Abstract
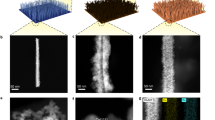
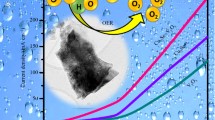
Herein, we report the synthesis of Cu(OH)2 nanobelts with high yield at low cost by a simple aqueous solution reaction. The Cu(OH)2-FTO electrode was then fabricated by a facile electrophoresis deposition method with the as-prepared Cu(OH)2 nanobelts, which require no binding agents. By subsequent heat treatment at 300 °C for 2 h, the Cu(OH)2-FTO electrode was converted to the CuO-FTO electrode. The investigation of electrocatalysis of the Cu(OH)2-FTO and CuO-FTO electrodes for water oxidation was conducted in a 0.2 M phosphate buffer solution at pH 12. The CuO-FTO electrode can catalyze water oxidation with an impressive onset overpotential of 370 mV and an overpotential of 500 mV for a current density of 1 mA/cm2 with a low Tafel slope of 57 mV/dec. This facile fabrication strategy is appealing for realizing the practical application of Cu-based electrocatalysts for water oxidation and is expected to be extended to prepare other heterocatalyst electrodes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.B. Gray: Powering the planet with solar fuel. Nat. Chem. 1, 7 (2009).
D.G. Nocera: Chemistry of personalized solar energy. Inorg. Chem. 48, 10001–10017 (2009).
N. Nelson and A. Ben-Shem: The complex architecture of oxygenic photosynthesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 5, 971–982 (2004).
T.R. Cook, D.K. Dogutan, S.Y. Reece, Y. Surendranath, T.S. Teets, and D.G. Nocera: Solar energy supply and storage for the legacy and nonlegacy worlds. Chem. Rev. 110, 6474–6502 (2010).
M.G. Walter, E.L. Warren, J.R. McKone, S.W. Boettcher, Q. Mi, E.A. Santori, and N.S. Lewis: Solar water splitting cells. Chem. Rev. 110, 6446–6473 (2010).
J.A. Turner: A realizable renewable energy future. Science 285, 687–689 (1999).
D.K. Zhong and D.R. Gamelin: Photoelectrochemical water oxidation by cobalt catalyst (“Co–Pi”)/α-Fe2O3 composite photoanodes: Oxygen evolution and resolution of a kinetic bottleneck. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 4202–4207 (2010).
R. Cao, W. Lai, and P. Du: Catalytic water oxidation at single metal sites. Energy Environ. Sci. 5, 8134 (2012).
J. Barber: Photosynthetic energy conversion: Natural and artificial. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 185–196 (2009).
A. Harriman, I.J. Pickering, J.M. Thomas, and P.A. Christensen: Metal-oxides as heterogeneous catalysts for oxygen evolution under photochemical conditions. J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1 (84), 2795–2806 (1988).
J. Horkans and M.W. Shafer: Investigation of electrochemistry of a series of metal dioxides with rutile-type structure—MoO2, WO2, ReO2, RuO2, OsO2, and IrO2. J. Electrochem. Soc. 124, 1202–1207 (1977).
M. Carmo, D.L. Fritz, J. Merge, and D. Stolten: A comprehensive review on PEM water electrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38, 4901–4934 (2013).
M. Chen, Y. Wu, Y. Han, X. Lin, J. Sun, W. Zhang, and R. Cao: An iron-based film for highly efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution from neutral aqueous solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 21852–21859 (2015).
K.S. Joya, Y.F. Joya, and H.J.M. de Groot: Ni-based electrocatalyst for water oxidation developed in situ in a HCO3−/CO2 system at near-neutral pH. Adv. Energy Mater. 4, 1301929 (2014).
J.L. Du, Z.F. Chen, S.R. Ye, B.J. Wiley, and T.J. Meyer: Copper as a robust and transparent electrocatalyst for water oxidation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 54, 2073–2078 (2015).
R. Tagore, R.H. Crabtree, and G.W. Brudvig: Oxygen evolution catalysis by a dimanganese complex and its relation to photosynthetic water oxidation. Inorg. Chem. 47, 1815–1823 (2008).
W.C. Ellis, N.D. McDaniel, S. Bernhard, and T.J. Collins: Fast water oxidation using iron. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 10990–10991 (2010).
J.G. McAlpin, Y. Surendranath, M. Dinca, T.A. Stich, S.A. Stoian, W.H. Casey, D.G. Nocera, and R.D. Britt: EPR evidence for Co(IV) species produced during water oxidation at neutral pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132, 6882–6883 (2010).
M. Dinca, Y. Surendranath, and D.G. Nocera: Nickel-borate oxygen-evolving catalyst that functions under benign conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107, 10337–10341 (2010).
H. Chen, Y. Gao, Z. Lu, L. Ye, and L. Sun: Copper oxide film in situ electrodeposited from Cu(II) complex as highly efficient catalyst for water oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 230, 501–507 (2017).
Z. Chen and T.J. Meyer: Copper(II) catalysis of water oxidation. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 52, 700–703 (2013).
S. Cui, X. Liu, Z. Sun, and P. Du: Noble metal-free copper hydroxide as an active and robust electrocatalyst for water oxidation at weakly basic pH. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 4, 2593–2600 (2016).
X. Liu, S.S. Cui, Z.J. Sun, and P.W. Du: Copper oxide nanomaterials synthesized from simple copper salts as active catalysts for electrocatalytic water oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 160, 202–208 (2015).
X. Liu, H.X. Jia, Z.J. Sun, H.Y. Chen, P. Xu, and P.W. Du: Nanostructured copper oxide electrodeposited from copper(II) complexes as an active catalyst for electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. Electrochem. Commun. 46, 1–4 (2014).
