Abstract
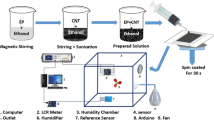
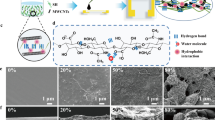
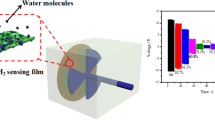
This study demonstrates a highly sensitive humidity sensor based on treated multiwalled carbon nanotube (tr-MWCNT) and hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) composite films. Tr-MWCNTs are obtained by mixed acid treatment to enhance their hydrophilicity and improve their dispersion in distilled water. Compared to tr-MWCNT/silicone rubber (SR) composite film, the humidity sensitivity of tr-MWCNT/HEC film is much higher than tr-MWCNT/SR film with the same film thickness. The humidity sensing mechanisms of tr-MWCNT/HEC composites are explained by electron donation model and swelling mechanism. Speaking and blowing experiments were also carried out and the results show that tr-MWCNT/HEC composite film is sensitive to both speaking and blowing; furthermore, it can distinguish the small humidity level difference between speaking and blowing. Other sensing characteristics, including response and recovery time, stability, and temperature effect, are also investigated. The high humidity sensitivity of tr-MWCNT/HEC composite film indicates that it can be an excellent humidity sensitive material.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.Y. Lee and G.B. Lee: Humidity sensors: A review. Sens. Lett. 3, 1 (2005).
B.M. Kulwicki: Humidity sensors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 74, 697 (1991).
N. Yamazoe and Y. Shimizu: Humidity sensors: Principles and applications. Sens. Actuators 10, 379 (1986).
Y. Sakai, Y. Sadaoka, and M. Matsuguchi: Humidity sensors based on polymer thin films. Sens. Actuators, B 35, 85 (1996).
E. Traversa: Ceramic sensors for humidity detection: The state-of-the-art and future developments. Sens. Actuators, B 23, 135 (1995).
S. Iijima: Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354, 56 (1991).
W.P. Chen, Z.G. Zhao, X.W. Liu, Z.X. Zhang, and C.G. Suo: A capacitive humidity sensor based on multi-wall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs). Sensors 9, 7431 (2009).
M. Saleem, K.S. Karimov, Z.M. Karieva, and A. Mateen: Humidity sensing properties of CNT–OD–VETP nanocomposite films. Phys. E 43, 28 (2010).
J.T.W. Yeow and J.P.M. She: Carbon nanotube-enhanced capillary condensation for a capacitive humidity sensor. Nanotechnology 17, 5441 (2006).
P.G. Su, Y.L. Sun, and C.C. Lin: A low humidity sensor made of quartz crystal microbalance coated with multi-walled carbon nanotubes/Nafion composite material films. Sens. Actuators, B 115, 338 (2006).
Y. Zhang, K. Yu, R. Xu, D. Jiang, L. Luo, and Z. Zhu: Quartz crystal microbalance coated with carbon nanotube films used as humidity sensor. Sens. Actuators, A 120, 142 (2005).
H.W. Chen, R.J. Wu, K.H. Chan, Y.L. Sun, and P.G. Su: The application of CNT/Nafion composite material to low humidity sensing measurement. Sens. Actuators, B 104, 80 (2005).
M. Matsuguch, T. Kuroiwa, T. Miyagishi, S. Suzuki, T. Ogura, and Y. Sakai: Stability and reliability of capacitive-type relative humidity sensors using crosslinked polyimide films. Sens. Actuators, B 52, 53 (1998).
J.H. Kim, S.M. Hong, J.S. Lee, B.M. Moon, and K. Kim: High sensitivity capacitive humidity sensor with a novel polyimide design fabricated by MEMS technology. In Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems, 2009. 4th IEEE International Conference on NEMS 2009, IEEE, pp. 703–706.
L. Liu, X. Ye, K. Wu, R. Han, Z. Zhou, and T. Cui: Humidity sensitivity of multi-walled carbon nanotube networks deposited by dielectrophoresis. Sensors 9, 1714 (2009).
P. Slobodian, P. Riha, A. Lengálová, P. Svoboda, and P. Sáha: Multi-wall carbon nanotube networks as potential resistive gas sensors for organic vapor detection. Carbon 49, 2499 (2011).
Y.M. Wong, W.P. Kang, J.L. Davidson, A. Wisitsora-At, and K.L. Soh: A novel microelectronic gas sensor utilizing carbon nanotubes for hydrogen gas detection. Sens. Actuators, B 93, 327 (2003).
