Abstract
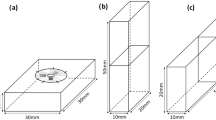
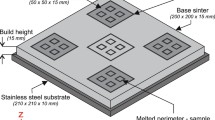
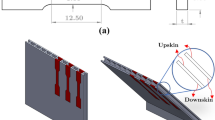
The effect of the beam scanning speed on part microstructures in the powder-bed electron beam additive manufacturing (EBAM) process was investigated in this research. Four levels of the beam speed were tested in building EBAM Ti–6Al–4V samples. The samples were subsequently used to prepare metallographic specimens for observations by optical microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. During the experiment, a near-infrared thermal imager was also used to acquire build surface temperatures for melt tool size estimates. It was found that the X-plane (side surface) shows columnar prior β grains, with the width in the range of about 40–110 µm, and martensitic structures. The width of columnar grains decreases with the increase of the scanning speed. In addition, the Z-plane (scanning surface) shows equiaxed grains, in the range of 50–85 µm. The grain size from the lowest beam speed (214 mm/s) is much larger compared to other samples of higher beam speeds (e.g., 376–689 mm/s). In addition, increasing the beam scanning speed will also result in finer α-lath. However, the porosity defect on the build surface also becomes severe at the highest scanning speed (689 mm/s).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.E. Murr, E.V. Esquivel, S.A. Quinones, S.M. Gaytan, M.I. Lopez, E.Y. Martinez, F. Medina, D.H. Hernandez, E. Martinez, J.L. Martinez, S.W. Stafford, D.K. Brown, T. Hoppe, W. Meyers, U. Lindhe, and R.B. Wicker: Microstructures and mechanical properties of electron beam-rapid manufactured Ti-6Al-4V biomedical prototypes compared to wrought Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Charact. 60, 96 (2009).
X. Gong and K. Chou: Characterizations of sintered Ti-6Al-4V powders in electron beam additive manufacturing. Proceedings of the ASME International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, L. Mears ed.; ASME, Madison, WI, 2013; p. V001T01A0022013.
M.F. Zäh and S. Lutzmann: Modelling and simulation of electron beam melting. Prod. Eng. 4, 15 (2010).
N. Shen and K. Chou: Thermal modeling of electron beam additive manufacturing process: Powder sintering effect. Proceedings of the ASME International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference, S.R. Schmid, H.Y. Greenslet, and L. Mears ed.; ASME, Notre Dame, IN, 2012; p. 287.
X. Gong, B. Cheng, S. Price, and K. Chou: Powder-bed electron-beam-melting additive manufacturing: Powder characterization, process simulation and metrology. Early Career Technical Conference, P. Durbetaki and J. Donnell ed.; ASME, Birmingham, AL, 2013; p. 59.
S. Price, K. Cooper, and K. Chou: Evaluations of temperature measurements by near-infrared thermography in powder-based electron-beam additive manufacturing. Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, D. Bourell, R.H. Crawford, C.C. Seepersad, J.J. Beaman, and H.L. Marcus ed.; University of Texas, Austin, TX, 2012; p. 761.
M. Koike, K. Martinez, L. Guo, G. Chahine, R. Kovacevic, and T. Okabe: Evaluation of titanium alloy fabricated using electron beam melting system for dental applications. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211, 1400 (2011).
A.L. Cooke and J.A. Soons: Variability in the geometric accuracy of additively manufactured test parts. Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, D. Bourell ed.; University of Texas, Austin, TX, 2010; pp. 1.
S.S. Al-Bermani, M.L. Blackmore, W. Zhang, and I. Todd: The origin of microstructural diversity, texture, and mechanical properties in electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 41A, 3422 (2010).
A. Safdar, L.Y. Wei, A. Snis, and Z. Lai: Evaluation of microstructural development in electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Charact. 65, 8 (2012).
A.A. Antonysamy, J. Meyer, and P.B. Prangnell: Effect of build geometry on the β-grain structure and texture in additive manufacture of Ti6Al4V by selective electron beam melting. Mater. Charact. 84, 153 (2013).
L. Facchini, E. Magalini, P. Robotti, and A. Molinari: Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V produced by electron beam melting of pre-alloyed powders. Rapid Prototyping J. 15, 171 (2009).
A. Christensen, R. Kircher, and A. Lippincott: Qualification of electron beam melted (EBM) Ti6Al4V-ELI for orthopaedic applications. Proceedings of the Materials Processes for Medical Devices Conference, J. Gilbert ed.; ASM International, Palm Desert, CA, 2007; pp. 48.
L.E. Murr, S.M. Gaytan, F. Medina, E. Martinez, J.L. Martinez, D.H. Hernandez, B.I. Machado, D.A. Ramirez, and R.B. Wicker: Characterization of Ti-6Al-4V open cellular foams fabricated by additive manufacturing using electron beam melting. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 1861–1868 (2010).
