Abstract
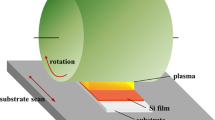
Hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H) films with a designed buffer layer of amorphous hydrogenated silicon carbide on the substrates were fabricated by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD). The effect of radio frequency (RF) power on the structural and optical properties of a-C:H films was investigated. The ratios of sp3 to sp2 of carbon atoms and hydrogen contents in the RF power range of 75–175 W are determined and a similar trend as a function of power. The increase of sp3 to sp2 ratio leads to the increase of transmittance and optical gap of a-C:H films. a-C:H film under an RF power of 175 W possesses high transmissive ability (>80%) in the visible wave length, even the highest transmittance value of about 94.2% is achieved at the wave length 550 nm. These results show the optimal a-C:H films which are promising for the applications in the area of solar cells acting a window layer and antireflection layer.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. Robertson: Diamond-like amorphous carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 37(4), 129 (2002).
F. Chuang, C. Sun, H. Cheng, C. Huang, and I. Lin: Enhancement of electron emission efficiency of Mo tips by diamond like carbon coatings. Appl. Phys. Lett. 68(12), 1666 (1996).
V. Aroutiounian, K. Martirosyan, and P. Soukiassian: Low reflectance of diamond-like carbon/porous silicon double layer antireflection coating for silicon solar cells. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 37(19), L25 (2004).
G. Pearce, N. Marks, D. McKenzie, and M. Bilek: Molecular dynamics simulation of the thermal spike in amorphous carbon thin films. Diamond Relat. Mater. 14(3), 921 (2005).
J. Robertson: Ultrathin carbon coatings for magnetic storage technology. Thin Solid Films 383(1), 81 (2001).
P.R. Goglia, J. Berkowitz, J. Hoehn, A. Xidis, and L. Stover: Diamond-like carbon applications in high density hard disc recording heads. Diamond Relat. Mater. 10(2), 271 (2001).
R. Hauert: A review of modified DLC coatings for biological applications. Diamond Relat. Mater. 12(3), 583 (2003).
A.C. Ferrari: Diamond-like carbon for magnetic storage disks. Surf. Coat. Technol. 180, 190 (2004).
S. Singh, M. Pandey, N. Chand, A. Biswas, D. Bhattacharya, S. Dash, A. Tyagi, R. Dey, S. Kulkarni, and D. Patil: Optical and mechanical properties of diamond like carbon films deposited by microwave ECR plasma CVD. Bull. Mater. Sci. 31(5), 813 (2008).
M. Allon-Alaluf, J. Appelbaum, M. Maharizi, A. Seidman, and N. Croitoru: The influence of diamond-like carbon films on the properties of silicon solar cells. Thin Solid Films 303(1), 273 (1997).
C.H. Lee and K.S. Lim: Carrier transport through boron-doped amorphous diamond-like carbon p layer of amorphous silicon based p–i–n solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 75(4), 569 (1999).
Y. Hattori, D. Kruangam, T. Toyama, H. Okamoto, and Y. Hamakawa: Highly conductive p-type microcrystalline SiC:H prepared by ECR plasma CVD. Appl. Surf. Sci. 33, 1276 (1988).
Y. Hamakawa, T. Toyama, and H. Okamoto: Blue light emission from a-C:H by thin film electroluminescence structure cell. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 115(1), 180 (1989).
J.Y. Shim, E.J. Chi, H.K. Baik, and S.M. Lee: Structural, optical, and field emission properties of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films grown by helical resonator plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 37(2R), 440 (1998).
Y. Lu, S. Huang, C. Huan, and X. Luo: Amorphous hydrogenated carbon synthesized by pulsed laser deposition from cyclohexane. Appl. Phys. A 68(6), 647 (1999).