C.L. Cao, C.G. Hu, L. Fang, S.X. Wang, Y.S. Tian, and C.Y. Pan: Humidity sensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotube thin films. J. Nanomater. 2011, 5 (2011).
P.G. Su and C.S. Wang: In situ synthesized composite thin films of MWCNTs/PMMA doped with KOH as a resistive humidity sensor. Sens. Actuators, B 124, 303 (2007).
S. Muto, O. Suzuki, T. Amano, and M. Morisawa: A plastic optical fibre sensor for real-time humidity monitoring. Meas. Sci. Technol. 14, 746 (2003).
S. Harun, M. Batumalay, A. Lokman, H. Arof, H. Ahmad, and F. Ahmad: Tapered plastic optical fiber coated with HEC/PVDF for measurement of relative humidity. IEEE Sens. J. 13, 4702 (2013).
L. Xia, L. Li, W. Li, T. Kou, and D. Liu: Novel optical fiber humidity sensor based on a no-core fiber structure. Sens. Actuators, A 190, 1 (2013).
J. Xiong, Z. Zheng, X. Qin, M. Li, H. Li, and X. Wang: The thermal and mechanical properties of a polyurethane/multi-walled carbon nanotube composite. Carbon 44, 2701 (2006).
H. Yu, T. Cao, L. Zhou, E. Gu, D. Yu, and D. Jiang: Layer-by-layer assembly and humidity sensitive behavior of poly (ethyleneimine)/multiwall carbon nanotube composite films. Sens. Actuators, B 119, 512 (2006).
K.P. Yoo, L.T. Lim, N.K. Min, M.J. Lee, C.J. Lee, and C.W. Park: Novel resistive-type humidity sensor based on multiwall carbon nanotube/polyimide composite films. Sens. Actuators, B 145, 120 (2010).
Q.Y. Tang, Y.C. Chan, and K. Zhang: Fast response resistive humidity sensitivity of polyimide/multiwall carbon nanotube composite films. Sens. Actuators, B 152, 99 (2011).
W.F. Jiang, S.H. Xiao, C.Y. Feng, H.Y. Li, and X.J. Li: Resistive humidity sensitivity of arrayed multi-wall carbon nanotube nests grown on arrayed nanoporous silicon pillars. Sens. Actuators, B 125, 651 (2007).
J. Chu, X. Peng, P. Feng, Y. Sheng, and J. Zhang: Study of humidity sensors based on nanostructured carbon films produced by physical vapor deposition. Sens. Actuators, B 178, 508 (2013).
O.K. Varghese, P.D. Kichambre, D. Gong, K.G. Ong, E.C. Dickey, and C.A. Grimes: Gas sensing characteristics of multi-wall carbon nanotubes. Sens. Actuators, B 81, 32 (2001).
A. Maiti, J. Andzelm, N. Tanpipat, and P. von Allmen: Effect of adsorbates on field emission from carbon nanotubes. Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 155502 (2001).
M. Bruzzi, S. Miglio, M. Scaringella, G. Bongiorno, P. Piseri, A. Podesta, and P. Milani: First study of humidity sensors based on nanostructured carbon films produced by supersonic cluster beam deposition. Sens. Actuators, B 100, 173 (2004).
H.P. Hong, K.H. Jung, J.H. Kim, K.H. Kwon, C.J. Lee, K.N. Yun, and N.K. Min: Percolated pore networks of oxygen plasma-activated multi-walled carbon nanotubes for fast response, high sensitivity capacitive humidity sensors. Nanotechnology 24, 085501 (2013).
K. Li, C. Zhang, Z. Du, H. Li, and W. Zou: Preparation of humidity-responsive antistatic carbon nanotube/PEI nanocomposites. Synth. Met. 162, 2010 (2012).
J. Lee, D. Cho, and Y. Jeong: A resistive-type sensor based on flexible multi-walled carbon nanotubes and polyacrylic acid composite films. Solid-State Electron. 87, 80 (2013).
Y. Wang, S. Park, J.T. Yeow, A. Langner, and F. Müller: A capacitive humidity sensor based on ordered macroporous silicon with thin film surface coating. Sens. Actuators, B 149, 136 (2010).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61471155 and 61401141).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Huang, Y., Ma, Y. et al. Research on highly sensitive humidity sensor based on Tr-MWCNT/HEC composite films. Journal of Materials Research 29, 2845–2853 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.328
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.328