Abstract
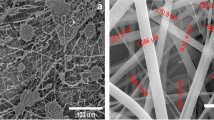
Nanometer-sized fibers are recently getting increased attention in heterogeneous catalysis due to the superior transport properties and effective dispersion they offer. A key challenge in this application is creation of nanofibers with internal open porosity that can provide larger accessible catalytic surface and easier mass transport into the fibers. The synthesis of potassium doped iron/aluminum oxides ceramic nanofibers with mesoporous structure is presented herein. Uniform fiber mats were prepared by electrospinning (ES) using two different precursors: an aqueous solution of metal nitrates and an organic solution of metal acetylacetonates. The organic precursors gave rise to a promising mesoporous structure with fibers diameter mainly in the 300–400 nm range. Precursor viscosity was used as a stability indicator and its influence on the ES process was studied. Collection efficiency of as high as 90% was achieved. The increased understanding in fiber morphological evolution can open new possibilities in heterogeneous catalysis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Formo, Z. Peng, E. Lee, X. Lu, H. Yang, and Y. Xia: Direct oxidation of methanol on Pt nanostructures supported on electrospun nanofibers of anatase. J. Phys. Chem. C 112(27), 9970 (2008).
E. Formo, P.H.C. Camargo, B. Lim, M. Jiang, and Y. Xia: Functionalization of ZrO2 nanofibers with Pt nanostructures: The effect of surface roughness on nucleation mechanism and morphology control. Chem. Phys. Lett. 476(1–3), 56 (2009).
S. Chuangchote, J. Jitputti, T. Sagawa, and S. Yoshikawa: Photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1(5), 1140 (2009).
S. Zhan, D. Chen, X. Jiao, and C. Tao: Long TiO2 hollow fibers with mesoporous walls: Sol−Gel combined electrospun fabrication and photocatalytic properties. J. Phys. Chem. B 110(23), 11199 (2006).
M.Y. Song, D.K. Kim, K.J. Ihn, S.M. Jo, and D.Y. Kim: Electrospun TiO2 electrodes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Nanotechnology 15(12), 1861 (2004).
M.Y. Song, D.K. Kim, K.J. Ihn, S.M. Jo, and D.Y. Kim: New application of electrospun TiO2 electrode to solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. Synth. Met. 153(1–3), 77 (2005).
M.Y. Song, D.K. Kim, S.M. Jo, and D.Y. Kim: Enhancement of the photocurrent generation in dye-sensitized solar cell based on electrospun TiO2 electrode by surface treatment. Synth. Met. 155(3), 635 (2005).
K. Onozuka: Electrospinning processed nanofibrous TiO2 membranes for photovoltaic applications. Nanotechnology 17(4), 1026 (2006).
M.Y. Song, Y.R. Ahn, S.M. Jo, D.Y. Kim, and J. Ahn: TiO2 single-crystalline nanorod electrode for quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87(11), 113113 (2005).
W. Zhang, R. Zhu, X. Liu, B. Liu, and S. Ramakrishna: Facile construction of nanofibrous ZnO photoelectrode for dye-sensitized solar cell applications. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95(4), 043304 (2009).
Y. Gu, D. Chen, and X. Jiao: Synthesis and electrochemical properties of nanostructured LiCoO2 fibers as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. B 109(38), 17901 (2005).
W. Zheng, Z. Li, H. Zhang, W. Wang, Y. Wang, and C. Wang: Electrospinning route for α-Fe2O3 ceramic nanofibers and their gas sensing properties. Mater. Res. Bull. 44(6), 1432 (2009).
H. Fan, T. Zhang, X. Xu, and N. Lv: Fabrication of N-type Fe2O3 and P-type LaFeO3 nanobelts by electrospinning and determination of gas-sensing properties. Sens. Actuators, B 153(1), 83 (2011).
R. Luoh and H.T. Hahn: Electrospun nanocomposite fiber mats as gas sensors. Compos. Sci. Technol. 66(14), 2436 (2006).
G. Wang, X. Gou, J. Horvat, and J. Park: Facile synthesis and characterization of iron oxide semiconductor nanowires for gas sensing application. J. Phys. Chem. C 112(39), 15220 (2008).
