Abstract
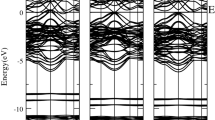
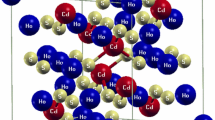
We have investigated theoretically the role of Cr-d states in the electronic and optical properties of the CdCr2X4 (X = S, Se) normal ferromagnetic spinels using the framework of an all-electron full-potential linearized augmented plane wave method. The calculations are performed using Coulomb corrected Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof (PBE+U) and Tran–Blaha modified-Becke–Johnson (TB-mBJ) approximations with the adding of spin–orbit coupling in both schemes. The lattice parameters have been optimized and are in agreement with the existing experimental values. We found band gap values 1.606 eV and 0.972 eV of CdCr2X4 (X = S, Se), respectively, using the TB-mBJ scheme. Analysis of the site and momentum projected densities shows that the larger splitting of Cr-d states is responsible for the larger band gap by the use of the TB-mBJ scheme. Optical properties along the directions of lattice constants are studied on the basis of band to band transitions. We found the isotropic nature of the optical properties. Reflectivity stays low up to 1.6 eV, consistent with the energy gaps obtained using the TB-mBJ scheme in both the compounds. The refractive index, n (ω), and the extinction coefficient, k (ω), are also studied by the PBE and the TB-mBJ schemes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. Ahmad, B. Amin, M. Maqbool, S. Muhammad, G. Murtaza, S. Ali, and N.A. Noor: Optoelectronic response of GeZn2O4 through the modified Becke–Johnson potential. Chin. Phys. Lett. 29, 097012 (2012).
F. Semari, R. Khenata, M. Rabah, A. Bouhemadou, S.B. Omran, A.H. Reshak, and D. Rached: Full potential study of the elastic, electronic, and optical properties of spinels MgIn2S4 and CdIn2S4 under pressure effect. J. Solid State Chem. 183, 2818 (2010).
M. Dekkers, G. Rijnders, and D.H.A. Blank: ZnIr2O4, a p-type transparent oxide semiconductor in the class of spinel zinc-d6-transition metal oxide. Appl. Phys. Lett. 90, 021903 (2007).
H.J. Kim, I.C. Song, J.H. Sim, H. Kim, D. Kim, Y.E. Ihm, and W.K. Choo: Electrical and magnetic properties of spinel type magnetic semiconductor ZnCo2O4 grown by reactive magnetron sputtering. Solid State Commun. 129, 627 (2004).
H. Mizoguchi, M. Hirano, S. Fujitsu, T. Takeuchi, K. Ueda, and H. Hosono: ZnRh2O4: A p-type semiconducting oxide with a valence band composed of a low spin state of Rh3+ in a 4d6 configuration. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 1207 (2002).
X. Wei, D. Chen, and W. Tang: Preparation and characterization of the spinel oxide ZnCo2O4 obtained by sol–gel method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 103, 54 (2007).
A. Bouhemadou, F. Zerarga, A. Almuhayya, and S.B. Omran: FP-LAPW study of the fundamental properties of the cubic spinel CdAl2O4. Mater. Res. Bull. 46, 2252 (2011).
M. Yousaf, M.A. Saeed, A.R.M. Isa, A. Shaari, and H.A.R. Aliabad: Electronic band structure and optical parameters of spinel SnMg2O4 by modified Becke–Johnson potential. Chin. Phys. Lett. 29, 107401 (2012).
H. Dixit, R. Saniz, S. Cottenier, D. Lamoen, and B. Partoens: Electronic structure of transparent oxides with the Tran-Blaha modified Becke–Johnson potential. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 24, 205503 (2012).
M.N. Amini, H. Dixit, R. Saniz, D. Lamoen, and B. Partoens: The origin of p-type conductivity in ZnM2O4 (M = Co, Rh, Ir) spinels. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 2588 (2014).
M. Stoica and C.S. Lo: p-Type zinc oxide spinels: Application to transparent conductors and spintronics. arXiv: 1312.1728v1.
F. Zerarga, A. Bouhemadou, R. Khenata, and S.B. Omran: Structural, electronic and optical properties of spinel oxides ZnAl2O4, ZnGa2O4 and ZnIn2O4. Solid State Sci. 13, 1638 (2011).
B. Amin, R. Khenata, A. Bouhemadou, I. Ahmad, and M. Maqbool: Opto-electronic response of spinels MgAl2O4 and MgGa2O4 through modified Becke–Johnson exchange potential. Phys. B 407, 2588 (2012).
Y. Sharma and P. Srivastava: Electronic, optical and transport properties of α-, β- and γ-phases of spinel indium sulphide: An ab initio study. Mater. Chem. Phys. 135, 385 (2012).
D.J. Singh, R.C. Rai, J.L. Musfeldt, S. Auluck, N. Singh, P. Khalifah, S. McClure, and D.G. Mandrus: Optical properties and electronic structure of spinel ZnRh2O4. Chem. Mater. 18, 2696 (2006).
N. Singh and U. Schwinggenschlogl: ZnIr2O4: An efficient photocatalyst with Rashba splitting. Europhys. Lett. 104, 37002 (2013).
S. Samanta and S.M. Saini: Full potential study of electronic and optical properties of transparent oxide ZnCo2O4 by use of PBE and TB-mBJ potentials. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 3659 (2014).
Landolt-Börnstein: Magnetic and other properties of oxides and related compounds. In New Series, Vol. III/4b, K-H. Hellwege, ed. (Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg, 1970).
