Abstract
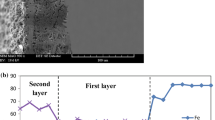
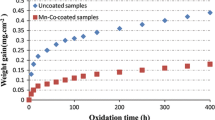
Practical implementation of oxide thermoelectrics on an industrial or commercial scale for waste heat energy conversion requires the development of chemically stable interfaces between metal interconnects and oxide thermoelements that exhibit low electrical contact resistances. A commercially available high-chrome iron alloy (i.e., Crofer® 22 APU) serving as the interconnect metal was spray coated with LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3 (LNFO) or (Mn,Co)3O4 spinel and then interfaced with a p-type thermoelectric material—calcium cobaltate (Ca3Co4O9)—using spark plasma sintering. The interfaces have been characterized in terms of their thermal and electronic transport properties and chemical stability. With long-term exposure of the interfaced samples to 800 °C in air, the cobalt–manganese spinel acted as a diffusion barrier between the Ca3Co4O9 and the Crofer® 22 APU alloy resulting in improved interfacial stability compared to that of samples containing LNFO as a barrier layer, and especially those without any barrier. The initial area specific interfacial resistance of the Ca3Co4O9/(Mn,Co)3O4/Crofer® 22 APU interface at 800 °C was found to be ∼1 mΩ·cm2.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. He, Y. Liu, and R. Funahashi: Oxide thermoelectrics: The challenges, progress, and outlook. J. Mater. Res. 26(15), 1762–1772 (2011).
R. Funahashi and S. Urata: Fabrication and application of an oxide thermoelectric system. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 4(4), 297–307 (2007).
J.G. Noudem, S. Lemonnier, M. Prevel, E.S. Reddy, E. Guilmeau, and C. Goupil: Thermoelectric ceramics for generators. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28(1), 41–48 (2008).
L. Han, Y. Jiang, S. Li, H. Su, X. Lan, K. Qin, T. Han, H. Zhong, L. Chen, and D. Yu: High temperature thermoelectric properties and energy transfer devices of Ca3Co4−xAgxO9 and Ca1−ySmyMnO3. J. Alloys Compd. 509(36), 8970–8977 (2011).
T.C. Holgate, L. Han, N. Wu, E.D. Bøjesen, M. Christensen, B.B. Iversen, N.V. Nong, and N. Pryds: Characterization of the interface between an Fe–Cr alloy and the p-type thermoelectric oxide Ca3Co4O9. J. Alloys Compd. 582, 827–833 (2014).
T. Komatsu, H. Arai, R. Chiba, K. Nozawa, M. Arakawa, and K. Sato: Cr poisoning suppression in solid oxide fuel cells using LaNi (Fe) O3 electrodes. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 9(1), A9–A12 (2006).
Z. Yang, G-G. Xia, X-H. Li, and J.W. Stevenson: (Mn,Co)3O4 spinel coatings on ferritic stainless steels for SOFC interconnect applications. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 32(16), 3648–3654 (2007).
G.V. Pattarkine, N. Dasgupta, and A.V. Virkar: Oxygen transport resistant and electrically conductive perovskite coatings for solid oxide fuel cell interconnects. J. Electrochem. Soc. 155(10), B1036–B1046 (2008).
W. Zhang, B. Hua, N. Duan, J. Pu, B. Chi, and J. Li: Cu-Fe spinel coating as oxidation barrier for Fe-16Cr metallic interconnect in solid oxide fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159(9), C388–C392 (2012).
N.S. Waluyo, B-K. Park, S-B. Lee, T-H. Lim, S-J. Park, R-H. Song, and J-W. Lee: (Mn,Cu)3O4-based conductive coatings as effective barriers to high-temperature oxidation of metallic interconnects for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Solid State Electrochem. 18(2), 445–452 (2014).
R.N. Basu, F. Tietz, O. Teller, E. Wessel, H.P. Buchkremer, and D. Stöver: LaNi0.6Fe0.4O3 as a cathode contact material for solid oxide fuel cells. J. Solid State Electrochem. 7(7), 416–420 (2003).
J. Wu and X. Liu: Recent development of SOFC metallic interconnect. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 26(4), 293–305 (2010).
T.C. Holgate, N. Wu, M. Søndergaard, B.B. Iversen, N.V. Nong, and N. Pryds: Kinetics, stability, and thermal contact resistance of nickel–Ca3Co4O9 interfaces formed by spark plasma sintering. J. Electron. Mater. 42(7), 1661–1668 (2013).
N. Wu, T.C. Holgate, N.V. Nong, N. Pryds, and S. Linderoth: Effects of synthesis and spark plasma sintering conditions on the thermoelectric properties of Ca3Co4O9+δ. J. Electron. Mater. 42(7), 2134–2142 (2013).
K. Wang, Y. Liu, and J.W. Fergus: Interactions between SOFC interconnect coating materials and chromia. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94(12), 4490–4495 (2011).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Ming Chen, Sebastian Molin, and Nikolaos Bonanos for many helpful discussions, as well as Ebtisam Abdellahi for assistance with sample preparation for SEM. The authors also thank the Programme Commission on Energy and Environment (EnMi), which is part of the Danish Council for Strategic Research (Contract No. 10-093971), for sponsoring the research of the OTE-POWER project, and the Danish National Research Foundation (DNRF93) for additional funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holgate, T.C., Han, L., Wu, N. et al. Effects of conducting oxide barrier layers on the stability of Crofer® 22 APU/Ca3Co4O9 interfaces. Journal of Materials Research 29, 2891–2897 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.320
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.320