Abstract
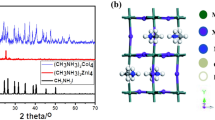
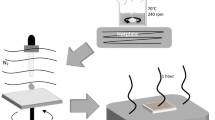
Photovoltaics made from organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite semiconductors are attracting significant interest due to their ability to harvest sunlight with remarkable efficiency. The presence of lead in the best performing devices raises concerns regarding their toxicity, a problem that may create barriers to commercialization. Hybrid perovskites with reduced lead content are being investigated to overcome this issue and here we evaluate bismuth as a possible lead substitute. For a series of hybrid perovskite films with the general composition CH3NH3(PbyBi1− y)I3− xClx, we characterize their optical and structural properties using UV–Vis spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and grazing incidence wide angle X-ray scattering. We show that they form crystalline structures with an optical band gap, around 2 eV for CH3NH3BiI3. However, preliminary solar cell tests show low power conversion efficiencies (<0.01%) due to both incomplete precursor conversion and material de-wetting from the substrate. The overall outcome is severely limited photocurrent. With current processing methods the general applicability of hybrid bismuth perovskites in photovoltaics may be limited.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
S.E. Shaheen, D.S. Ginley, and G.E. Jabbour: Organic-based photovoltaics: Toward low-cost power generation. MRS Bull. 30(1), 10 (2005).
D.Y. Liu and T.L. Kelly: Perovskite solar cells with a planar heterojunction structure prepared using room-temperature solution processing techniques. Nat. Photonics 8(2), 133 (2014).
M.Z. Liu, M.B. Johnston, and H.J. Snaith: Efficient planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells by vapour deposition. Nature 501(7467), 395 (2013).
J. Burschka, N. Pellet, S.J. Moon, R. Humphry-Baker, P. Gao, M.K. Nazeeruddin, and M. Gratzel: Sequential deposition as a route to high-performance perovskite-sensitized solar cells. Nature 499(7458), 316 (2013).
J.M. Ball, M.M. Lee, A. Hey, and H.J. Snaith: Low-temperature processed meso-superstructured to thin-film perovskite solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 6(6), 1739 (2013).
M.M. Lee, J. Teuscher, T. Miyasaka, T.N. Murakami, and H.J. Snaith: Efficient hybrid solar cells based on meso-superstructured organometal halide perovskites. Science 338(6107), 643 (2012).
G.E. Eperon, S.D. Stranks, C. Menelaou, M.B. Johnston, L.M. Herz, and H.J. Snaith: Formamidinium lead trihalide: A broadly tunable perovskite for efficient planar heterojunction solar cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 7(3), 982 (2014).
N. Pellet, P. Gao, G. Gregori, T.Y. Yang, M.K. Nazeeruddin, J. Maier, and M. Gratzel: Mixed-organic-cation perovskite photovoltaics for enhanced solar-light harvesting. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 53(12), 3151 (2014).
S.P. Pang, H. Hu, J.L. Zhang, S.L. Lv, Y.M. Yu, F. Wei, T.S. Qin, H.X. Xu, Z.H. Liu, and G.L. Cui: NH2CH=NH2PbI3: An alternative organolead iodide perovskite sensitizer for mesoscopic solar cells. Chem. Mater. 26(3), 1485 (2014).
J.H. Noh, S.H. Im, J.H. Heo, T.N. Mandal, and S.I. Seok: Chemical management for colorful, efficient, and stable inorganic–organic hybrid nanostructured solar cells. Nano Lett. 13(4), 1764 (2013).
N.K. Noel, S.D. Stranks, A. Abate, C. Wehrenfennig, S. Guarnera, A.A. Haghighirad, A. Sadhanala, G.E. Eperon, S.K. Pathak, M.B. Johnston, A. Petrozza, L.M. Herz, and H.J. Snaith: Lead-free organic–inorganic tin halide perovskites for photovoltaic applications. Energy Environ. Sci. 7(9), 3061 (2014).
NREL: http://www.nrel.gov/ncpv/images/efficiency_chart.jpg, (National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, CO).
P.J. Landrigan: Toxicity of lead at low-dose. Br. J. Ind. Med. 46(9), 593 (1989).
G. Flora, D. Gupta, and A. Tiwari: Toxicity of lead: A review with recent updates. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 5(2), 47 (2012).
A. Babayigit, A. Ethirajan, M. Muller, and B. Conings: Toxicity of organometal halide perovskite solar cells. Nat. Mater. 15(3), 247 (2016).
Y. Ogomi, A. Morita, S. Tsukamoto, T. Saitho, N. Fujikawa, Q. Shen, T. Toyoda, K. Yoshino, S.S. Pandey, T.L. Ma, and S. Hayase: CH3NH3SnxPb(1− x)I3 perovskite solar cells covering up to 1060 nm. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 5(6), 1004 (2014).
F. Hao, C.C. Stoumpos, D.H. Cao, R.P.H. Chang, and M.G. Kanatzidis: Lead-free solid-state organic–inorganic halide perovskite solar cells. Nat. Photonics 8(6), 489 (2014).
W. Travis, E.N.K. Glover, H. Bronstein, D.O. Scanlon, and R.G. Palgrave: On the application of the tolerance factor to inorganic and hybrid halide perovskites: A revised system. Chem. Sci. 7, 4548 (2016).
B.W. Park, B. Philippe, X.L. Zhang, H. Rensmo, G. Boschloo, and E.M.J. Johansson: Bismuth based hybrid perovskites A(3)Bi(2)I(9) (A: methylammonium or cesium) for solar cell application. Adv. Mater. 27(43), 6806 (2015).