V. Samohvalov: PAC investigations of ferromagnetic spinel semiconductors. Ph.D. Dissertation, The Technical University of Freiberg (2003).
Y.D. Park, A.T. Hanbicki, J.E. Mattson, and B.T. Jonker: Epitaxial growth of an n-type ferromagnetic semiconductor CdCr2Se4 on GaAs (001) and GaP (001). Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 1471 (2002).
K.G. Nikiforov: Magnetically ordered multinary semiconductors. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 39, 1–104 (1999).
T.H. Lee, T. Coburn, and R. Gluck: Infrared optical properties and Faraday rotation of ferromagnetic HgCr2Se4. Solid State Commun. 9, 1821 (1971).
S. Shanthi, P. Mahadevan, and D.D. Sarma: Electronic band structure of cadmium chromium chalcogenide spinels: CdCr2S4 and CdCr2Se4. J. Solid State Chem. 155, 198 (2000).
Y-H.A. Wang, A. Gupta, M. Chshiev, and W.H. Butler: Half-metallic electronic structures of quaternary ferromagnetic chalcospinels: CdxCu1−xCr2S4CdxCu1−xCr2S4 and CdxCu1−xCr2Se4CdxCu1−xCr2Se4. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 062507 (2008).
C.J. Fennie and K.M. Rabe: Polar phonons and intrinsic dielectric response of the ferromagnetic insulating spinel CdCr2S4 from first principles. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 72, 214123 (2005).
K. Ohgushi, Y. Okimoto, T. Ogasawara, S. Miyasaka, and Y.M. Tokura: Magnetic, optical and magneto-optical properties of spinel-type ACr2X4 (A = Mn, Fe, Co, Cu, Zn, Cd; X = O, S, Se). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 77, 034713 (2008).
F. Tran and P. Blaha: Accurate band gaps of semiconductors and insulators with a semilocal exchange-correlation potential. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 226401 (2009).
D. Koller, F. Tran, and P. Blaha: Merits and limits of the modified Becke–Johnson exchange potential. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 83, 195134 (2011).
A.H. Reshak, H. Kamaruddin, and S. Auluck: Acentric nonlinear optical 2,4-dihydroxyl hydrazone isomorphic crystals with large linear, nonlinear optical susceptibilities and hyperpolarizability. J. Phys. Chem. B 116, 4677 (2012).
A.H. Reshak, H. Kamaruddin, I.V. Kityk, and S. Auluck: Dispersion of linear, nonlinear optical susceptibilities and hyperpolarizability of C11H8N2O (o-methoxydicyanovinylbenzene) crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 116, 13338 (2012).
G.K.H. Madsen, P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, E. Sjostedt, and L. Nordstrom: Efficient linearization of the augmented plane-wave method. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 64, 195134 (2001).
E. Sjostedt, L. Nordstrom, and D.J. Singh: An alternative way of linearizing the augmented plane-wave method. Solid State Commun. 114, 15 (2000).
K. Schwarz, P. Blaha, and G.K.H. Madsen: Electronic structure calculations of solids using the WIEN2k package for material sciences. Comput. Phys. Commun. 147, 71 (2002).
V.I. Anisimov, J. Zaanen, and O.K. Andersen: Band theory and Mott insulators: Hubbard U instead of Stoner. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 44, 943 (1991).
V.I. Anisimov, I.V. Solovyev, M.A. Korotin, M.T. Czyzyk, and G.A. Sawatzky: Density-functional theory and NiO photoemission spectra. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 48, 16929 (1993).
P. Hohenberg and W. Kohn: Inhomogeneous electron gas. Phys. Rev. 36, 864 (1964).
P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, G.K.H. Madsen, D. Kvasnicka, and J. Luitz: WIEN2k, An Augmented Plane Wave + Local Orbitals Program for Calculating Crystal Properties (Karlheinz Schwarz, Techn. Universitat WIEN, Austria, 2001).
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 77, 3865 (1996).
H.D. Monkhorst and J.D. Pack: Special points for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 13, 5188 (1976).
P.E. Blochl, O. Jepson, and O.K. Anderson: Improved tetrahedron method for Brillouin-zone integrations. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 49, 16223 (1994).
A.N. Yaresko: Electronic band structure and exchange coupling constants in ACr2X4 spinels (A = Zn, Cd, Hg; X = O, S, Se). Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 77, 115106 (2008).
K. Sato: Crystal growth and characterization of magnetic semiconductors. In Advances in Crystal Growth Research, K. Sato, Y. Furukawa, and K. Nakajima, eds. (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2001); pp. 303–309.
H.B. Zhao, Y.H. Ren, G. Lupke, A.T. Hanbicki, and B.T. Jonker: Band offsets at CdCr2Se4–(AlGa)As and CdCr2Se4–ZnSe interfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1422 (2003).
D. Santos-Carballal, A. Roldan, R. Grau-Crespo, and N.H. De Leeuw: First-principles study of the inversion thermodynamics and electronic structure of FeM2X4 (thio) spinels (M = Cr, Mn, Co, Ni; X = O, S). Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 91, 195106 (2015).
F. Wooten: Optical Properties of Solids (Academic Press, New York, 1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samanta, S., Saini, S.M. Role of Cr-d states in the electronic and optical properties of the CdCr2X4 (X = S, Se) normal ferromagnetic spinels using PBE+U and TB-mBJ potentials. Journal of Materials Research 32, 2431–2437 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.159
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.159