X. Gong, T. Anderson, and K. Chou: Review on powder-based electron beam additive manufacturing technology. In International Symposium on Flexible Automation, M. Leu ed.; ASME, St. Louis, MO, 2012; p. 507.
L.E. Murr, S.M. Gaytan, F. Medina, E. Martinez, D.H. Hernandez, L. Martinez, M.I. Lopez, R.B. Wicker, and S. Collins: Effect of build parameters and build geometries on residual microstructures and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V components built by electron beam melting (EBM). Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, D. Bourell ed.; University of Texas, Austin, TX, 2009; p. 374.
S. Bontha, N.W. Klingbeil, P.A. Kobryn, and H.L. Fraser: Effects of process variables and size-scale on solidification microstructure in beam-based fabrication of bulky 3D structures. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 513–514, 311 (2009).
L.E. Murr, S.A. Quinones, S.M. Gaytan, M.I. Lopez, A. Rodela, E.Y. Martinez, D.H. Hernandez, E. Martinez, F. Medina, and R.B. Wicker: Microstructure and mechanical behavior of Ti-6Al-4V produced by rapid-layer manufacturing, for biomedical applications. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2, 20 (2009).
M. Jamshidinia, F. Kong, and R. Kovacevic: The coupled CFD-FEM model of electron beam melting (EBM). Proceedings of the Early Career Technical Conference (ECTC), P. Durbetaki and J. Donnell ed.; ASME, Birmingham, AL, 2013; p. 163.
T.R. Mahale: Electron beam melting of advanced materials and structures. Ph.D. Dissertation, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC, 2009.
K. Wang, W. Zeng, Y. Shao, Y. Zhao, and Y. Zhou: Quantification of microstructural features in titanium alloys based on stereology. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 38, 398 (2009).
S.M. Kelly: Thermal and microstructure modeling of metal deposition processes with application to Ti-6Al-4V. Ph.D. Dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, 2004.
X. Wu, J. Liang, J. Mei, C. Mitchell, P.S. Goodwin, and W. Voice: Microstructures of laser-deposited Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Des. 25, 137 (2004).
T. Ahmed and H.J. Rack: Phase transformations during cooling in α + β titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 243, 206 (1998).
J.W. Elmer, T.A. Palmer, S.S. Babu, W. Zhang, and T. Debroy: Phase transformation dynamics during welding of Ti-6Al-4V. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 8327 (2004).
B. Baufeld, E. Brandl, and O. van der Biest: Wire based additive layer manufacturing: Comparison of microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V components fabricated by laser-beam deposition and shaped metal deposition. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211, 1146 (2011).
W. Lu, Y. Shi, Y. Lei, and X. Li: Effect of electron beam welding on the microstructures and mechanical properties of thick TC4-DT alloy. Mater. Des. 34, 509–515 (2012).
K. Amato, J. Hernandez, L.E. Murr, E. Martinez, S.M. Gaytan, P.W. Shindo, and S. Collins: Comparison of microstructures and properties for a Ni-base superalloy (alloy 625) fabricated by electron beam melting. J. Mater. Sci. Res. 1, 3 (2012).
L.E. Murr, S.M. Gaytan, A. Ceylan, E. Martinez, J.L. Martinez, D.H. Hernandez, B.I. Machado, D.A. Ramirez, F. Medin, S. Collins, and R.B. Wicker: Characterization of titanium aluminide alloy components fabricated by additive manufacturing using electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 58, 1887 (2010).
J. Gockel and J. Beuth: Understanding Ti-6Al-4V microstructure control in additive manufacturing via process maps. Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium, D. Bourell ed.; University of Texas, Austin, TX, 2013; p. 666.
F.J. Gil, M.P. Ginebra, J.M. Manero, and J.A. Planell: Formation of α-Widmanstätten structure: Effects of grain size and cooling rate on the Widmanstätten morphologies and on the mechanical properties in Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 329, 142 (2001).
Y. Xi, M. Bermingham, G. Wang, and M. Dargusch: Finite element modeling of cutting force and chip formation during thermally assisted machining of Ti6Al4V alloy. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 135, 061014 (2013).
A. Safdar: A study on electron beam melted Ti-6Al-4V. M.S. Thesis, Lund University, Lund, Sweden, 2012.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research is supported by NASA (award No. NNX11AM11A). Steven Price provided the temperature measurement results. XG also acknowledges AL EPSCoR GRSP for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, X., Lydon, J., Cooper, K. et al. Beam speed effects on Ti–6Al–4V microstructures in electron beam additive manufacturing. Journal of Materials Research 29, 1951–1959 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.125
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.125