X. Zhang, H. Liu, S. Petnikota, S. Ramakrishna, and H.J. Fan: Electrospun Fe2O3-carbon composite nanofibers as durable anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2(28), 10835 (2014).
A. Mahapatra, B.G. Mishra, and G. Hota: Electrospun Fe2O3–Al2O3 nanocomposite fibers as efficient adsorbent for removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 258–259, 116 (2013).
S. Chaudhari and M. Srinivasan: 1D hollow α-Fe2O3 electrospun nanofibers as high performance anode material for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. 22(43), 23049 (2012).
J. Sundaramurthy, P.S. Kumar, M. Kalaivani, V. Thavasi, S.G. Mhaisalkar, and S. Ramakrishna: Superior photocatalytic behaviour of novel 1D nanobraid and nanoporous α-Fe2O3 structures. RSC Adv. 2(21), 8201 (2012).
H. Shao, X. Zhang, F. Chen, S. Liu, Y. Ji, Y. Zhu, and Y. Feng: Preparation of α-Fe2O3 nanotubes via electrospinning and research on their catalytic properties. Appl. Phys. A 108(4), 961 (2012).
Y.K. Sung, B.W. Ahn, and T.J. Kang: Magnetic nanofibers with core (Fe3O4 nanoparticle suspension)/sheath (poly ethylene terephthalate) structure fabricated by coaxial electrospinning. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324(6), 916 (2012).
S. Wang, C. Wang, B. Zhang, Z. Sun, Z. Li, X. Jiang, and X. Bai: Preparation of Fe3O4/PVA nanofibers via combining in-situ composite with electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 64(1), 9 (2010).
B.W. Ahn and T.J. Kang: Preparation and characterization of magnetic nanofibers with iron oxide nanoparticles and poly(ethylene terephthalate). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 125(2), 1567 (2012).
X. Bai, J. Zhang, N. Ning, L. Zhang, T. Nishi, and M. Tian: Enhanced magnetic property of Fe3O4 nano-particles/elastomeric composite membrane by using electrospinning and in-situ crosslinking technique. J. Polym. Res. 21(5), 1 (2014).
M.V. Landau, R. Vidruk, and M. Herskowitz: Sustainable production of green feed from carbon dioxide and hydrogen. ChemSusChem 7(3), 785 (2014).
F. Morales and B.M. Weckhuysen: In Promotion Effects in Co-based Fischer-Tropsch Catalysis, Vol. 19; J.J. Spivey and K.M. Dooley eds. (Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry, 2006), pp. 1–40.
J.J. Stanger: Effect of salts on the electrospinning of poly (vinyl alcohol). AIP Conf. Proc. 1151, 118 (2009).
C.J. Angammana and S.H. Jayaram: Analysis of the effects of solution conductivity on electrospinning process and fiber morphology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 47(3), 1109 (2011).
S. De Vrieze, T. Van Camp, A. Nelvig, B. Hagström, P. Westbroek, and K. De Clerck: The effect of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 44(5), 1357 (2009).
V.E. Kalayci, P.K. Patra, Y.K. Kim, S.C. Ugbolue, and S.B. Warner: Charge consequences in electrospun polyacrylonitrile (PAN) nanofibers. Polymer 46(18), 7191 (2005).
A. Gevorkyan, G.E. Shter, Y. Shmueli, A. Buk, R. Meir, and G.S. Grader: Branching effect and morphology control in electrospun PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 nanofibers. J. Mater. Res. 29(16), 1721 (2014).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Supported by the I-CORE Program of the Planning and Budgeting Committee and The Israel Science Foundation (Grant No. 152/11), Israel Ministry of Infrastructures, Energy and Water (Grant No. 880002) and by joint grant of the Council for Higher Education and by the Center for Absorption in Science (Israel) under the KAMEA program. Authors acknowledge the support of the RBNI, the Adelis Foundation and the Grand Technion Energy Program (GTEP) and the Arturo Gruenbaum Chair in Material Engineering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halperin, V., Shter, G.E., Beilin, V. et al. Mesoporous K/Fe–Al–O nanofibers by electrospinning of solution precursors. Journal of Materials Research 30, 3142–3150 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.296
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.296