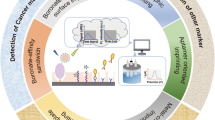
Abstract
As an atomic-thick layer material, graphene has a large specific surface area, high electron mobility, and high sensitivity to electronic perturbations from the binding of molecules, all of which are attractive properties for developing electronic sensing devices. This article focuses on graphene-based electronic sensors [field effect transistor (FET) sensors] for detecting biomolecules, including DNA, protein, and bacteria, among others. This article will cover three morphologies of graphene materials in biosensing applications: graphene nanosheet, graphene nanoribbon, and vertically-aligned graphene. The unique structure and electronic properties of graphene enable the FET sensor for the low concentration and rapid detection of biomolecules, thereby addressing the limitations of conventional optical sensing technologies such as ELISA, Western Blot, and electrochemical method. The advantages of graphene-based sensing technology are highlighted and recent progress on graphene-based electronic sensors for detecting biomolecules is reviewed and discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Mao, J. Chang, G. Zhou, and J. Chen: Nanomaterial-enabled rapid detection of water contaminants. Small 11(40), 5336 (2015).
A. Zhang and C.M. Lieber: Nano-bioelectronics. Chem. Rev. 116(1), 215 (2016).
R. Freeman, T. Finder, R. Gill, and I. Willner: Probing protein kinase (CK2) and alkaline phosphatase with CdSe/ZnS quantum dots. Nano Lett. 10(6), 2192 (2010).
J.A. Hansen, J. Wang, A.N. Kawde, Y. Xiang, K.V. Gothelf, and G. Collins: Quantum-dot/aptamer-based ultrasensitive multi-analyte electrochemical biosensor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128(7), 2228 (2006).
Z. Li, Y. Wang, J. Wang, Z. Tang, J.G. Pounds, and Y. Lin: Rapid and sensitive detection of protein biomarker using a portable fluorescence biosensor based on quantum dots and a lateral flow test strip. Anal. Chem. 82(16), 7008 (2010).
X-Y. Lang, H-Y. Fu, C. Hou, G-F. Han, P. Yang, Y-B. Liu, and Q. Jiang: Nanoporous gold supported cobalt oxide microelectrodes as high-performance electrochemical biosensors. Nat. Commun. 4, 2169 (2013).
G. Liu, X. Mao, J.A. Phillips, H. Xu, W. Tan, and L. Zeng: Aptamer-nanoparticle strip biosensor for sensitive detection of cancer cells. Anal. Chem. 81(24), 10013 (2009).
X.J. Zhao, L.R. Hilliard, S.J. Mechery, Y.P. Wang, R.P. Bagwe, S.G. Jin, and W.H. Tan: A rapid bioassay for single bacterial cell quantitation using bioconjugated nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101(42), 15027 (2004).
Y. Cui, Q.Q. Wei, H.K. Park, and C.M. Lieber: Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Science 293(5533), 1289 (2001).
F. Patolsky, G.F. Zheng, and C.M. Lieber: Nanowire-based biosensors. Anal. Chem. 78(13), 4260 (2006).
G.F. Zheng, F. Patolsky, Y. Cui, W.U. Wang, and C.M. Lieber: Multiplexed electrical detection of cancer markers with nanowire sensor arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 23(10), 1294 (2005).
B.L. Allen, P.D. Kichambare, and A. Star: Carbon nanotube field-effect-transistor-based biosensors. Adv. Mater. 19(11), 1439 (2007).
J. Chang, S. Mao, Y. Zhang, S. Cui, D.A. Steeber, and J. Chen: Single-walled carbon nanotube field-effect transistors with graphene oxide passivation for fast, sensitive, and selective protein detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 42, 186 (2013).
A. Star, J.C.P. Gabriel, K. Bradley, and G. Gruner: Electronic detection of specific protein binding using nanotube FET devices. Nano Lett. 3(4), 459 (2003).
Y. Liu, X. Dong, and P. Chen: Biological and chemical sensors based on graphene materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41(6), 2283 (2012).
W. Yang, K.R. Ratinac, S.P. Ringer, P. Thordarson, J.J. Gooding, and F. Braet: Carbon nanomaterials in Biosensors: Should you use nanotubes or graphene? Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 49(12), 2114 (2010).
B. Zhan, C. Li, J. Yang, G. Jenkins, W. Huang, and X. Dong: Graphene field-effect transistor and its application for electronic sensing. Small 10(20), 4042 (2014).
