Abstract
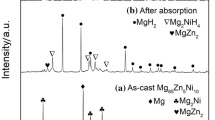
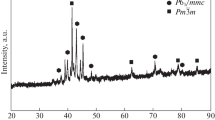
Ti was added to Mg–Ni alloy (Mg95Ni5) by a novel hydriding combustion synthesis (HCS) process. The effect of Ti on hydrogen absorption/desorption kinetics of Mg95Ni5 was investigated. The results showed that Ti had superior catalytic effects on hydrogen storage properties of Mg95Ni5, which required only 80 s to reach its saturated hydrogen absorption capacity of 6.29 wt% at 473 K and released 5.49 wt% hydrogen within 900 s at 553 K. Based on an Arrhenius analysis, the activation energy of the hydrogen desorption process was 80.8 kJ mol−1 for the main phase of MgH2 in the Ti-doped Mg95Ni5. The excellent hydriding/dehydriding properties were related to the existence of TiH1.924, which improved the efficiency of mechanical milling and was helpful in the refinement of the crystallite size of MgH2, resulting in more fresh surface area and grain boundary area. Besides, it was thought to restrain the Mg particles from growth during the hydrogenation/dehydrogenation cycles.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Schlapbach and A. Züttel: Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. Nature 414, 353 (2001).
M.X. Gao, J. Gu, H.G. Pan, Y.L. Wang, Y.F. Liu, C. Liang, and Z.X. Guo: Ca(BH4)2-LiBH4-MgH2: A novel ternary hydrogen storage system with superior long-term cycling performance. J. Mater. Chem. 1, 12285 (2013).
P.B. Amama, J.T. Grant, J.E. Spowart, P.J. shamberger, A.A. Voevodin, and T.S. Fisher: Catalytic influence of Ni-based additives on the dehydrogenation properties of ball milled MgH2. J. Mater. Res. 26, 2725 (2011).
Y. Jia, Y.A. Guo, J. Zou, and X.D. Yao: Hydrogenation/dehydrogenation in MgH2-activated carbon composites prepared by ball milling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37, 7579 (2012).
L.Z. Ouyang, Z.J. Cao, H. Wang, J.W. Liu, D.L. Sun, Q.A. Zhang, and M. Zhu: Enhanced dehydriding thermodynamics and kinetics in Mg(In)–MgF2 composite directly synthesized by plasma milling. J. Alloys Compd. 586, 113 (2014).
Q. Li, Q. Lin, K.C. Chou, L.J. Jiang, and F. Zhan: Hydrogen storage properties of mechanically alloyed Mg–8 mol% LaNi0.5 composite. J. Mater. Res. 19, 2871 (2011).
P. Li, Q. Wan, Z.L. Li, F.Q. Zhai, Y.L. Li, L.Q. Cui, X.H. Qu, and A.A. Volinsky: MgH2 dehydrogenation properties improved by MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Power Sources 239, 201 (2013).
L.P. Ma, P. Wang, X.D. Kang, and H.M. Chen: Preliminary investigation on the catalytic mechanism of TiF3 additive in MgH2–TiF3 H-storage system. J. Mater. Res. 22, 1779 (2011).
C.S. Zhou, Z.Z. Fang, C. Ren, J.Z. Li, and J. Lu: Effect of Ti intermetallic catalysts on hydrogen storage properties of magnesium hydride. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 12973 (2013).
L.P. Ma, P. Wang, and H.M. Cheng: Hydrogen sorption kinetics of MgH2 catalyzed with titanium compounds. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35, 3046 (2010).
E. Grigorova, M. Spassova, T. Spassov, and M. Khristov: Hydrogen sorption properties of 90 wt% MgH2–10 wt% MeSi2 (Me = Ti, Cr). J. Mater. Sci. 49, 2647 (2014).
J. Zhang, Y.N. Huang, C. Mao, and P. Peng: Synergistic effect of Ti and F co-doping on dehydrogenation properties of MgH2 from first-principles calculations. J. Alloys Compd. 528, 205 (2012).
X.F. Liu, Y.F. Zhu, and L.Q. Li: Hydrogen storage properties of Mg100-xNix (x=5, 11.3, 20, 25) composites prepared by hydriding combustion synthesis followed by mechanical milling (HCS+MM). Intermetallics 15, 1582 (2007).