A.H. Slavney, T. Hu, A.M. Lindenberg, and H.I. Karunadasa: A bismuth-halide double perovskite with long carrier recombination lifetime for photovoltaic applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 138(7), 2138 (2016).
S. Colella, E. Mosconi, P. Fedeli, A. Listorti, F. Gazza, F. Orlandi, P. Ferro, T. Besagni, A. Rizzo, G. Calestani, G. Gigli, F. De Angelis, and R. Mosca: MAPbl(3− x)Clx mixed halide perovskite for hybrid solar cells: The role of chloride as dopant on the transport and structural properties. Chem. Mater. 25(22), 4613 (2013).
S.A. Kulkarni, T. Baikie, P.P. Boix, N. Yantara, N. Mathews, and S. Mhaisalkar: Band-gap tuning of lead halide perovskites using a sequential deposition process. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(24), 9221 (2014).
C. Bi, Y.C. Shao, Y.B. Yuan, Z.G. Xiao, C.G. Wang, Y.L. Gao, and J.S. Huang: Understanding the formation and evolution of interdiffusion grown organolead halide perovskite thin films by thermal annealing. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(43), 18508 (2014).
Y. Tian and I.G. Scheblykin: Artifacts in absorption measurements of organometal halide perovskite materials: What are the real spectra? J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 6(17), 3466 (2015).
T. Ondarçuhu and J.P. Aimé: Nanoscale Liquid Interfaces: Wetting, Patterning and Force Microscopy at the Molecular Scale (Pan Stanford publishing, Singapore, 2013).
Y.X. Zhao and K. Zhu: CH3NH3Cl-assisted one-step solution growth of CH(3)NH(3)Pbl(3): Structure, charge-carrier dynamics, and photovoltaic properties of perovskite solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 118(18), 9412 (2014).
H. Yu, F. Wang, F.Y. Xie, W.W. Li, J. Chen, and N. Zhao: The role of chlorine in the formation process of “CH3NH3PbI3− xCl(x)” perovskite. Adv. Funct. Mater. 24(45), 7102 (2014).
E.L. Unger, A.R. Bowring, C.J. Tassone, V.L. Pool, A. Gold-Parker, R. Cheacharoen, K.H. Stone, E.T. Hoke, M.F. Toney, and M.D. McGehee: Chloride in lead chloride-derived organo-metal halides for perovskite-absorber solar cells. Chem. Mater. 26(24), 7158 (2014).
L.Q. Zhang, X.W. Zhang, Z.G. Yin, Q. Jiang, X. Liu, J.H. Meng, Y.J. Zhao, and H.L. Wang: Highly efficient and stable planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells via a low temperature solution process. J. Mater. Chem. A 3(23), 12133 (2015).
K.W. Tan, D.T. Moore, M. Saliba, H. Sai, L.A. Estroff, T. Hanrath, H.J. Snaith, and U. Wiesner: Thermally induced structural evolution and performance of mesoporous block copolymer-directed alumina perovskite solar cells. ACS Nano 8(5), 4730 (2014).
B.W. Park, B. Philippe, T. Gustafsson, K. Sveinbjornsson, A. Hagfeldt, E.M.J. Johansson, and G. Boschloo: Enhanced crystallinity in organic–inorganic lead halide perovskites on mesoporous TiO2 via disorder-order phase transition. Chem. Mater. 26(15), 4466 (2014).
T. Baikie, Y.N. Fang, J.M. Kadro, M. Schreyer, F.X. Wei, S.G. Mhaisalkar, M. Graetzel, and T.J. White: Synthesis and crystal chemistry of the hybrid perovskite (CH3NH3) PbI3 for solid-state sensitised solar cell applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 1(18), 5628 (2013).
J.H. Im, C.R. Lee, J.W. Lee, S.W. Park, and N.G. Park: 6.5% efficient perovskite quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell. Nanoscale 3(10), 4088 (2011).
C.C. Stoumpos, C.D. Malliakas, and M.G. Kanatzidis: Semiconducting tin and lead iodide perovskites with organic cations: phase transitions, high mobilities, and near-infrared photoluminescent properties. Inorg. Chem. 52(15), 9019 (2013).
S.J. Yoon, K.G. Stamplecoskie, and P.V. Kamat: How lead halide complex chemistry dictates the composition of mixed halide perovskites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 7(7), 1368 (2016).
CrystalMaker Software Limited: http://www.crystalmaker.com/crystaldiffract/. Centre for Innovation & Enterprise, Oxford University Begbroke Science Park, Woodstock Road Begbroke, Oxfordshire, OX5 1PF UK.
A.T. Barrows, A.J. Pearson, C.K. Kwak, A.D.F. Dunbar, A.R. Buckley, and D.G. Lidzey: Efficient planar heterojunction mixed-halide perovskite solar cells deposited via spray-deposition. Energy Environ. Sci. 7(9), 2944 (2014).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We gratefully acknowledge funding from the EPSRC through research grants EP/M025020/1 “High resolution mapping of performance and degradation mechanisms in printable photovoltaic devices” and EP/J017361/1 “Supergen Supersolar Hub.” We thank Diamond Light Source for access to beamline I07 (SI11676-1) that contributed to the results presented here and we acknowledge Jonathan Rawle and Jonathan Griffin for their assistance during the GIWAXS experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
43578_2017_32101888_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supporting Information: An x-ray scattering and electron microscopy study of methylammonium bismuth perovskites for solar cell applications (approximately 15.3 MB)







Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kwak, C.K., Barrows, A.T., Pearson, A.J. et al. An X-ray scattering and electron microscopy study of methylammonium bismuth perovskites for solar cell applications. Journal of Materials Research 32, 1888–1898 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.499
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.499