J. Chang, S. Mao, Y. Zhang, S. Cui, G. Zhou, X. Wu, C-H. Yang, and J. Chen: Ultrasonic-assisted self-assembly of monolayer graphene oxide for rapid detection of Escherichia coli bacteria. Nanoscale 5(9), 3620 (2013).
A.K. Geim and K.S. Novoselov: The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater. 6(3), 183 (2007).
S. Mao, G. Lu, and J. Chen: Nanocarbon-based gas sensors: Progress and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(16), 5573 (2014).
Q. He, S. Wu, Z. Yin, and H. Zhang: Graphene-based electronic sensors. Chem. Sci. 3(6), 1764 (2012).
H. Chen, P. Chen, J. Huang, R. Selegard, M. Platt, A. Palaniappan, D. Aili, A.I.Y. Tok, and B. Liedberg: Detection of matrilysin activity using polypeptide functionalized reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistor sensor. Anal. Chem. 88(6), 2994 (2016).
Z. Gao, H. Kang, C.H. Naylor, F. Streller, P. Ducos, M.D. Serrano, J. Ping, J. Zauberman Rajesh, R.W. Carpick, Y-J. Wang, Y.W. Park, Z. Luo, L. Ren, and A.T.C. Johnson: Scalable production of sensor arrays based on high-mobility hybrid graphene field effect transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 27546 (2016).
M. Soikkeli, K. Kurppa, M. Kainlauri, S. Arpiainen, A. Paananen, D. Gunnarsson, J.J. Joensuu, P. Laaksonen, M. Prunnila, M.B. Linder, and J. Ahopelto: Graphene biosensor programming with genetically engineered fusion protein monolayers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(12), 8257 (2016).
C. Zhu, D. Du, and Y. Lin: Graphene-like 2D nanomaterial-based biointerfaces for biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 89(Pt 1), 43 (2017).
X. Dong, Q. Long, J. Wang, M.B. Chan-Park, Y. Huang, W. Huang, and P. Chen: A graphene nanoribbon network and its biosensing application. Nanoscale 3(12), 5156 (2011).
X. Tan, H-J. Chuang, M-W. Lin, Z. Zhou, and M.M-C. Cheng: Edge effects on the pH response of graphene nanoribbon field effect transistors. J. Phys. Chem. C 117(51), 27155 (2013).
Z. Bo, S. Mao, Z.J. Han, K. Cen, J. Chen, and K. Ostrikov: Emerging energy and environmental applications of vertically-oriented graphenes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 44(8), 2108 (2015).
F. Schedin, A.K. Geim, S.V. Morozov, E.W. Hill, P. Blake, M.I. Katsnelson, and K.S. Novoselov: Detection of individual gas molecules adsorbed on graphene. Nat. Mater. 6(9), 652 (2007).
J.T. Robinson, F.K. Perkins, E.S. Snow, Z. Wei, and P.E. Sheehan: Reduced graphene oxide molecular sensors. Nano Lett. 8(10), 3137 (2008).
N. Mohanty and V. Berry: Graphene-based single-bacterium resolution biodevice and DNA transistor: Interfacing graphene derivatives with nanoscale and microscale biocomponents. Nano Lett. 8(12), 4469 (2008).
X. Dong, Y. Shi, W. Huang, P. Chen, and L-J. Li: Electrical detection of DNA hybridization with single-base specificity using transistors based on CVD-grown graphene sheets. Adv. Mater. 22(14), 1649 (2010).
X. Dong, W. Huang, and P. Chen: In situ synthesis of reduced graphene oxide and gold nanocomposites for nanoelectronics and biosensing. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 6, 60 (2011).
Z. Yin, Q. He, X. Huang, J. Zhang, S. Wu, P. Chen, G. Lu, P. Chen, Q. Zhang, Q. Yan, and H. Zhang: Real-time DNA detection using Pt nanoparticle-decorated reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistors. Nanoscale 4(1), 293 (2012).
X. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Q. Liao, Y. Song, and S. Ma: Reduced graphene oxide-functionalized high electron mobility transistors for novel recognition pattern label-free DNA sensors. Small 9(23), 4045 (2013).
B. Cai, S. Wang, L. Huang, Y. Ning, Z. Zhang, and G-J. Zhang: Ultrasensitive label-free detection of PNA–DNA hybridization by reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistor biosensor. ACS Nano 8(3), 2632 (2014).
