Abstract
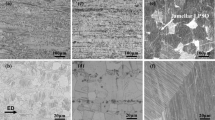
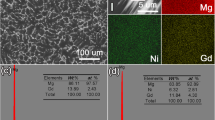
In this paper, corrosion behaviors of Mg–10Gd–5Y–2Zn–0.5Zr (wt%) alloy (GWZ1052K) in different aging stages are investigated using immersion tests and electrochemical measurements in 3.5 wt% NaCl aqueous solution. The corrosion resistance is found to increase from the solution-anneal to peak-aged condition, which is attributed to microstructure evolutions of β′ precipitates and nearly unchanged long period stacking ordered (LPSO) structures. The broken network LPSO structures no more act as corrosion barriers, thus inversely worsening the galvanic corrosion. β′ precipitates uniformly surround the LPSO lamellas, those partly enhancing corrosion resistance. The potentiodynamic polarization curves also show the best corrosion resistance in the peak-aged stage, suggesting the similar tendency of corrosion behaviors. And the results of electrochemical impedance spectrum are consistent with the morphology of the corrosion surface. Further equivalent circuit is established to investigate the corrosion mechanism.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.L. Shreir: Corrosion. Metal/environment Reactions, Vol. I (Taylor and Francis, Oxford, England, 1976).
C.B. Wilson, K.G. Claus, M.R. Earlam, J.E. Hillis, C.B. Wilson, K.G. Claus, M.R. Earlam, and J.E. Hillis: Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys (Macmillan Education, London, U.K., 1978).
L.L. Rokhlin: Magnesium Alloys Containing Rare Earth Metals (Taylor and Francis, Oxford, England, 2003).
W. Ding, D. Li, Q. Wang, and Q. Li: Microstructure and mechanical properties of hot-rolled Mg–Zn–Nd–Zr alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 483, 228 (2008).
H.R.J. Nodooshan, W. Liu, G. Wu, Y. Rao, C. Zhou, S. He, W. Ding, and R. Mahmudi: Effect of Gd content on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloys under peak-aged condition. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 615, 79 (2014).
S. Pang, G. Wu, W. Liu, M. Sun, Y. Zhang, Z. Liu, and W. Ding: Effect of cooling rate on the microstructure and mechanical properties of sand-casting Mg–10Gd–3Y–0.5Zr magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 562, 152 (2013).
W. Wang, G. Wu, Q. Wang, Y. Huang, and W. Ding: Gd contents, mechanical and corrosion properties of Mg–10Gd–3Y–0.5Zr alloy purified by fluxes containing GdCl3 additions. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 507, 207 (2009).
G. Wu, Y. Zhang, W. Liu, and W. Ding: Microstructure evolution of semi-solid Mg–10Gd–3Y–0.5Zr alloy during isothermal heat treatment. J. Magnesium Alloys 1, 39 (2013).
W.X. Wu, L. Jin, J. Dong, Z.Y. Zhang, and W.J. Ding: Hot deformation behavior and microstructural evolution of Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 747–748, 320 (2013).
X. Zheng, J. Dong, D. Yin, W. Liu, F. Wang, L. Jin, and W. Ding: Forgeability and die-forging forming of direct chill casting Mg–Nd–Zn–Zr magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 3690 (2010).
T. Honma, T. Ohkubo, S. Kamado, and K. Hono: Effect of Zn additions on the age-hardening of Mg–2.0Gd–1.2Y–0.2Zr alloys. Acta Mater. 55, 4137 (2007).
X.B. Liu, R.S. Chen, and E.H. Han: Effects of ageing treatment on microstructures and properties of Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloys with and without Zn additions. J. Alloys Compd. 465, 232 (2008).
C. Xu, S.W. Xu, M.Y. Zheng, K. Wu, E.D. Wang, S. Kamado, G.J. Wang, and X.Y. Lv: Microstructures and mechanical properties of high-strength Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr alloy sheets processed by severe hot rolling. J. Alloys Compd. 524, 46 (2012).
C. Xu, M.Y. Zheng, S.W. Xu, K. Wu, E.D. Wang, S. Kamado, G.J. Wang, and X.Y. Lv: Ultra high-strength Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr alloy sheets processed by large-strain hot rolling and ageing. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 547, 93 (2012).
C. Xu, M.Y. Zheng, S.W. Xu, K. Wu, E.D. Wang, S. Kamado, G.J. Wang, and X.Y. Lv: Microstructure and mechanical properties of rolled sheets of Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr alloy: As-cast versus as-homogenized. J. Alloys Compd. 528, 40 (2012).