Y.F. Zhu, Y.F. Liu, H. Gu, and L.Q. Li: Structural and hydriding/dehydriding properties of Mg–La–Ni-based composites. J. Alloys Compd. 477, 440 (2009).
H. Gu, Y.F. Zhu, and L.Q. Li: Hydrogen storage properties of Mg–Ni–Cu prepared by hydriding combustion synthesis and mechanical milling (HCS+MM). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 34, 2654 (2009).
Y.F. Zhu, Z.B. Liu, Y. Yang, H. Gu, L.Q. Li, and M. Cai: Hydrogen storage properties of Mg-Ni-C system hydrogen storage materials prepared by hydriding combustion synthesis and mechanical milling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35, 6350 (2010).
Y.F. Zhu, Y. Yang, L.J. Wei, Z.L. Zhao, and L.Q. Li: Hydrogen storage properties of Mg–Ni–Fe composites prepared by hydriding combustion synthesis and mechanical milling. J. Alloys Compd. 520, 207 (2012).
R.R. Shahi, A.P. Tiwari, M.A. Shaz, and O.N. Srivastava: Studies on de/rehydrogenation characteristics of nanocrystalline MgH2 co-catalyzed with Ti, Fe and Ni. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38, 2778 (2013).
J. Cui, H. Wang, J.W. Liu, L.Z. Ouyang, Q.A. Zhang, D.L. Sun, X.D. Yao, and M. Zhu: Remarkable enhancement in dehydrogenation of MgH2 by a nano-coating of multi-valence Ti-based catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 5603 (2013).
M.P. Pitt, M. Paskevicius, C.J. Webb, D.A. Sheppard, C.E. Buckley, and E.M. Gray: The synthesis of nanoscopic Ti based alloys and their effects on the MgH2 system compared with the MgH2 + 0.01Nb2O5 benchmark. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37, 4227 (2012).
Y.P. Pang, Y.F. Liu, X. Zhang, M.X. Gao, and H.G. Pang: Role of particle size, grain size, microstrain and lattice distortion in improved dehydrogenation properties of the ball-milled Mg(AlH4)2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38, 1460 (2013).
R.R. Shahi, A. Bhatnagar, S.K. Pandey, V. Dixit, and O.N. Srivastava: Effects of Ti-based catalysts and synergistic effect of SWCNTs-TiF3 on hydrogen uptake and release from MgH2. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39, 14255 (2014).
C.Y. Zhu and T. Akiyama: Zebra-striped fibers in relation to the H2 sorption properties for MgH2 nanofibers produced by a vapor–solid process. Cryst. Growth Des. 12, 4043 (2012).
J. Huot, G. Liang, S. Boily, A.V. Neste, and R. Schulz: Structural study and hydrogen sorption kinetics of ball-milled magnesium hydride. J. Alloys Compd. 293–295, 495 (1999).
T. Liu, C.G. Qin, M. Zhu, Y.R. Cao, H.L. Shen, and X.G. Li: Synthesis and hydrogen storage properties of Mg–La–Al nanoparticles. J. Power Sources 219, 100 (2012).
Z.S. Wronski, G.J.C. Carpenter, T. Czujko, and R.A. Varin: A new nanonickel catalyst for hydrogen storage in solid-state magnesium hydrides. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 36, 1159 (2010).
Y.J. Choi, J. Lu, H.Y. Sohn, and Z.Z. Fang: Hydrogen storage properties of the Mg–Ti–H system prepared by high-energy–high-pressure reactive milling. J. Power Sources 180, 491 (2008).
M.Y. Song, Y.J. Kwak, S.H. Lee, J. Song, and D.R. Mumm: Enhancement of hydrogen-storage performance of MgH2 by Mg2Ni formation and hydride-forming Ti addition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37, 18133 (2012).
M.Y. Song, Y.J. Kwak, H.S. Shin, S.H. Lee, and B.G. Kim: Improvement of hydrogen-storage properties of MgH2 by Ni, LiBH4, and Ti addition. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38, 1910 (2013).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51471087, 51171079), Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (13KJA430003), Innovation Foundation for Graduate Students of Jiangsu Province (KYLX_0741, CXZZ13_0420), Qing Lan Project and the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Y., Zhu, Y., Yuan, J. et al. Improved hydrogen storage properties of Ti-doped Mg95Ni5 powder produced by hydriding combustion synthesis. Journal of Materials Research 30, 967–972 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.62
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.62