J. Ping, R. Vishnubhotla, A. Vrudhula, and A.T.C. Johnson: Scalable production of high-sensitivity, label-free DNA biosensors based on back-gated graphene field effect transistors. ACS Nano 10(9), 8700 (2016).
Y. Ohno, K. Maehashi, Y. Yamashiro, and K. Matsumoto: Electrolyte-gated graphene field-effect transistors for detecting pH protein adsorption. Nano Lett. 9(9), 3318 (2009).
Q. He, H.G. Sudibya, Z. Yin, S. Wu, H. Li, F. Boey, W. Huang, P. Chen, and H. Zhang: Centimeter-long and large-scale micropatterns of reduced graphene oxide films: Fabrication and sensing applications. ACS Nano 4(6), 3201 (2010).
Y. Ohno, K. Maehashi, and K. Matsumoto: Label-free biosensors based on aptamer-modified graphene field-effect transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(51), 18012 (2010).
Q. He, S. Wu, S. Gao, X. Cao, Z. Yin, H. Li, P. Chen, and H. Zhang: Transparent, flexible, all-reduced graphene oxide thin film transistors. ACS Nano 5(6), 5038 (2011).
Y. Chen, H. Vedala, G.P. Kotchey, A. Audfray, S. Cecioni, A. Imberty, S. Vidal, and A. Star: Electronic detection of lectins using carbohydrate-functionalized nanostructures: Graphene versus carbon nanotubes. ACS Nano 6(1), 760 (2012).
O.S. Kwon, S.J. Park, J-Y. Hong, A.R. Han, J.S. Lee, J.S. Lee, J.H. Oh, and J. Jang: Flexible FET-type VEGF aptasensor based on nitrogen-doped graphene converted from conducting polymer. ACS Nano 6(2), 1486 (2012).
S.J. Park, O.S. Kwon, S.H. Lee, H.S. Song, T.H. Park, and J. Jang: Ultrasensitive flexible graphene based field-effect transistor (FET)-type bioelectronic nose. Nano Lett. 12(10), 5082 (2012).
D-J. Kim, I.Y. Sohn, J-H. Jung, O.J. Yoon, N.E. Lee, and J-S. Park: Reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistor for label-free femtomolar protein detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 41, 621 (2013).
J. Kim, M-S. Lee, S. Jeon, M. Kim, S. Kim, K. Kim, F. Bien, S.Y. Hong, and J-U. Park: Highly transparent and stretchable field-effect transistor sensors using graphene-nanowire hybrid nanostructures. Adv. Mater. 27(21), 3292 (2015).
E. Piccinini, C. Bliem, C. Reiner-Rozman, F. Battaglini, O. Azzaroni, and W. Knoll: Enzyme-polyelectrolyte multilayer assemblies on reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistors for biosensing applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 92, 661 (2016).
S. Mao, G. Lu, K. Yu, Z. Bo, and J. Chen: Specific protein detection using thermally reduced graphene oxide sheet decorated with gold nanoparticle-antibody conjugates. Adv. Mater. 22(32), 3521 (2010).
S. Mao, K. Yu, G. Lu, and J. Chen: Highly sensitive protein sensor based on thermally-reduced graphene oxide field-effect transistor. Nano Res. 4(10), 921 (2011).
B-Y. Kim, I-y. Sohn, D. Lee, G.S. Han, W-I. Lee, H.S. Jung, and N-E. Lee: Ultrarapid and ultrasensitive electrical detection of proteins in a three-dimensional biosensor with high capture efficiency. Nanoscale 7(21), 9844 (2015).
S.S. Kwon, J. Yi, W.W. Lee, J.H. Shin, S.H. Kim, S.H. Cho, S. Nam, and W.I. Park: Reversible and irreversible responses of defect-engineered graphene-based electrolyte-gated pH sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8(1), 834 (2016).
J-L. Her, T-M. Pan, W-Y. Lin, K-S. Wang, and L-J. Li: Label-free detection of alanine aminotransferase using a graphene field-effect biosensor. Sens. Actuators, B 182, 396 (2013).
U. Ghoshdastider, R. Wu, B. Trzaskowski, K. Mlynarczyk, P. Miszta, M. Gurusaran, S. Viswanathan, V. Renugopalakrishnan, and S. Filipek: Molecular effects of encapsulation of glucose oxidase dimer by graphene. RSC Adv. 5(18), 13570 (2015).
Y. Huang, X. Dong, Y. Shi, C.M. Li, L-J. Li, and P. Chen: Nanoelectronic biosensors based on CVD grown graphene. Nanoscale 2(8), 1485 (2010).