C. Weissmantel, K. Bewilogua, D. Dietrich, H-J. Erler, H-J. Hinneberg, S. Klose, W. Nowick, and G. Reisse: Structure and properties of quasi-amorphous films prepared by ion beam techniques. Thin Solid Films 72(1), 19 (1980).
Y.S. Park, H.J. Cho, and B. Hong: Characteristics of conductive amorphous carbon (aC) films prepared by using the magnetron sputtering method. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 51(3), 1119 (2007).
B. Tay, Z. Zhao, and D. Chua: Review of metal oxide films deposited by filtered cathodic vacuum arc technique. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 52(1), 1 (2006).
N. Dwivedi, S. Kumar, H. Malik, C. Rauthan, and O. Panwar: Correlation of sp3 and sp2 fraction of carbon with electrical, optical and nano-mechanical properties of argon-diluted diamond-like carbon films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257(15), 6804 (2011).
É.C. Oliveira, S.A. Cruz, and P.H. Aguiar: Effect of PECVD deposition parameters on the DLC/PLC composition of a-C:H thin films. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 23(9), 1657 (2012).
J. Wu, Y-L. Wang, and C-T. Kuo: Plasma treatment effects on hydrogenated amorphous carbon films prepared by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 69(2), 505 (2008).
I. Ahmad, S. Roy, M.A. Rahman, T. Okpalugo, P. Maguire, and J. Mc Laughlin: Substrate effects on the microstructure of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films. Curr. Appl. Phys. 9(5), 937 (2009).
C. Schwarz, J. Heeg, M. Rosenberg, and M. Wienecke: Investigation on wear and adhesion of graded Si/SiC/DLC coatings deposited by plasma-enhanced-CVD. Diamond Relat. Mater. 17(7), 1685 (2008).
F. Cemin, L. Bim, C. Menezes, C. Aguzzoli, M.M. da Costa, I. Baumvol, F. Alvarez, and C. Figueroa: On the hydrogenated silicon carbide (SiCx:H) interlayer properties prompting adhesion of hydrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H) deposited on steel. Vacuum 109, 180 (2014).
A.S. Glaude, L. Thomas, E. Tomasella, J. Badie, and R. Berjoan: Selective effect of ion/surface interaction in low frequency PACVD of SiC:H films: Part B. Microstructural study. Surf. Coat. Technol. 201(1), 174 (2006).
K. Nass, P. Radi, D. Leite, M. Massi, A. da Silva Sobrinho, R. Dutra, L. Vieira, and D. Reis: Tribomechanical and structural properties of a-SiC:H films deposited using liquid precursors on titanium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 284, 240 (2015).
A. Soum-Glaude, L. Thomas, E. Tomasella, J. Badie, and R. Berjoan: Selective effect of ion/surface interaction in low frequency PACVD of SiC:H films: Part A. Gas phase considerations. Surf. Coat. Technol. 200(1), 855 (2005).
B. Dischler, A. Bubenzer, and P. Koidl: Bonding in hydrogenated hard carbon studied by optical spectroscopy. Solid State Commun. 48(2), 105 (1983).
P. Couderc and Y. Catherine: Structure and physical properties of plasma-grown amorphous hydrogenated carbon films. Thin Solid Films 146(1), 93 (1987).
Z. Akkerman, H. Efstathiadis, and F. Smith: Thermal stability of diamond like carbon films. J. Appl. Phys. 80(5), 3068 (1996).
D. Basa and F. Smith: Annealing and crystallization processes in a hydrogenated amorphous SiC alloy film. Thin Solid Films 192(1), 121 (1990).
Y. Lifshitz, S. Kasi, J. Rabalais, and W. Eckstein: Subplantation model for film growth from hyperthermal species. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 41(15), 10468 (1990).
J. Robertson: The deposition mechanism of diamond-like a-C and a-C:H. Diamond Relat. Mater. 3(4–6), 361 (1994).
A. Rhallabi and Y. Catherine: Computer simulation of a carbon-deposition plasma in CH4. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 19(2), 270 (1991).
