Abstract
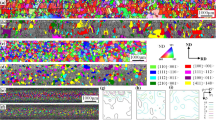
Precipitates and grain sizes in non-oriented silicon steel samples, which were hot-rolled (HR), continuously annealed (CA), and stress-relief-annealed (SA), were characterized using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) equipped with electron back-scattered diffraction. The average grain sizes of the HR, CA, and SA samples were 28, 46, and 46 μm, respectively. SEM observations revealed that the precipitates were mainly dispersed inside grains in the HR and the CA samples, but mainly at grain boundaries in the SA sample. The density of precipitates was highest in the SA sample and lowest in the HR sample. Precipitates at the grain boundaries, which were identified as manganese sulfides, were nearly spherical, their diameter ranging from 0.3 to 0.7 μm. We calculated the pining force exerted by grain-boundary precipitates and found that it outweighed the driving force of the grain growth that was controlled by boundary curvature.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
P.D. Steiner: Non-oriented electrical steel sheets. Mater. Technol. 44, 317 (2010).
A.J. Moses: Electrical steel: Past, present and future developments. IEE Proc., Part A: Phys. Sci., Meas. Instrum., Manage. Educ. 137, 233 (1990).
G. Lyudkovsky, P.K. Rastogi, and M. Bala: Non-oriented electrical steel. JOM 38, 18 (1986).
K. Matsumura and R. Fukuda: Recent developments of non-oriented electrical samples. IEEE Trans. Magn. 20, 1533 (1984).
J.A. Szpunar and H.J. Bunge, eds.: Texture, Anisotropy in Magnetic Steel, Directional Properties of Materials (Cuvllier Verlag, Gttingen, 1988); p. 129.
M. Shiozaki and Y. Kurosaki: The effects of grain size on the magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical samples. J. Mater. Eng. 11, 37 (1989).
Y. Sidor and F. Kovac: Microstructural aspects of grain growth kinetics in non-oriented electrical steel. Mater. Charact. 55, 1 (2005).
D.S. Petrovic, B. Arh, F. Tehovnik, and M. Pirnat: Magnesium non-metallic precipitates in non-oriented electrical samples. ISIJ Int. 51, 2069 (2011).
C.R. Hutchinson, H.S. Zurob, C.W. Sinclair, and Y.J.M. Brechet: The comparative effectiveness of Nb solute and NbC precipitates at impeding grain-boundary motion in Nb steels. Scr. Mater. 59, 635 (2008).
S. Lee and B.C.D. Cooman: Effect of phosphorus on the magnetic losses of non-oriented 2% Si steel. ISIJ Int. 52, 1162 (2012).
T. Irie, K. Matsumura, H. Nakamura, H. Shianaka, and T. Suzuki: Method of producing non-oriented silicon steel sheets having an excellent electromagnetic property. U.S. Patent No. 4 204 890, Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, 1980.
A. Chojecki and T. Bogacz: Formation of the sulfide inclusions during the solidification of cast Fe–Mn–CS alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 215, 385 (1996).
K. Oikawa, K. Ishida, and T. Nishizawa: Effect of titanium addition on the formation and distribution of MnS inclusions in steel during solidification. ISIJ Int. 37, 332 (1997).
Z. Liu, Y. Kobayashi, F. Yin, M. Kuwabara, and K. Nagai: Nucleation of acicular ferrite on sulfide inclusion during rapid solidification of low carbon steel. ISIJ Int. 47, 1781 (2007).
M. Wakoh, T. Sawai, and S. Mizoguchi: Effect of S content on the MnS precipitation in steel with oxide nuclei. ISIJ Int. 36, 1014 (1996).
A.S. Osio, S. Liu, and D.L. Olson: The Effect of solidification on the formation and growth of inclusions in low carbon steel welds. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 221, 122 (1996).
C.S. Smith: Grains, phases, interfaces: An interpretation of microstructure. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 175, 15 (1948).
T. Gladman: Grain Size Control (Maney Publishers, London, 2004); p. 183. (in England).
A.J. DeArdo, G.A. Ratz, and P.J. Wray: Thermomechanical processing of microalloyed austenite. Proceedings of the International Conference on the Thermomechanical Processing of Microalloyed Austenite (Metall. Soc. AIME, New York, 1982).
N. Sun, B.R. Patterson, J.P. Suni, H. Weiland, and L.F. Allard: Characterization of particle pinning potential. Acta Mater. 54, 4091 (2006).
E.J. Palmiere, C.I. Garcia, and A.J. DeArdo: Processing, Microstructure and Properties of Microalloyed and Other Modern HSLA Steel (Iron. Steel. Soc. AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1992); p. 113.
S.S. Hansen, J.B. Vander Sande, and M. Cohen: Niobium carbonitride precipitation and austenite recrystallization in hot-rolled microalloyed steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 11, 387 (1980).
T. Nakayama and N. Honjou: Effect of aluminum and nitrogen on the magnetic properties of non-oriented semi-processed electrical steel sheet. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 213, 87 (2000).
A.V. Karasev and H. Suito: Effect of particle size distribution on austenite grain growth in Fe–0.05 mass% C alloy deoxidized with Mn–Si, Ti, Mg, Zr and Ce. ISIJ Int. 46, 718 (2006).
A. Titov, R. Inoue, and H. Suito: Grain-growth-inhibiting effects of TiC and ZrC precipitates in Fe–0.15–0. 30 mass% C alloy. ISIJ Int. 48, 301 (2008).
J. Janis, A. Karasev, K. Nakajima, and P.G. Jőnsson: Effect of secondary nitride particles on grain growth in a Fe–20 mass% Cr alloy deoxidised with Ti and Zr. ISIJ Int. 53, 476 (2013).
