stainless steel weld in an acidic chloride environment. Journal of Materials Research 32, 1343–1350 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.65
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.65