N.V. Mantzaris, E. Gogolides, A.G. Boudouvis, A. Rhallabi, and G. Turban: Surface and plasma simulation of deposition processes: CH4 plasmas for the growth of diamond like carbon. J. Appl. Phys. 79(7), 3718 (1996).
N. Mutsukura and K. Saitoh: Temperature dependence of a-C:H film deposition in a CH4 radio frequency plasma. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 14(4), 2666 (1996).
J. Robertson: Properties of diamond-like carbon. Surf. Coat. Technol. 50(3), 185 (1992).
X. Liu, R. Yamaguchi, N. Umehara, X. Deng, H. Kousaka, and M. Murashima: Clarification of high wear resistance mechanism of ta-CNx coating under poly alpha-olefin (PAO) lubrication. Tribol. Int. 105, 193 (2017).
J. Schwan, S. Ulrich, V. Batori, H. Ehrhardt, and S. Silva: Raman spectroscopy on amorphous carbon films. J. Appl. Phys. 80(1), 440 (1996).
A. Ferrari and J. Robertson: Resonant Raman spectroscopy of disordered, amorphous, and diamond like carbon. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 64(7), 075414 (2001).
N. Colthup, L. Daly, and S. Wiberley: Introduction to Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy, Vol. 23 (Academic Press, New York, 1975).
L.C. Nistor, J. Van Landuyt, V. Ralchenko, T. Kononenko, E.D. Obraztsova, and V. Strelnitsky: Direct observation of laser-induced crystallization of a-C:H films. Appl. Phys. A 58(2), 137 (1994).
E. Cappelli, S. Orlando, G. Mattei, S. Zoffoli, and P. Ascarelli: SEM and Raman investigation of RF plasma assisted pulsed laser deposited carbon films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 197, 452 (2002).
T. Paulmier, J.M. Bell, and P.M. Fredericks: Deposition of nano-crystalline graphite films by cathodic plasma electrolysis. Thin Solid Films 515(5), 2926 (2007).
J. Sui, Z. Gao, W. Cai, and Z. Zhang: Corrosion behavior of NiTi alloys coated with diamond-like carbon (DLC) fabricated by plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 452, 518 (2007).
J-K. Shin, C.S. Lee, K-R. Lee, and K.Y. Eun: Effect of residual stress on the Raman-spectrum analysis of tetrahedral amorphous carbon films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78(5), 631 (2001).
A. Ferrari, S. Rodil, and J. Robertson: Interpretation of infrared and Raman spectra of amorphous carbon nitrides. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 67(15), 155306 (2003).
R. Al-Jishi and G. Dresselhaus: Lattice-dynamical model for graphite. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 26(8), 4514 (1982).
R. Dillon, J.A. Woollam, and V. Katkanant: Use of Raman scattering to investigate disorder and crystallite formation in as-deposited and annealed carbon films. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 29(6), 3482 (1984).
N. Cho, D. Veirs, J. Ager Iii, M. Rubin, C. Hopper, and D. Bogy: Effects of substrate temperature on chemical structure of amorphous carbon films. J. Appl. Phys. 71(5), 2243 (1992).
T. Herak, R. McLeod, K. Kao, H. Card, H. Watanabe, K. Katoh, M. Yasui, and Y. Shibata: Undoped amorphous SiNx:H alloy semiconductors: Dependence of electronic properties on composition. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 69(1), 39 (1984).
J. Robertson and E. O’reilly: Electronic and atomic structure of amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 35(6), 2946 (1987).
J. Robertson: Gap states in diamond-like amorphous carbon. Philos. Mag. B 76(3), 335 (1997).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11374181 and 61604087).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Tan, X., Jiang, L. et al. The effect of radio frequency power on the structural and optical properties of a-C:H films prepared by PECVD. Journal of Materials Research 32, 1231–1238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.522
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.522