Abstract
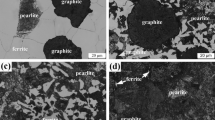
The effects of carbon equivalent on thermal and mechanical properties of compacted graphite cast irons were investigated at ambient temperature, 300 and 500 °C, respectively. The group implied the change of carbon content to control the carbon equivalent. The results indicated that with the increasing carbon equivalent from 4.43 to 4.74, the graphite count increase. The thermal conductivity was 48.64, 44.55, 49.04, and 50.36 W/mK for carbon equivalent about 4.43–4.74 of compacted graphite cast irons at ambient temperature, respectively. With an increase in temperature, the thermal conductivity decrease. Moreover, with the increasing carbon equivalent, the tensile strength and yield strength increase initially, and then decrease at ambient temperature, 300 and 500 °C, respectively. With an increase in temperature, the tensile strength and yield strength decrease. Characterization of fracture surface indicated that the mixed ductile-brittle fracture mode prevailed in the compacted graphite cast irons with different carbon equivalents.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Bazdar, H.R. Abbasi, A.H. Yaghtin, and J. Rassizadehghani: Effect of sulfur on graphite aspect ratio and tensile properties in compacted graphite irons. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209(4), 1701–1705 (2009).
M. Górny and M. Kawalec: Effects of titanium addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of thin-walled compacted graphite iron castings. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 22(5), 1519–1524 (2013).
M. Selin, D. Holmgren, and I.L. Svensson: Effect of alloying elements on graphite morphology in CGI. Mater. Sci. Forum 649, 171–176 (2010).
S. Dawson and T. Schroeder: Practical applications for compacted graphite iron. AFS Trans. 47(5), 1–9 (2004).
J. Liu and N.X. Ding: Effect of type and amount of treatment alloy on compacted graphite produced by the flotret process. AFS Trans. 93, 675–688 (1985).
G. Cueva, A. Sinatora, W.L. Guesser, and A.P. Tschiptschin: Wear resistance of cast irons used in brake disc rotors. Wear 255(7), 1256–1260 (2003).
G.F. Geier, W. Bauer, B.J. McKay, and P. Schumacher: Microstructure transition from lamellar to compacted graphite using different modification agents. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 413, 339–345 (2005).
W. Guesser, T. Schroeder, and S. Dawson: Production experience with compacted graphite iron automotive components. AFS Trans. 01–071, 1–11 (2001).
H.Q. Qiu and Z.D. Chen: The forty years of vermicular graphite cast iron development in China (part I). China Foundry 4(2), 91–98 (2007).
X. Yang, Z.H. Zhang, J.T. Wang, and L.Q. Ren: Investigation of nanomechanical properties and thermal fatigue resistance of gray cast iron processed by laser alloying. J. Alloys Compd. 626, 260–263 (2015).
J.M. Chou, M.H. Hou, and J.L. Lee: Affects of graphite morphology and matrix structure on mechanical properties of cast ions. J. Mater. Sci. 25(4), 1965–1972 (1990).
M. Selin, D. Holmgren, and I.L. Svensson: Influence of alloying additions on microstructure and thermal properties in compacted graphite irons. Int. J. Cast. Met. Res. 22(1–4), 283–285 (2009).
M. König and M. Wessén: Influence of alloying elements on microstructure and mechanical properties of CGI. Int. J. Cast. Met. Res. 23(2), 97–110 (2010).
V. Fourlakidis and A. Diószegi: A generic model to predict the ultimate tensile strength in pearlitic lamellar graphite iron. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 618, 161–167 (2014).
H. Pirgazi, S. Ghodrat, and L.A.I. Kestens: Three-dimensional EBSD characterization of thermo-mechanical fatigue crack morphology in compacted graphite iron. Mater. Charact. 90, 13–20 (2014).
Y.H. Shy, C.H. Hsu, S.C. Lee, and C.Y. Hou: Effects of titanium addition and section size on microstructure and mechanical properties of compacted graphite cast iron. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 278(1), 54–60 (2000).
I. Hervas, M.B. Bettaieb, A. Thuault, and E. Hug: Graphite nodule morphology as an indicator of the local complex strain state in ductile cast iron. Mater. Des. 52, 524–532 (2013).
R.A. Gonzaga: Influence of ferrite and pearlite content on mechanical properties of ductile cast irons. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 567, 1–8 (2013).
S. Kim, S.L. Cockcroft, A.M. Omran, and H. Hwang: Mechanical, wear and heat exposure properties of compacted graphite cast iron at elevated temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 487(1), 253–257 (2009).
M. Moonesan, A. Honarbakhsh raouf, F. Madah, and A. Habibollah zadeh: Effect of alloying elements on thermal shock resistance of gray cast iron. J. Alloys Compd. 520, 226–231 (2012).
H.T. Angus: Cast Iron: Physical, and Engineering Properties, 2nd ed. (British Cast Iron Research Association, London, 1978).
W.J. Parker, R.J. Jenkins, C.P. Butler, and G.L. Abbott: Flash method of determining thermal diffusivity, heat capacity, and thermal conductivity. J. Appl. Phys. 32(9) 1679–1784 (1961).
ASTM E8M-91: Annual Book of ASTM Standards, 1986 (ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 1986); pp. 637–644.
ASTM A247-67: Annual Book of ASTM Standards, 1990 (ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 1990); pp. 129–130.
E.F. Ryntz, Jr: Prediction of nodular iron microstructure using thermal analysis. AFS Trans. 79, 141–144 (1971).
N. Fatahalla, A. Abuelezz, and M. Semeida: C, Si and Ni as alloying elements to vary carbon equivalent of austenitic ductile cast iron: Microstructure and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 504(1), 81–89 (2009).
P.A. Blackmore and K. Morton: Structure-property relationships in graphitic cast irons. Int. J. Fatigue 4(3), 149–155 (1982).
D. Holmgren, R. Källbom, and I.L. Svensson: Influences of the graphite growth direction on the thermal conductivity of cast iron. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 38(2), 268–275 (2007).
I. Asenjo, P. Larranaga, and J. Sertucha: Effect of mould inoculation on formation of chunky graphite in heavy section spheroidal graphite cast iron parts. Int. J. Cast. Met. Res. 20(6), 319–324 (2007).
M. König: Literature review of microstructure formation in compacted graphite iron. Int. J. Cast. Met. Res. 23(3), 185–192 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Xing, J., Li, Y. et al. Effect of carbon equivalent on thermal and mechanical properties of compacted graphite cast iron. Journal of Materials Research 31, 2516–2523 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.263
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.263