Abstract
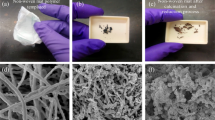
We present a novel route to fabricate 3D nanoporous α-Ti foams by dealloying of TiCu master alloy in solid state using Mg powders. Pure open-cell nanoporous α-Ti foams are fabricated with BET surface area of 34.4 ± 0.8 m2/g and pore size in the range of 2–50 nm. The dealloying using powders is a solid state chemical reaction process to form Cu2Mg phase and Ti/Mg nanocomposites. The constituent of Cu in the TiCu alloy was dissolved into Mg powders thanks to the kinetics of interface reaction and volume diffusion. The pore-forming mechanism is a solid-state interdiffusion process. The ligament coarsening is from 492 to 650 nm with increasing of the dealloying temperature. The hardness and elastic modulus in nanoporous α-Ti foam follow linear decay fit with ligament size increasing. Our results demonstrate a facile strategy for the fabrication of nanoporous Ti foams with novel nanostructures and tailored properties.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.C. Tappan, S.A. Steiner, III, and E.P. Luther: Nanoporous metal foams. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 49, 4544 (2010).
H.J. Jin, X.L. Wang, S. Parida, K. Wang, M. Seo, and J. Weissmuller: Nanoporous Au–Pt alloys as large strain electrochemical actuators. Nano Lett. 10, 187 (2010).
X. Li, Q. Chen, I. McCue, J. Snyder, P. Crozier, J. Erlebacher, and K. Sierzdzki: Dealloying of noble-metal alloy nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 14, 2569 (2014).
S. Ghosh: Switching magnetic order in nanoporous Pd–Ni by electrochemical charging. J. Mater. Res. 28, 3010 (2013).
Z. Qi and J. Weissmueller: Hierarchical nested-network nanostructure by dealloying. ACS Nano 7, 5948 (2013).
J. Erlebacher, M.J. Aziz, A. Karma, N. Dimitrov, and K. Sieradzk: Evolution of nanoporosity in dealloying. Nature 410, 450 (2001).
K. Shin, K.A. Leach, J.T. Goldbach, D.H. Kim, J.Y. Jho, M. Tuominen, C.J. Hawker, and T.P. Russell: A simple route to metal nanodots and nanoporous metal films. Nano Lett. 2, 933 (2002).
O. Naeth, A. Stephen, J. Roesler, and F. Vollertsen: Structuring of nanoporous nickel-based superalloy membranes via laser etching. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209, 4739 (2009).
B.C. Tappan, M.H. Huynh, M.A. Hiskey, D.E. Chavez, E.P. Luther, J.T. Mang, and S.F. Son: Ultralow-density nanostructured metal foams: combustion synthesis, morphology, and composition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 6589 (2006).
Z. Qi, U. Vainio, A. Kornowski, M. Ritter, H. Weller, H. Jin, and J. Weissmueller: Porous gold with a nested-network architecture and ultrafine structure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 2530 (2015).
J.C. Thorp, K. Sieradzki, L. Tang, P.A. Crozier, A. Misra, M. Nastasi, D. Mitlin, and S.T. Picraux: Formation of nanoporous noble metal thin films by electrochemical dealloying of PtxSi1 x. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 033110 (2006).
M. Hakamada and M. Mabuchi: Fabrication of nanoporous palladium by dealloying and its thermal coarsening. J. Alloys Compd. 479, 326 (2009).
Y. Tang, Y. Liu, L. Lian, X. Zhou, and L. He: Formation of nanoporous copper through dealloying of dual-phase Cu–Mn–Al alloy: The evolution of microstructure and composition. J. Mater. Res. 27, 2771 (2012).
M. Hakamada and M. Mabuchi: Preparation of nanoporous Ni and Ni–Cu by dealloying of rolled Ni–Mn and Ni–Cu–Mn alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 485, 583 (2009).
F. Zhang, A. Weidmann, J.B. Nebe, U. Beck, and E. Burkel: Preparation, microstructures, mechanical properties and cytocompatibility of TiMn alloys for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., B 94, 406 (2010).