K. Yamada, Y. Okubo, M. Shiono, H. Watanabe, S. Kamado, and Y. Kojima: Alloy development of high toughness Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr alloys. Mater. Trans. 47, 1066 (2006).
Q. Yang, B.L. Xiao, Q. Zhang, M.Y. Zheng, and Z.Y. Ma: Exceptional high-strain-rate superplasticity in Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr alloy with long-period stacking ordered phase. Scr. Mater. 69, 801 (2013).
Z. Yang, Y.C. Guo, J.P. Li, F. He, F. Xia, and M.X. Liang: Plastic deformation and dynamic recrystallization behaviors of Mg–5Gd–4Y–0.5Zn–0.5Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 485, 487 (2008).
Z. Yang, J.P. Li, Y.C. Guo, T. Liu, F. Xia, Z.W. Zeng, and M.X. Liang: Precipitation process and effect on mechanical properties of Mg–9Gd–3Y–0.6Zn–0.5Zr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 454–455, 274 (2007).
S. Zhang, G.Y. Yuan, C. Lu, and W.J. Ding: The relationship between (Mg, Zn) 3 RE phase and 14H-LPSO phase in Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr alloys solidified at different cooling rates. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 3515 (2011).
Y.X. Li, G.Z. Zhu, D. Qiu, D.D. Yin, Y.H. Rong, and M.X. Zhang: The intrinsic effect of long period stacking ordered phases on mechanical properties in Mg–RE based alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 660, 252 (2015).
D.D. Yin, Q.D. Wang, Y. Gao, C.J. Chen, and J. Zheng: Effects of heat treatments on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–11Y–5Gd–2Zn–0.5Zr (wt%) alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 1696 (2011).
S. Zhang, W. Liu, X. Gu, C. Lu, G. Yuan, and W. Ding: Effect of solid solution and aging treatments on the microstructures evolution and mechanical properties of Mg–14Gd–3Y–1.8Zn–0.5Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 557, 91 (2013).
J. Zheng and B. Chen: Interactions between long-period stacking ordered phase and β′ precipitate in Mg–Gd–Y–Zn–Zr alloy: Atomic-scale insights from HAADF-STEM. Mater. Lett. 176, 223 (2016).
J. Zheng, X. Xu, K. Zhang, and B. Chen: Novel structures observed in Mg–Gd–Y–Zr during isothermal ageing by atomic-scale HAADF-STEM. Mater. Lett. 152, 287 (2015).
J.X. Zheng, Z. Li, L.D. Tan, X.S. Xu, R.C. Luo, and B. Chen: Precipitation in Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloy: Atomic-scale insights into structures and transformations. Mater. Charact. 117, 76 (2016).
A. Atrens: Understanding magnesium corrosion, recent progress at UQ, Vol. III (Curran Associates, Perth, Australia, 2011), pp. 1893.
A. Atrens and W. Dietzel: The negative difference effect and unipositive Mg+. Adv. Eng. Mater. 9, 292 (2007).
A. Atrens, G.L. Song, F. Cao, Z. Shi, and P.K. Bowen: Advances in Mg corrosion and research suggestions. J. Alloys Compd. 1, 177 (2013).
A. Atrens, G.L. Song, M. Liu, Z. Shi, F. Cao, and M.S. Dargusch: Review of recent developments in the field of magnesium corrosion: Recent developments in Mg corrosion. Adv. Eng. Mater. 17, 400 (2015).
F. Cao, G.L. Song, and A. Atrens: Corrosion and passivation of magnesium alloys. Corros. Sci. 111, 835 (2016).
G. Song and A. Atrens: Understanding the Corrosion Mechanism: A Framework for Improving the Performance of Magnesium Alloys (John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New Jersey, USA, 2004); p. 507.
G.L. Song and A. Atrens: Corrosion mechanisms of magnesium alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 1, 11 (1999).
S. Thomas, N.V. Medhekar, G.S. Frankel, and N. Birbilis: Corrosion mechanism and hydrogen evolution on Mg. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 19, 85 (2015).
G. Williams, N. Birbilis, and H.N. Mcmurray: The source of hydrogen evolved from a magnesium anode. Electrochem. Commun. 36, 1 (2013).
G. Williams, A.L. Dafydd, H.N. Mcmurray, and N. Birbilis: The influence of arsenic alloying on the localised corrosion behaviour of magnesium. Electrochim. Acta 219, 401 (2016).
B.L. Dong: High temperature oxidation of AZ31 + 0.3 wt% Ca and AZ31 + 0.3 wt% CaO magnesium alloys. Corros. Sci. 70, 243 (2013).
D. Sachdeva: Insights into microstructure based corrosion mechanism of high pressure die cast AM50 alloy. Corros. Sci. 60, 18 (2012).
