Abstract
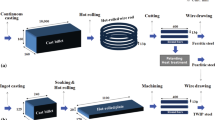
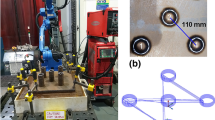
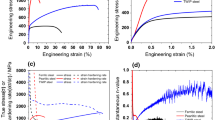
A novel stainless steel porous twisted wire material (PTWM) is made of twisted short wires by compaction followed by vacuum high-temperature solid-phase sintering. The twisted short wires are fabricated by using a self-developed rotary multicutter tool to cut stainless steel wire ropes. The PTWMs with 46–70% porosities have been investigated in terms of porous structures and Charpy impact behavior. The PTWMs with spatial composite intertexture structures exhibit interconnected open-pore microstructures with a variety of shapes and sizes. The pore size distributions became convergent with decreasing porosities. The span of pore distribution of the PTWM with a diameter of 90 μm was half than that of the PTWM with a diameter of 160 μm under 65–66% porosity. The impact toughness of the former is 2.6 times than that of the latter. By increasing the porosity from 46 to 70%, the impact toughness decreases from 17.9 to 9.1 J/cm2. Macroscopically integral failure-morphologies of the PTWMs present mixed ductile–brittle failure mechanisms, but microscopic impact deformation and failure mechanisms mainly show the ductile failure and fracture of pore skeletons. The PTWMs demonstrate complex energy absorption mechanisms.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.P. Lefebvre, J. Banhart, and D.C. Dunand: Porous metals and metallic foams: Current status and recent developments. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10 (9), 775–787 (2008).
K.J. Kang: Wire-woven cellular metals: The present and future. Prog. Mater. Sci. 69, 213–307 (2015).
M.G. Lee, K.W. Lee, H.K. Hur, and K.J. Kang: Mechanical behavior of a wire-woven metal under compression. Compos. Struct. 95, 264–277 (2013).
M.G. Lee, J.W. Yoon, S.M. Han, Y.S. Suh, and K.J. Kang: In-plane compression response of wire-woven metal cored sandwich panels. Mater. Des. 55, 718–726 (2014).
B.K. Lee and K.J. Kang: A parametric study on compressive characteristics of wire-woven bulk Kagome truss cores. Compos. Struct. 92, 445–453 (2010).
K.J. Kang: A wire-woven cellular metal of ultrahigh strength. Acta Mater. 57, 1865–1874 (2009).
W. Yuan, Y. Tang, X.J. Yang, B. Liu, and Z.P. Wan: Manufacture, characterization and application of porous metal-fiber sintered felt used as mass-transfer-controlling medium for direct methanol fuel cells. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23, 2085–2093 (2013).
W. Zhou, Y. Tang, Z.P. Wan, L.S. Lu, Y. Chi, and M.Q. Pan: Preparation of oriented linear copper fiber sintered felt and its performance. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 17, 1028–1033 (2007).
W. Zhou, Y. Tang, M.Q. Pan, X.L. Wei, and J.H. Xiang: Experimental investigation on uniaxial tensile properties of high-porosity metal fiber sintered sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 525, 133–137 (2009).
J.C. Tan and T.W. Clyne: Ferrous fibre network materials for jet noise reduction in eroengines part II: Thermo-mechanical stability. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10, 201–209 (2008).
A.E. Markaki, V. Gergely, A. Cockburn, and T.W. Clyne: Production of a highly porous materials by liquid phase sintering of short ferritic stainless steel fibres and a preliminary study of its mechanical behavior. Compos. Sci. Technol. 63, 2345–2351 (2003).
P. Liu, G. He, and L.H. Wu: Uniaxial tensile stress–strain behavior of entangled steel wire material. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 509, 69–75 (2009).
J.C. Qiao, Z.P. Xi, H.P. Tang, J.Y. Wang, and J.L. Zhu: Influence of porosity on quasi-static compressive properties of porous metal media fabricated by stainless steel fibers. Mater. Des. 30, 2737–2740 (2009).
P. Liu, G. He, and L.H. Wu: Fabrication of sintered steel wire mesh and its compressive properties. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 489, 21–28 (2008).
P. Liu, G. He, and L.H. Wu: Impact behavior of entangled steel wire material. Mater. Charact. 60, 900–906 (2009).
P. Liu, Q.B. Tan, L.H. Wu, and G. He: Compressive and pseudo-elastic hysteresis behavior of entangled titanium wire materials. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 52, 3301–3309 (2010).
Q. Tan, P. Liu, C. Du, L.H. Wu, and G. He: Mechanical behaviors of quasi-ordered entangled aluminum alloy wire material. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 38–44 (2009).
M.G. Lee, G.D. Ko, J.Y. Song, and K.J. Kang: Compressive characteristics of a wire-woven cellular metal. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 539, 185–193 (2012).
F. Wu, Z.Y. Zhou, L.Y. Duan, and Z.Y. Xiao: Processing, structural characterization and comparative studies on uniaxial tensile properties of a new type of porous twisted wire material. Materials 8 (9), 5606–5620 (2015).
A. Jean and K. Gupta: Liquid extrusion techniques for pore structure evaluation of nonwovens. Int. Nonwovens J. 12, 45–53 (2003).
B. Tang, Y. Tang, R. Zhou, L.S. Lu, and X.M. Qu: Low temperature solid-phase sintering of sintered metal fibrous media with high specific surface area. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 21, 1755–1760 (2011).
Q.B. Tan and G. He: Stretching behaviors of entangled materials with spiral wire structure. Mater. Des. 46, 61–65 (2013).
M. Zhang, G.Y. Zu, G.C. Yao, and Y.H. Liu: Preparation impact properties and of aluminum foam sandwich panels. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 60 (3), 14–17 (2008).
G.Y. Zu, J. Liu, X.B. Li, and S.L. Sun: Research on the low-velocity impact performance of aluminum foam sandwich panels. J. Northeast. Univ. 35 (11), 1583–1587 (2014).
G.P. Zou, Z.L. Chang, R.H. Ming, P.X. Xia, and Q. Wang: Study on impact performances of sandwich panel with foam aluminum. Acta Armamentarii S2, 276–279 (2009).
D. Zhou and W.J. Stronge: Mechanical properties of fibrous core sandwich panels. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 47 (4–5), 775–798 (2005).
T.W. Clyne, A.E. Markaki, and J.C. Tan: Mechanical and magnetic properties of metal fibre networks with and without a polymeric matrix. Compos. Sci. Technol. 65 (15–16), 2492–2499 (2005).
M. Kiser, M.Y. He, and F.W. Zok: The mechanical response of ceramic microballoon reinforced aluminum matrix composites under compressive loading. Acta Mater. 47 (9), 2685–2694 (1999).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research work was supported by the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou, China (No. 201604016015) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51274103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Duan, L. & Wu, F. Investigation of Charpy impact behavior of porous twisted wire material. Journal of Materials Research 32, 2276–2285 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.195
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.195