Abstract
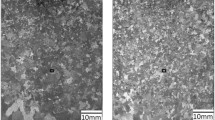
The refinement mechanism of alternating current pulse (ACP) on the solidification macrostructures of pure Al and the characterization of refining efficiency were investigated by embedding the wire mesh in the mold. The experiment results showed that ACP treatment during solidification led to the formation of fine equiaxed grain. There were remarkably differences with respect to the area of fine equiaxed zone inside and outside the tube. Lorentz force, induced melt flow and the rest of intrinsic effects of ACP inside and outside the tube were discussed in the present study. It demonstrated that the forced melt flow could lead to the columnar fragmentation and make the crystal nucleus on the mold wall fall off and drift in the liquid, leading to grain refinement. In addition, Reynolds number was suitable to characterize the refining efficiency of pure Al under ACP.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Nakada, Y. Shiohara, and M.C. Flemings: Modification of solidification structures by pulse electric discharging. ISIJ Int. 30, 27 (1990).
J.P. Barnak, A.F. Sprecher, and H. Conrad: Colony (grain) size reduction in eutectic Pb–Sn castings by electropulsing. Scr. Metall. Mater. 32, 879 (1995).
J.H. Ma, J. Li, Y.L. Gao, and Q.J. Zhai: Grain refinement of pure Al with different electric current pulse modes. Mater. Lett. 63, 142 (2009).
X.B. Li, F.G. Lu, H.C. Cui, and X.H. Tang: Effect of electric current pulse on flow behaviour of Al melt in parallel electrode process. Mater. Sci. Technol. 29, 226 (2013).
Y.B. Jiang, G.Y. Tang, L. Guan, S.N. Wang, Z.H. Xu, C. Shek, and Y.H. Zhu: Effect of electropulsing treatment on solid solution behavior of an aged Mg alloy AZ61 strip. J. Mater. Res. 23, 2685 (2008).
X.L. Wang, W.B. Dai, R. Wang, X.Z. Tian, and X. Zhao: Enhanced phase transformation and variant selection by electric current pulses in a Cu–Zn alloy. J. Mater. Res. 29, 975 (2014).
A. Rahnama and R.S. Qin: Electropulse-induced microstructural evolution in a ferritic–pearlitic 0.14% C steel. Scr. Mater. 96, 17 (2015).
Y.Z. Zhou, R.S. Qin, and S.H. Xiao: Reversing effect of electropulsing on damage of 1045 steel. J. Mater. Res. 15, 1056 (2000).
W.R. Osório, E.S. Freitas, and A. Garcia: EIS and potentiodynamic polarization studies on immiscible monotectic Al–In alloys. Electrochim. Acta 102, 436 (2013).
L.R. Garcia, W.R. Osório, and A. Garcia: The effect of cooling rate on the dendritic spacing and morphology of Ag3Sn intermetallic particles of a SnAg solder alloy. Mater. Des. 32, 3008 (2011).
W.R. Osorio, C.M.A. Freire, and A. Garcia: The role of macrostructural morphology and grain size on the corrosion resistance of Zn and Al castings. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 402, 22 (2005).
X.F. Zhang, W.J. Lu, and R.S. Qin: Removal of MnS inclusions in molten steel using electropulsing. Scr. Mater. 69, 453 (2013).
J.G. Qi, J.Z. Wang, and L.J. He: An investigation for structure transformation in electric pulse modified liquid aluminum. Phys. B 406, 846 (2011).
J.Z. Wang, J.Q. Qi, Z.F. Zhao, H.S. Guo, and T. Zhao: Effects of electric pulse modification on liquid structure of Al–5%Cu alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 23, 2792 (2013).
J. Li, J.H. Ma, Y.L. Gao, and Q.J. Zhai: Research on solidification structure refinement of pure aluminum by electric current pulse with parallel electrodes. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 490, 452 (2008).