Y.H. Kwak, D.S. Choi, Y.N. Kim, H. Kim, D.H. Yoon, S-S. Ahn, J-W. Yang, W.S. Yang, and S. Seo: Flexible glucose sensor using CVD-grown graphene-based field effect transistor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 37(1), 82 (2012).
S. Viswanathan, T.N. Narayanan, K. Aran, K.D. Fink, J. Paredes, P.M. Ajayan, S. Filipek, P. Miszta, H.C. Tekin, F. Inci, U. Demirci, P. Li, K.I. Bolotin, D. Liepmann, and V. Renugopalakrishanan: Graphene–protein field effect biosensors: glucose sensing. Mater. Today 18(9), 513 (2015).
M. Zhang, C. Liao, C.H. Mak, P. You, C.L. Mak, and F. Yan: Highly sensitive glucose sensors based on enzyme-modified whole-graphene solution-gated transistors. Sci. Rep. 5, 8311 (2015).
T. Kavitha, A.I. Gopalan, K-P. Lee, and S-Y. Park: Glucose sensing, photocatalytic and antibacterial properties of graphene–ZnO nanoparticle hybrids. Carbon 50(8), 2994 (2012).
P.K. Ang, A. Li, M. Jaiswal, Y. Wang, H.W. Hou, J.T.L. Thong, C.T. Lim, and K.P. Loh: Flow sensing of single cell by graphene transistor in a microfluidic channel. Nano Lett. 11(12), 5240 (2011).
Y. Huang, X. Dong, Y. Liu, L-J. Li, and P. Chen: Graphene-based biosensors for detection of bacteria and their metabolic activities. J. Mater. Chem. 21(33), 12358 (2011).
M.S. Mannoor, H. Tao, J.D. Clayton, A. Sengupta, D.L. Kaplan, R.R. Naik, N. Verma, F.G. Omenetto, and M.C. McAlpine: Graphene-based wireless bacteria detection on tooth enamel. Nat. Commun. 3, 763 (2012).
G. Lu, K. Yu, Z. Wen, and J. Chen: Semiconducting graphene: converting graphene from semimetal to semiconductor. Nanoscale 5(4), 1353 (2013).
K. Tamersit and F. Djeffal: Double-gate graphene nanoribbon field-effect transistor for DNA and gas sensing applications: Simulation study and sensitivity analysis. IEEE Sens. J. 16(11), 4180 (2016).
S.K. Min, W.Y. Kim, Y. Cho, and K.S. Kim: Fast DNA sequencing with a graphene-based nanochannel device. Nat. Nanotechnol. 6(3), 162 (2011).
S. Mao, K. Yu, S. Cui, Z. Bo, G. Lu, and J. Chen: A new reducing agent to prepare single-layer, high-quality reduced graphene oxide for device applications. Nanoscale 3(7), 2849 (2011).
B. Zhang and T. Cui: Suspended graphene nanoribbon ion-sensitive field-effect transistors formed by shrink lithography for pH/cancer biomarker sensing. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 22(5), 1140 (2013).
S. Mao, K. Yu, J. Chang, D.A. Steeber, L.E. Ocola, and J. Chen: Direct growth of vertically-oriented graphene for field-effect transistor biosensor. Sci. Rep. 3, 1696 (2013).
D.H. Seo, A.E. Rider, S. Kumar, L.K. Randeniya, and K. Ostrikou: Vertical graphene gas- and bio-sensors via catalyst-free, reactive plasma reforming of natural honey. Carbon 60, 221 (2013).
K. Yu, G. Lu, Z. Bo, S. Mao, and J. Chen: Carbon nanotube with chemically bonded graphene leaves for electronic and optoelectronic applications. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2(13), 1556 (2011).
K. Yu, P. Wang, G. Lu, K-H. Chen, Z. Bo, and J. Chen: Patterning vertically oriented graphene sheets for nanodevice applications. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2(6), 537 (2011).
J. Basu and C. RoyChaudhuri: Graphene nanogrids FET immunosensor: Signal to noise ratio enhancement. Sensors 16(10), 1481 (2016).
C. Mackin and T. Palacios: Large-scale sensor systems based on graphene electrolyte-gated field-effect transistors. Analyst 141(9), 2704 (2016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, S., Chen, J. Graphene-based electronic biosensors. Journal of Materials Research 32, 2954–2965 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.129
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.129