C. Lu, J. Wang, and Z. Chen: Water oxidation by copper-amino acid catalysts at low overpotentials. ChemCatChem 8, 2165–2170 (2016).
F. Yu, F. Li, B. Zhang, H. Li, and L. Sun: Efficient electrocatalytic water oxidation by a copper oxide thin film in borate buffer. ACS Catal. 5, 627–630 (2015).
M.T. Zhang, Z. Chen, P. Kang, and T.J. Meyer: Electrocatalytic water oxidation with a copper(II) polypeptide complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 2048–2051 (2013).
W. Zhang, J. Qi, K. Liu, and R. Cao: A nickel-based integrated electrode from an autologous growth strategy for highly efficient water oxidation. Adv. Energy Mater. 6, 1502489 (2016).
J. Wang, L. Ji, S. Zuo, and Z. Chen: Hierarchically structured 3D integrated electrodes by galvanic replacement reaction for highly efficient water splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1700107 (2017).
J.R. McKone, B.F. Sadtler, C.A. Werlang, N.S. Lewis, and H.B. Gray: Ni–Mo nanopowders for efficient electrochemical hydrogen evolution. ACS Catal. 3, 166–169 (2013).
J. Qi, W. Zhang, R. Xiang, K. Liu, H.Y. Wang, M. Chen, Y. Han, and R. Cao: Porous nickel-iron oxide as a highly efficient electrocatalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Adv. Sci. 2, 1500199 (2015).
X. Liu, Z.J. Sun, S.S. Cui, and P.W. Du: Cuprous oxide thin film directly electrodeposited from a simple copper salt on conductive electrode for efficient oxygen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta 187, 381–388 (2016).
X. Lu and C. Zhao: Electrodeposition of hierarchically structured three-dimensional nickel-iron electrodes for efficient oxygen evolution at high current densities. Nat. Commun. 6, 6616 (2015).
J. Wang, L. Ji, and Z. Chen: In situ rapid formation of a nickel–iron-based electrocatalyst for water oxidation. ACS Catal. 6, 6987–6992 (2016).
X. Wen, W. Zhang, and S. Yang: Synthesis of Cu(OH)2 and CuO nanoribbon arrays on a copper surface. Langmuir 19, 5898–5903 (2003).
W. Wang, O.K. Varghese, C. Ruan, M. Paulose, and C.A. Grimes: Synthesis of CuO and Cu2O crystalline nanowires using Cu(OH)2 nanowire templates. J. Mater. Res. 18, 2756–2759 (2011).
C. Lu, L. Qi, J. Yang, D. Zhang, N. Wu, and J. Ma: Simple template-free solution route for the controlled synthesis of Cu(OH)2 and CuO nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 17825–17831 (2004).
Y. Deng, A.D. Handoko, Y. Du, S. Xi, and B.S. Yeo: In situ raman spectroscopy of copper and copper oxide surfaces during electrochemical oxygen evolution reaction: Identification of CuIII oxides as catalytically active species. ACS Catal. 6, 2473–2481 (2016).
C. Lu, J. Du, X-J. Su, M-T. Zhang, X. Xu, T.J. Meyer, and Z. Chen: Cu(II) aliphatic diamine complexes for both heterogeneous and homogeneous water oxidation catalysis in basic and neutral solutions. ACS Catal. 6, 77–83 (2016).
M. Durando, R. Morrish, and A.J. Muscat: Kinetics and mechanism for the reaction of hexafluoroacetylacetone with CuO in supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 16659–16668 (2008).
N.S. McIntyre, S. Sunder, D.W. Shoesmith, and F.W. Stanchell: Chemical information from XPS—Applications to the analysis of electrode surfaces. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 18, 714–721 (1981).
K.S. Joya and H.J.M. de Groot: Controlled surface-assembly of nanoscale leaf-type Cu-oxide electrocatalyst for high activity water oxidation. ACS Catal. 6, 1768–1771 (2016).
T.T. Li, S. Cao, C. Yang, Y. Chen, X.J. Lv, and W.F. Fu: Electrochemical water oxidation by in situ-generated copper oxide film from [Cu(TEOA)(H2O)2][SO4] complex. Inorg. Chem. 54, 3061–3067 (2015).
E.L. Tae, J. Song, A.R. Lee, C.H. Kim, S. Yoon, I.C. Hwang, M.G. Kim, and K.B. Yoon: Cobalt oxide electrode doped with iridium oxide as highly efficient water oxidation electrode. ACS Catal. 5, 5525–5529 (2015).
D.K. Bediako, Y. Surendranath, and D.G. Nocera: Mechanistic studies of the oxygen evolution reaction mediated by a nickel-borate thin film electrocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 3662–3674 (2013).
F. Li, L. Bai, H. Li, Y. Wang, F. Yu, and L. Sun: An iron-based thin film as a highly efficient catalyst for electrochemical water oxidation in a carbonate electrolyte. Chem. Commun. 52, 5753–5756 (2016).
W. Zhang, Y. Wu, J. Qi, M. Chen, and R. Cao: A thin NiFe hydroxide film formed by stepwise electrodeposition strategy with significantly improved catalytic water oxidation efficiency. Adv. Energy Mater. 7, 1602547 (2017).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21573160 and 21405114) and Science & Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (14DZ2261100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhu, L., Ji, L. et al. Preparation of nanostructured Cu(OH)2 and CuO electrocatalysts for water oxidation by electrophoresis deposition. Journal of Materials Research 33, 581–589 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.378
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.378