Abstract
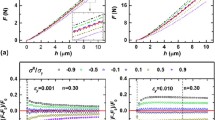
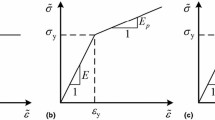
In this paper, a novel method is proposed to determine surface residual stress components and their directions based on the spherical indentation. To obtain the direction and the components of a uniaxial or biaxial residual stress, the relationship between the pile-up deformation around an indentation after unloading and the residual stress was firstly systematically studied and established by using numerical simulation. Through theoretical analysis and numerical simulation, we found that the position of the maximum residual stress is dependent on the maximum pile-up around an indentation after unloading. The direction and components of residual stress can be correctly determined by the unique relationship between pile-up after unloading and biaxial residual stress. This conclusion has been verified by the experiment results in the residual stress measurements of a welded specimen with spherical indentation and x-ray diffraction methods. Meanwhile, the influences of friction between the object surface and the indenter, the material hardening exponent of the specimen, and the elastic deformation upon the residual stress are discussed.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Arsenault and M. Taya: Thermal residual stress in metal matrix composite. Acta Metall. 35(3), 651 (1987).
P. Dong and F.W. Brust: Welding residual stresses and effects on fracture in pressure vessel and piping components: A millennium review and beyond. J. Pressure Vessel Technol. 122(3), 329 (2000).
Y.I. Golovin: Nanoindentation and mechanical properties of solids in submicrovolumes, thin near-surface layers, and films: A review. Phys. Solid State 50(12), 2205 (2008).
E. Hu, Y. He, and Y. Chen: Experimental study on the surface stress measurement with Rayleigh wave detection technique. Appl. Acoust. 70(2), 356 (2009).
J. Gauthier, T.W. Krause, and D.L. Atherton: Measurement of residual stress in steel using the magnetic Barkhausen noise technique. NDT&E Int. 31(1), 23 (1998).
R. Gou, Y. Zhang, X. Xu, L. Sun, and Y. Yang: Residual stress measurement of new and in-service X70 pipelines by X-ray diffraction method. NDT&E Int. 44(5), 387 (2011).
M.F. Doerner and W.D. Nix: A method for interpreting the data from depth-sensing indentation instruments. J. Mater. Res. 1(4), 601 (1986).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7(6), 1564 (1992).
M. Dao, N. Chollacoop, K.J. Van Vliet, T.A. Venkatesh, and S. Suresh: Computational modeling of the forward and reverse problems in instrumented sharp indentation. Acta Mater. 49(19), 3899 (2001).
J-I. Jang, Y. Choi, J-S. Lee, Y-H. Lee, D. Kwon, M. Gao, and R. Kania: Application of instrumented indentation technique for enhanced fitness-for-service assessment of pipeline crack. Int. J. Fract. 131(1), 15 (2005).
J.S. Field and M.V. Swain: Determining the mechanical properties of small volumes of material from submicrometer spherical indentations. J. Mater. Res. 10(1), 101 (1995).
M.V. Swain: Mechanical property characterisation of small volumes of brittle materials with spherical tipped indenters. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 253(1), 160 (1998).
A.J. Bushby and D.J. Dunstan: Plasticity size effects in nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 19(1), 137 (2004).
T.T. Zhu, A.J. Bushby, and D.J. Dunstan: Size effect in the initiation of plasticity for ceramics in nanoindentation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56(4), 1170 (2008).
S. Suresh and A.E. Giannakopoulos: A new method for estimating residual stresses by instrumented sharp indentation. Acta Mater. 46(16), 5755 (1998).
Y-T. Cheng and C-M. Cheng: Scaling, dimensional analysis, and indentation measurements. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44(4), 91 (2004).
T.Y. Tsui, W.C. Oliver, and G.M. Pharr: Influences of stress on the measurement of mechanical properties using nanoindentation: Part I. Experimental studies in an aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Res. 11(3), 752 (1996).
A.C. Fischer-Cripps: A simple phenomenological approach to nanoindentation creep. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 385(1), 74 (2004).
A. Gouldstone, N. Chollacoop, M. Dao, J. Li, A.M. Minor, and Y-L. Shen: Indentation across size scales and disciplines: Recent developments in experimentation and modeling. Acta Mater. 55(12), 4015 (2007).
S.H. Kim, B.W. Lee, Y. Choi, and D. Kwon: Quantitative determination of contact depth during spherical indentation of metallic materials—A FEM study. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 415(1), 59 (2006).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19(1), 3 (2004).
X. Chen, J. Yan, and A.M. Karlsson: On the determination of residual stress and mechanical properties by indentation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 416(1), 139 (2006).
Y-H. Lee and D. Kwon: Estimation of biaxial surface stress by instrumented indentation with sharp indenters. Acta Mater. 52(6), 1555 (2004).
Y-H. Lee, K. Takashima, Y. Higo, and D. Kwon: Prediction of stress directionality from pile-up morphology around remnant indentation. Scr. Mater. 51(9), 887 (2004).
D.I. Kwon, J.S. Lee, J.H. Han, G.J. Lee, Y.H. Lee, M.J. Choi, and K.H. Kim: Residual stress estimation with identification of stress directionality using instrumented indentation technique. Key Eng. Mater. 345, 1125 (2007).
A. Bolshakov and G.M. Pharr: Influences of pileup on the measurement of mechanical properties by load and depth sensing indentation techniques. J. Mater. Res. 13(4), 1049 (1998).
J.H. Underwood: Residual-stress measurement using surface displacements around an indentation. Exp. Mech. 13(9), 373 (1973).
Y.M. He, C.J. Tay, and H.M. Shang: Digital phase-shifting shearography for slope measurement. Opt. Eng. 38(9), 1586 (1999).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was financially supported by the NSFC (Nos. 11272131, 11472114), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (No. 20110142110039), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST: No. 2013KXYQ008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., He, Y., Liu, D. et al. A novel method for determining surface residual stress components and their directions in spherical indentation. Journal of Materials Research 30, 1078–1089 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.87
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.87