C.Y. Ban, Y. Han, Q.X. Ba, and J.Z. Cui: Influence of pulse electric current on solidification structures of Al–Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Forum 546–549, 723 (2007).
X.L. Liao, Q.J. Zhai, C.J. Song, W.J. Chen, and Y.Y. Gong: Effects of electric current pulse on stability of solid/liquid interface of Al–4.5 wt.% Cu alloy during directional solidification. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 466, 56 (2007).
J. Zhu, T. Wang, F. Cao, W.X. Huang, H. Fu, and Z. Chen: Real time observation of equiaxed growth of Sn–Pb alloy under an applied direct current by synchrotron microradiography. Mater. Lett. 89, 137 (2012).
X.L. Liao, Q.J. Zhai, J. Luo, W.J. Chen, and Y.Y. Gong: Refining mechanism of the electric current pulse on the solidification structure of pure aluminum. Acta Mater. 55, 3103 (2007).
L.M. Zhang, R. Zhang, W. Chen, Y. Wu, and N. Li: Effect of a novel low-voltage alternating current pulse on solidification structure of Al-7Si-0.52Mg alloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 482, 1431 (2012).
M.C. Gui, J. Jia, Q.C. Li, and J.H. Feng: Design and application of the instrument of electrical resistivity measurement for liquid metal. J. Mater. Eng. 7, 29 (1994). (In Chinese).
D. Räbiger, Y. Zhang, V. Galindo, S. Franke, B. Willers, and S. Eckert: The relevance of melt convection to grain refinement in Al–Si alloys solidified under the impact of electric currents. Acta Mater. 79, 327 (2014).
M.J. Li, T. Tamura, N. Omura, and K. Miwa: Effects of magnetic field and electric current on the solidification of AZ91D magnesium alloys using an electromagnetic vibration technique. J. Alloys Compd. 487, 187 (2009).
L.M. Zhang, N. Li, H. Xing, R. Zhang, K. Song, L. Du, P. Yin, and C. Yang: Microstructure evolution of directionally solidified Sn–Bi alloy under different medium-density direct current. J. Cryst. Growth 430, 80 (2015).
I. Kaldre, Y. Fautrelle, J. Etay, A. Bojarevics, and L. Buligins: Influence on the macrosegregation of binary metallic alloys by thermoelectromagnetic convection and electromagnetic stirring combination. J. Cryst. Growth 402, 230 (2014).
E. Liotti, A. Lui, R. Vincent, S. Kumar, Z. Guo, T. Connolley, I.P. Dolbnya, M. Hart, L. Arnberg, R.H. Mathiesen, and P.S. Grant: A synchrotron X-ray radiography study of dendrite fragmentation induced by a pulsed electromagnetic field in an Al–15Cu alloy. Acta Mater. 70, 228 (2014).
V. Sklyarchuk, Y. Plevachuk, A. Yakymovych, S. Eckert, G. Gerbeth, and K. Eigenfeld: Structure sensitive properties of liquid Al–Si alloys. Int. J. Thermophys. 30, 1400 (2009).
M.H. Sun, H.R. Geng, X.F. Bian, and Y. Liu: Abnormal changes in aluminum viscosity and its relationship with the microstructure of melts. Acta Metall. Sin. 36, 1135 (2000). (In Chinese).
X. Li, Y. Fautrelle, and Z.M. Ren: Influence of thermoelectric effects on the solid-liquid interface shape and cellular morphology in the mushy zone during the directional solidification of Al–Cu alloys under a magnetic field. Acta Mater. 55, 3803 (2007).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of the NPU Foundation for Fundamental Research in China (No. JC201272), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities on Northwestern Polytechnical University (GEKY1008 and No. 3102014KYJD026) and the National Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province in China (No. 2015JQ5125).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Liu, H., Li, N. et al. The relevance of forced melt flow to grain refinement in pure aluminum under a low-frequency alternating current pulse. Journal of Materials Research 31, 396–404 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.17
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.17