J. Chang, X. Guo, S. He, P. Fu, L. Peng, and W. Ding: Investigation of the corrosion for Mg–x Gd–3Y–0.4Zr ( x = 6, 8, 10, 12 wt%) alloys in a peak-aged condition. Corros. Sci. 50, 166 (2008).
S. Liang, D. Guan, and X. Tan: The relation between heat treatment and corrosion behavior of Mg–Gd–Y–Zr alloy. Mater. Des. 32, 1194 (2011).
L.M. Peng, J.W. Chang, and X.W. Guo: Influence of heat treatment and microstructure on the corrosion of magnesium alloy Mg–10Gd–3Y–0.4Zr. J. Appl. Electrochem. 39, 913 (2009).
M. Sun, G. Wu, W. Wang, and W. Ding: Effect of Zr on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of Mg–10Gd–3Y magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 523, 145 (2009).
T. Zhang, X. Liu, Y. Shao, G. Meng, and F. Wang: Electrochemical noise analysis on the pit corrosion susceptibility of Mg–10Gd–2Y–0.5Zr, AZ91D alloy and pure magnesium using stochastic model. Corros. Sci. 50, 3500 (2008).
J. Zhang, J. Xu, W. Cheng, C. Chen, and J. Kang: Corrosion behavior of Mg–Zn–Y alloy with long-period stacking ordered structures. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28, 1157 (2012).
X. Zhang, Z. Ba, Q. Wang, Y. Wu, Z. Wang, and Q. Wang: Uniform corrosion behavior of GZ51K alloy with long period stacking ordered structure for biomedical application. Corros. Sci. 88, 1 (2014).
X. Zhang, Z. Ba, Z. Wang, and Y. Xue: Microstructures and corrosion behavior of biodegradable Mg–6Gd–x Zn–0.4Zr alloys with and without long period stacking ordered structure. Corros. Sci. 105, 68 (2016).
X. Zhang, Y. Wu, Y. Xue, Z. Wang, and L. Yang: Biocorrosion behavior and cytotoxicity of a Mg–Gd–Zn–Zr alloy with long period stacking ordered structure. Mater. Lett. 86, 42 (2012).
J.N. Hryn: An Hydrogen Evolution Method for the Estimation of the Corrosion Rate of Magnesium Alloys (John Wiley & Sons, Inc, New Jersey, USA, 1993).
F. Cao, Z. Shi, J. Hofstetter, P.J. Uggowitzer, G. Song, M. Liu, and A. Atrens: Corrosion of ultra-high-purity Mg in 3.5% NaCl solution saturated with Mg(OH)2. Corros. Sci. 75, 78 (2013).
F. Cao, Z. Shi, G.L. Song, M. Liu, and A. Atrens: Corrosion behaviour in salt spray and in 3.5% NaCl solution saturated with Mg(OH)2 of as-cast and solution heat-treated binary Mg–X alloys: X = Mn, Sn, Ca, Zn, Al, Zr, Si, Sr. Corros. Sci. 76, 60 (2013).
Z. Shi and A. Atrens: An innovative specimen configuration for the study of Mg corrosion. Corros. Sci. 53, 226 (2011).
G.V. Baril, C. Blanc, M. Keddam, and N. PéBèRe: Local electrochemical impedance spectroscopy applied to the corrosion behavior of an AZ91 magnesium alloy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 150, B488 (2003).
N. Pebere, C. Riera, and F. Dabosi: Investigation of magnesium corrosion in aerated sodium sulfate solution by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta. 35, 555 (1990).
A.L. Rudd, C.B. Breslin, and F. Mansfeld: The corrosion protection afforded by rare earth conversion coatings applied to magnesium. Corros. Sci. 42, 275 (2000).
L.B. Tong, Q.X. Zhang, Z.H. Jiang, J.B. Zhang, J. Meng, L.R. Cheng, and H.J. Zhang: Microstructures, mechanical properties and corrosion resistances of extruded Mg–Zn–Ca–x Ce/La alloys. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 62, 57 (2016).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research is supported by open fund of the State Key Laboratory of Refractories and Metallurgy (Grant No. G201702). Thanks to Frontier Research Center for Materials Structure, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, for its supports of JEM-ARM200F Atomic Scale High Angle Annular Dark Field-Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (HAADF-STEM) and FEI Versa 3D Dual Beam Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FE-SEM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, Y., Chen, X. & Chen, B. Influence of interactions between β′ precipitates and long period stacking ordered structures on corrosion behaviors of Mg–10Gd–5Y–2Zn–0.5Zr (wt%) alloy. Journal of Materials Research 33, 745–757 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.448
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.448