Abstract
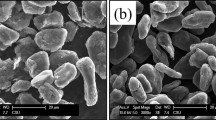
MgO/Cu composites containing a 1.0% volume fraction of MgO particles were prepared by internal oxidation and powder metallurgy, respectively. The interfacial bonding state between the MgO particles and Cu matrix was characterized by scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The effect of the MgOp/Cu interfacial bonding state on the arc erosion resistance of the MgO/Cu composites was investigated, and the arc erosion resistance was examined using a JF04C electrical composite testing system. The results indicate that the 1.0 vol% MgO/Cu composite with a semicoherent MgOp/Cu interface experiences a lower arc erosion rate and smaller fluctuations of arcing energy than those of the 1.0 vol% MgO/Cu composite with an incoherent MgOp/Cu interface. Erosion morphology observations further indicate that a solid to liquid phase transformation occurs under arcing and MgO particles dispersed in the molten copper both prevent the copper matrix from splashing and enhance the arc erosion resistance of the MgO/Cu composites. While the shallow electric erosion pits are distributed uniformly on the arc surface of the MgO/Cu composites with a semicoherent interface, the MgO/Cu composite with an incoherent interface has deep and uneven pits on its arc surface, characterized by large electric erosion molten droplets.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Zhang, B. Tian, A.A. Volinsky, X. Chen, H. Sun, Z. Chai, P. Liu, and Y. Liu: Dynamic recrystallization model of the Cu–Cr–Zr–Ag alloy under hot deformation. J. Mater. Res. 31(9), 1275 (2016).
K.X. Song, P. Liu, B.H. Tian, Q.M. Dong, and J.D. Xing: Stabilization of nano-Al2O3p/Cu composite after high temperature annealing treatment. Mater. Sci. Forum 475–479, 993 (2005).
X. Guo, K. Song, S. Liang, X. Wang, and Y. Zhang: Effect of Al2O3 particle size on electrical wear performance of Al2O3/Cu composites. Tribol. Trans. 59(1), 170 (2016).
S. Huang, Y. Feng, H. Liu, K. Ding, and G. Qian: Electrical sliding friction and wear properties of Cu–MoS2–graphite–WS2 nanotubes composites in air and vacuum conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 560, 685 (2013).
X. Guo, K. Song, S. Liang, and C. Zheng: Thermal expansion behavior of MgO/Cu composite with lower MgO volume fraction. Mater. Res. Bull. 47(11), 3211 (2012).
D.B.V. Rajkovic, M. Popovic, and M.T. Jovanovic: The influence of powder particle size on properties of Cu–Al2O3 composites. Sci. Sintering 41, 185 (2009).
Y.G. Wang and J.T.M. De Hosson: Secondary interface dislocations in internally oxidized MgO/Cu composite. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 20(5), 389 (2001).
M. Varga, Á. Molnár, G. Mulas, M. Mohai, I. Bertóti, and G. Cocco: Cu–MgO samples prepared by mechanochemistry for catalytic application. J. Catal. 206(1), 71 (2002).
D.A. Muller, D.A. Shashkov, R. Benedek, L.H. Yang, J. Silcox, and D.N. Seidman: Atomic scale observations of metal-induced gap states at {222} MgO/Cu interfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80(21), 4741 (1998).
Y.Z. Tian and Z.F. Zhang: Stability of interfaces in a multilayered Ag–Cu composite during cold rolling. Scr. Mater. 68(7), 542 (2013).
K. Chu, C. Jia, L. Jiang, and W. Li: Improvement of interface and mechanical properties in carbon nanotube reinforced Cu–Cr matrix composites. Mater. Des. 45, 407 (2013).
K.M. Shorowordi, T. Laoui, A.S.M.A. Haseeb, J.P. Celis, and L. Froyen: Microstructure and interface characteristics of B4C, SiC and Al2O3 reinforced Al matrix composites: A comparative study. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 142(3), 738 (2003).
Y.G. Wang, Z. Zhang, G.H. Yan, and J.T.M. De Hosson: Determination of near coincident site lattice orientations in MgO/Cu composite. J. Mater. Sci. 37(12), 2511 (2002).
M.V. Speight: Growth kinetics of grain-boundary precipitates. Acta Metall. 16(1), 133 (1968).
C. Tatar and N. Özdemir: Investigation of thermal conductivity and microstructure of the α-Al2O3 particulate reinforced aluminum composites (Al/Al2O3-MMC) by powder metallurgy method. Phys. B 405(3), 896 (2010).
F.S. Roig and J.E. Schoutens: Theory of electrical resistivity of metal–matrix composites at cryogenic and higher temperatures. J. Mater. Sci. 21(7), 2409 (1986).
L. Ruihua, S. Kexing, J. Shuguo, X. Xiaofeng, G. Jianxin, and G. Xiuhua: Morphology and frictional characteristics under electrical currents of Al2O3/Cu composites prepared by internal oxidation. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 21(3), 281 (2008).
F. Shojaeepour, P. Abachi, K. Purazrang, and A.H. Moghanian: Production and properties of Cu/Cr2O3 nano-composites. Powder Metall. 222, 80 (2012).
V. Rajkovic, D. Bozic, and M.T. Jovanovic: Effects of copper and Al2O3 particles on characteristics of Cu–Al2O3 composites. Mater. Des. 31(4), 1962 (2010).
B. Tian, P. Liu, K. Song, Y. Li, Y. Liu, F. Ren, and J. Su: Microstructure and properties at elevated temperature of a nano-Al2O3 particles dispersion-strengthened copper base composite. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 435–436, 705 (2006).
K. Song, J. Xing, Q. Dong, P. Liu, B. Tian, and X. Cao: Optimization of the processing parameters during internal oxidation of Cu–Al alloy powders using an artificial neural network. Mater. Des. 26(4), 337 (2005).
X. Wang, S. Liang, P. Yang, and Z. Fan: Effect of milling time on electrical breakdown behavior of Al2O3/Cu composite. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 19(6), 906 (2010).
X. Wang, S. Liang, P. Yang, and Z. Fan: Effect of Al2O3 particle size on vacuum breakdown behavior of Al2O3/Cu composite. Vacuum 83(12), 1475 (2009).
H. Li, X. Wang, X. Guo, X. Yang, and S. Liang: Material transfer behavior of AgTiB2 and AgSnO2 electrical contact materials under different currents. Mater. Des. 114, 139 (2017).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51605146 and No. U1502274), the International Scientific and Technological Cooperation Project of Henan Province (No. 172102410046), Key Science and Technology Program of Henan Province (No. 172102410046), and the fund of the Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory for Technology and Application of Metal Toughening (GKL201601).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, X., Song, K., Liang, S. et al. Relationship between the MgOp/Cu interfacial bonding state and the arc erosion resistance of MgO/Cu composites. Journal of Materials Research 32, 3753–3760 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.321
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.321