B. Zhou, G. Li, X. Wan, Y. Li, and K. Wu: In situ observation of grain refinement in the simulated heat-affected zone of high-strength low-alloy steel by Zr–Ti combined deoxidation. Met. Mater. Int. 22, 267 (2016).
B.J. Skromme, Y. Zhang, D.J. Smith, and S. Sivananthan: Growth and characterization of pseudomorphic single crystal zinc blende MnS. Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 2690 (1995).
L. Wang, S. Sivananthan, and R. Sporken: Interface properties and valence-band discontinuity of MnS/ZnSe heterostructures. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 54, 2718 (1996).
N. Zhang, R. Yi, Z. Wang, R. Shi, H. Wang, G. Qiu, and X. Liu: Hydrothermal synthesis and electrochemical properties of alpha-manganese sulfide submicrocrystals as an attractive electrode material for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Chem. Phys. 111, 13 (2008).
A.L. Geiger: Effects of internal oxidation and nitridation on the magnetic properties of non-oriented electrical steel. J. Appl. Phys. 50, 2366 (1979).
C.R. Heiple, J.R. Roper, and R.T. Stagner: Surface active element effects on the shape of GTA, laser and electron beam welds. Weld. J. 62, 72 (1983).
T.D. Xu and B.Y. Cheng: Kinetics of non-equilibrium grain-boundary segregation. Prog. Mater. Sci. 49, 109 (2004).
D. McLean: Grain Boundaries in Metals (Oxford Univ. Press, London, 1957).
K.T. Aust, J.S. Armijo, E.F. Koch, and J.H. Westbrook: Intergranular corrosion and electron microscopic studies of austenitic stainless steel. ASM Trans. Q. 60, 3 (1967).
T.R. Anthony: Solute segregation in vacancy gradients generated by sintering and temperature changes. Acta Metall. 17, 603 (1969).
Z. Zhang, Q. Lin, and Z. Yu: Grain boundary segregation in ultra-low carbon steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 291, 22 (2000).
R.G. Faulkner: Non-equilibrium grain-boundary segregation in austenitic alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 16, 373 (1981).
T.D. Xu: The critical time and critical cooling rate of non-equilibrium grain-boundary segregations. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 7, 241 (1988).
T.D. Xu: Non-equilibrium grain-boundary segregation kinetics. J. Mater. Sci. 22, 337 (1987).
W.F. Gale and T.C. Totemeier: Smithells Metals Reference Book, 8th ed. (Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann Publishers, Burlington, 2003). (in America).
L.H. Van Vlack, O.K. Riegger, R.J. Warrick, and J.M. Dahl: Sulfide inclusions in steel. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 28, 220 (1961).
S.Q. Xiao, P.J. Wilbrandt, and P. Haasen: HREM observation of the nucleation of γ′-precipitates at dislocations in a Ni–12 at.% Al alloy. Scr. Metall. 23, 295 (1989).
Y.U. Hao, Y.L. Kang, Z.Z. Zhao, and S. Hao: Morphology and precipitation kinetics of MnS in low-carbon steel during thin slab continuous casting process. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 13, 30 (2006).
J.K. Mason: Grain boundary energy and curvature in Monte Carlo and cellular automata simulations of grain boundary motion. Acta Mater. 55, 2217 (2015).
D.J. Srolovitz, G.S. Grest, M.P. Anderson, and A.D. Rollet: Computer simulation of recrystallization—II. Heterogeneous nucleation and growth. Acta Metall. 94, 162 (2015).
A.M. Deus, M.A. Fortes, P.J. Ferreira, and J.B. Vander Sande: A general approach to grain growth driven by energy density differences. Acta Mater. 36, 2115 (1988).
S. Shahandeh and M. Militzer: Grain boundary curvature and grain growth kinetics with particle pinning. Philos. Mag. 50, 3317 (2002).
G.K. Williamson and W.H. Hall: X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 93, 3231 (2013).
G.K. Williamson and R.E. Smallman, III: Dislocation densities in some annealed and cold-worked metals from measurements on the X-ray Debye-Scherrer spectrum. Philos. Mag. 1, 22 (1953).
A. Kisko, J. Talonen, D.A. Porter, and L.P. Karjalainen: Effect of Nb microalloying on reversion and grain growth in a high-Mn 204 Cu austenitic stainless steel. ISIJ Int. 1, 34 (1956).
C. Yang, H. Huang, G.J. Thorogood, L. Jiang, X. Ye, Z. Li, and X. Zhou: The effect of grain size and dislocation density on the tensile properties of Ni–SiCNP composites during annealing. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25, 726 (2016).
P.A. Beck and P.R. Sperry: Strain induced grain boundary migration in high purity aluminum. J. Appl. Phys. 21, 150 (1950).
F. Haessner, ed.: Recrystallization of Metallic Materials (Riederer Verlag, Stuttgart, 1971); p. 21.
T. Gladman: On the theory of the effect of precipitate particles on grain growth in metals. Proc. R. Soc. London 294, 298 (1966).
A.J. DeArdo, G.A. Ratz and P.J. Wray, eds.: Thermomechanical processing of microalloyed austenite. Proceedings of the international conference on the thermomechanical processing of microalloyed austenite (Metall. Soc. of AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1982).
M. Chapa, S.F. Medina, V. López, and B. Femández: Influence of Al and Nb on optimum Ti/N ratio in controlling austenite grain growth at reheating temperatures. ISIJ Int. 42, 1288 (2002).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1460103). We thank Dr. Han in the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory of USA for insights, Dr. Tyler for editing, and the Instrumental Analysis & Research Center in Shanghai University for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Li, H., Wu, Y. et al. Effect of precipitates on grain growth in non-oriented silicon steel. Journal of Materials Research 32, 2307–2314 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.115
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2017.115