T. Wada, K. Yubuta, A. Inoue, and H. Kato: Dealloying by metallic melt. Mater. Lett. 65, 1076 (2011).
N.T. Panagiotopoulos, A. Moreira Jorge, I. Rebai, K. Georgarakis, W.J. Botta, and A.R. Yavari: Nanoporous titanium obtained from a spinodally decomposed Ti alloy. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 222, 26 (2016).
H. Tsuchiya, S. Berger, and J.M. Macak: Self-organized porous and tubular oxide layers on TiAl alloys. Electrochem. Commun. 9, 2397 (2007).
H. Abe, K. Sato, H. Nishikawa, T. Takemoto, M. Fukuhara, and A. Inoue: Dealloying of Cu–Zr–Ti bulk metallic glass in hydrofluoric acid solution. Mater. Trans. 50, 1255–1258 (2009).
M. Tsuda, T. Wada, and H. Kato: Kinetics of formation and coarsening of nanoporous-titanium dealloyed with Mg melt. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 113503 (2013).
T. Wada, A.D. Setyawan, K. Yubuta, and H. Kato: Nano- to submicro-porous beta-Ti alloy prepared from dealloying in a metallic melt. Script. Mater. 65, 532 (2011).
J.W. Kim, M. Tsuda, T. Wada, K. Yubuta, S.G. Kim, and H. Kato: Optimizing niobium dealloying with metallic melt to fabricate porous structure for electrolytic capacitors. Acta Mater. 84, 497 (2015).
T. Wada and H. Kato: Three-dimensional open-cell macroporous iron, chromium and ferritic stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 68, 723 (2013).
Y.K. Chen-Wiegart, T. Wada, N. Butakov, X. Xiao, F. De Carlo, H. Kato, J. Wang, D.C. Dunand, and E. Maire: 3D morphological evolution of porous titanium by X-ray micro- and nano-tomography. J. Mater. Res. 28, 2444 (2013).
D.C. Dunand: Processing of titanium foams. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 369 (2004).
F. Zhang, E. Otterstein, and E. Burkel: Spark plasma sintering, microstructures and mechanical properties of macroporous titanium foams. Adv. Eng. Mater. 12, 863 (2010).
O. Guillon, J.G. Julian, B. Dargatz, T. Kessel, G. Schierning, J. Rathel, and M. Herrmann: Field-assisted sintering technology/spark plasma sintering: Mechanisms, materials, and technology developments. Adv. Eng. Mater. 16, 830 (2014).
F. Zhang, M. Reich, O. Kessler, and E. Burkel: Potential of rapid cooling spark plasma sintering for metallic materials. Mater. Today 16, 192–195 (2013).
A. Takeuchi and A. Inoue: Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element. Mater. Trans. 46, 2817 (2005).
J. Erlebacher and R. Seshadri: Hard materials with tunable porosity. MRS Bull. 34, 561 (2009).
K. Meguro, M. O, and M. Kajihara: Growth behavior of compounds due to solid-state reactive diffusion between Cu and Al. J. Mater. Sci. 47, 4955–4964 (2012).
Y.L. Corcoran, A.H. King, N.D. Lanerolle, and B. Kim: Grain boundary diffusion and growth of titanium silicide layers on silicon. J. Electron. Mater. 19, 1177 (1990).
O. Taguchi, Y. Iijima, and K. Hirono: Reaction diffusion in the Cu–Ti system. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 54, 619 (1990).
M. Hakamada and M. Mabuchi: Mechanical strength of nanoporous gold fabricated by dealloying. Scr. Mater. 56, 1003 (2007).
T. Wada, K. Yubuta, and H. Kato: Evolution of a biocontinuous nanostructure via a solid-state interfacial dealloying reaction. Scr. Mater. 118, 33 (2016).
B.S. Necula, I. Apachitei, L.E. Fratila-Apachitei, E.J. van Langelaan, and J. Duszczyk: Titanium bone implants with superimposed micro/nano-scale porosity and antibacterial capability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 273, 310 (2013).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial supports from the State Key Laboratory for Powder Metallurgy at Central South University, Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20161419), Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars at State Education Ministry (No. 2015-1098), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 11572087), Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Advanced Metallic Materials (No. BM2007204) at Southeast University, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2242016K40013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F., Li, P., Yu, J. et al. Fabrication, formation mechanism and properties of three-dimensional nanoporous titanium dealloyed in metallic powders. Journal of Materials Research 32, 1528–1540 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.19
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.19