Abstract
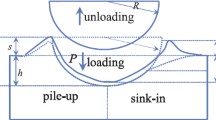
Indentation method has been widely used in the measurement of material mechanical properties and residual stress for its simple, fast and nondestructive characteristics. In the indentation test, because of the plastic deformation of the material, the material accumulation and subsidence occurs around the indentation. It is found that the deformation amount of the indentation, especially the maximum pile-up around the indentation after unloading, is related to the magnitude and direction of the residual stress. In this paper, an experimental study on the pile-up morphology around an indentation for determining the direction and magnitude of residual stress is reported. Nonsymmetrical morphology of spherical indenting deformation on artificially strained steel specimen was measured with a laser scanning confocal system. A unique relationship between pile-up after unloading and biaxial residual stress was set up based on the experimental results. The direction and components of nonequibiaxial residual stress can be determined by the proposed method.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Tebedge, G. Alpsten, and L. Tall: Residual-stress measurement by the sectioning method. Exp. Mech. 13(2), 88 (1973).
D. Nelson and J. McCrickerd: Residual-stress determination through combined use of holographic interferometry and blind-hole drilling. Exp. Mech. 26(4), 371 (1986).
J. Gauthier, T. Krause, and D. Atherton: Measurement of residual stress in steel using the magnetic Barkhausen noise technique. NDT&E Int. 31(1), 23 (1998).
R. Gou, Y. Zhang, X. Xu, L. Sun, and Y. Yang: Residual stress measurement of new and in-service X70 pipelines by x-ray diffraction method. NDT&E Int. 44(5), 387 (2011).
E. Hu, Y. He, and Y. Chen: Experimental study on the surface stress measurement with Rayleigh wave detection technique. Appl. Acoust. 70(2), 356 (2009).
M. Doerner and W. Nix: A method for interpreting the data from depth-sensing indentation instruments. J. Mater. Res. 1(4), 601 (1986).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7(6), 1564 (1992).
J. Field and M. Swain: Determining the mechanical properties of small volumes of material from submicrometer spherical indentations. J. Mater. Res. 10(1), 101 (1995).
M. Swain: Mechanical property characterisation of small volumes of brittle materials with spherical tipped indenters. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 253(1), 160 (1998).
M. Dao, N. Chollacoop, K. Van Vliet, T. Venkatesh, and S. Suresh: Computational modeling of the forward and reverse problems in instrumented sharp indentation. Acta Mater. 49(19), 3899 (2001).
S. Suresh and A. Giannakopoulos: A new method for estimating residual stresses by instrumented sharp indentation. Acta Mater. 46(16), 5755 (1998).
X. Chen, J. Yan, and A.M. Karlsson: On the determination of residual stress and mechanical properties by indentation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 416(1), 139 (2006).
J-I. Jang, D. Son, Y-H. Lee, Y. Choi, and D. Kwon: Assessing welding residual stress in A335 P12 steel welds before and after stress-relaxation annealing through instrumented indentation technique. Scr. Mater. 48(6), 743 (2003).
Y.B. Gerbig, S.J. Stranick, and R.F. Cook: Measurement of residual stress field anisotropy at indentations in silicon. Scr. Mater. 63(5), 512 (2010).
J. Swadener, B. Taljat, and G. Pharr: Measurement of residual stress by load and depth sensing indentation with spherical indenters. J. Mater. Res. 16(07), 2091 (2001).
Y-H. Lee and D. Kwon: Estimation of biaxial surface stress by instrumented indentation with sharp indenters. Acta Mater. 52(6), 1555 (2004).
Y-H. Lee, K. Takashima, Y. Higo, and D. Kwon: Prediction of stress directionality from pile-up morphology around remnant indentation. Scr. Mater. 51(9), 887 (2004).
D.I. Kwon, J.S. Lee, J.H. Han, G.J. Lee, Y.H. Lee, M.J. Choi, and K.H. Kim: Residual stress estimation with identification of stress directionality using instrumented indentation technique. Key Eng. Mater. 345, 1125 (2007).
A. Bolshakov and G. Pharr: Influences of pileup on the measurement of mechanical properties by load and depth sensing indentation techniques. J. Mater. Res. 13(4), 1049 (1998).
M. Khan, S. Hainsworth, M. Fitzpatrick, and L. Edwards: A combined experimental and finite element approach for determining mechanical properties of aluminium alloys by nanoindentation. Comput. Mater. Sci. 49(4), 751 (2010).
S.H. Kim, B.W. Lee, Y. Choi, and D. Kwon: Quantitative determination of contact depth during spherical indentation of metallic materials—A FEM study. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 415(1), 59 (2006).
J.H. Underwood: Residual-stress measurement using surface displacements around an indentation. Exp. Mech. 13(9), 373 (1973).
Y. Bisrat and S. Roberts: Residual stress measurement by Hertzian indentation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 288(2), 148 (2000).
L. Shen, Y. He, D. Liu, Q. Gong, B. Zhang, and J. Lei: A novel method for determining surface residual stress components and their directions in spherical indentation. J. Mater. Res. 30(08), 1078 (2015).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by the NSFC (Nos 11272131, 11472114).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., He, Y., Liu, D. et al. Prediction of residual stress components and their directions from pile-up morphology: An experimental study. Journal of Materials Research 31, 2392–2397 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.270
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.270