Abstract
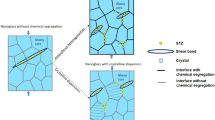
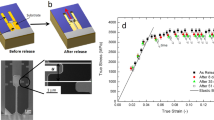
The mechanical and thermal behavior of nanoglasses (NGs) were studied with a focus on the effect of the microstructure. The thermal expansion was measured to track changes in excess free volume during heating. It was found that the excess free volume, which is initially more dominant in the interphase region between the denser amorphous particles, is partially lost as well as redistributed during annealing. This relaxation during heating causes the nanoglass to behave like a melt-spun ribbon after heating while remaining amorphous. Nanomechanical tests were used to probe the local incipient plasticity and the influence of the interphase region. This interphase appears to affect the mechanical response of the NGs by inhibiting the propagation of shear bands and thus offers a novel approach for the introduction of plasticity in bulk metallic glasses. The results suggest that the NGs consist of two distinct amorphous phases with different glass transition temperatures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ghafari, H. Hahn, H. Gleiter, Y. Sakurai, M. Itou, and S. Kamali: Evidence of itinerant magnetism in a metallic nanoglass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 101 (24), 243104 (2012).
J.X. Fang, U. Vainio, W. Puff, R. Wurschum, X.L. Wang, D. Wang, M. Ghafari, F. Jiang, J. Sun, H. Hahn, and H. Gleiter: Atomic structure and structural stability of Sc75Fe25 nanoglasses. Nano Lett. 12 (1), 458 (2012).
M. Ghafari, S. Kohara, H. Hahn, H. Gleiter, T. Feng, R. Witte, and S. Kamali: Structural investigations of interfaces in Fe90Sc10 nanoglasses using high-energy x-ray diffraction. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100 (13), 133111 (2012).
H. Gleiter: Nanostructured materials: Basic concepts and microstructure. Acta Mater. 48 (1), 1 (2000).
X.D. Wang, Q.P. Cao, J.Z. Jiang, H. Franz, J. Schroers, R.Z. Valiev, Y. Ivanisenko, H. Gleiter, and H.J. Fecht: Atomic-level structural modifications induced by severe plastic shear deformation in bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 64 (1), 81 (2011).
X.T.S.N. Chen, A. Takeuchi, K.S. Nakayama, H.K. Wu, M. Esashi, A. Inoue, and D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin: A representative of a new class of materials: Nanograined metallic glasses showing unique properties. AIP Conf. Proc. 1518, 682 (2013).
Y. Ritter, D. Sopu, H. Gleiter, and K. Albe: Structure, stability and mechanical properties of internal interfaces in Cu64Zr36 nanoglasses studied by MD simulations. Acta Mater. 59 (17), 6588 (2011).
D. Sopu, K. Albe, Y. Ritter, and H. Gleiter: From nanoglasses to bulk massive glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 (19), 191911 (2009).
C.A. Schuh, A.C. Lund, and T.G. Nieh: New regime of homogeneous flow in the deformation map of metallic glasses: elevated temperature nanoindentation experiments and mechanistic modeling. Acta Mater. 52 (20), 5879 (2004).
C.A. Schuh and T.G. Nieh: A nanoindentation study of serrated flow in bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 51 (1), 87 (2003).
C.A. Schuh, T.C. Hufnagel, and U. Ramamurty: Mechanical behavior of amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 55 (12), 4067 (2007).
A.S. Argon: Plastic-deformation in metallic glasses. Acta Metall. 27 (1), 47 (1979).
C. Suryanarayana: Mechanical behavior of emerging materials. Mater. Today 15 (11), 486 (2012).
C.C. Hays, C.P. Kim, and W.L. Johnson: Improved mechanical behavior of bulk metallic glasses containing in situ formed ductile phase dendrite dispersion. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 304–306, 650 (2001).
M. Calin, J. Eckert, and L. Schultz: Improved mechanical behavior of Cu–Ti-based bulk metallic glass by in situ formation of nanoscale precipitates. Scr. Mater. 48 (6), 653 (2003).
J. Eckert, J. Das, S. Pauly, C. Duhamel, K.B. Kim, S. Yi, and W.H. Wang: Impact of microstructural inhomogenities on the ductility of bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Trans. 48 (7), 1806 (2007).
Y.M. Chen, T. Ohkubo, T. Mukai, and K. Hono: Structure of shear bands in Pd40Ni40P20 bulk metallic glass. J. Mater. Res. 24 (1), 1 (2009).
Y. Shi and M.L. Falk: Does metallic glass have a backbone? The role of percolating short range order in strength and failure. Scr. Mater. 54 (3), 381 (2006).
Y. Ritter and K. Albe: Thermal annealing of shear bands in deformed metallic glasses: Recovery mechanisms in Cu64Zr36 studied by molecular dynamics simulations. Acta Mater. 59 (18), 7082 (2011).
C.A. Pampillo: Localized shear deformation in a glassy metal. Scr. Metall. 6 (10), 915 (1972).
F.E.P.W.H. Jiang and M. Atzmon: Mechanical behavior of shear bands and the effect of their relaxation in a rolled amorphous Al-based alloy. Acta Mater. 53, 3469 (2005).
G.W. Koebrugge, J. Sietsma, and A. van den Beukel: Structural relaxation in amorphous Pd40Ni40P20. Acta Metall. Mater. 40 (4), 753 (1992).
Y. Shibutani, M. Wakeda, S. Ogata, and J. Park: Computational relationship of deformation behavior and materials strength of amorphous alloys to short-ranged local structures. In THERMEC 2006, Pts 1–5, T. Chandra, K. Tsuzaki, M. Militzer, and C. Ravindran eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd: Switzerland, 2007, 1911.
N. Chen, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, G.Q. Xie, P. Sharma, J.H. Perepezko, M. Esashi, A.R. Yavari, and A. Inoue: Structural investigation and mechanical properties of a representative of a new class of materials: nanograined metallic glasses. Nanotechnology 24 (4), 045610 (2013).
J.X. Fang, U. Vainio, W. Puff, R. Wurschum, X.L. Wang, D. Wang, M. Ghafari, F. Jiang, J. Sun, H. Hahn, and H. Gleiter: Atomic structure and structural stability of Sc75Fe25 nanoglasses. Nano Lett. 12 (9), 5058 (2012).
C. Eberl, D.S. Gianola, and K.J. Hemker: Mechanical characterization of coatings using microbeam bending and digital image correlation techniques. Exp. Mech. 50 (1), 85 (2010).
A.R. Yavari, A.L. Moulec, A. Inoue, N. Nishiyama, N. Lupu, E. Matsubara, W.J. Botta, G. Vaughan, M. Di Michiel, and Ö. Kvick: Excess free volume in metallic glasses measured by x-ray diffraction. Acta Mater. 53 (6), 1611 (2005).
N. Chen, R. Frank, N. Asao, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, P. Sharma, J.Q. Wang, G.Q. Xie, Y. Ishikawa, N. Hatakeyama, Y.C. Lin, M. Esashi, Y. Yamamoto, and A. Inoue: Formation and properties of Au-based nanograined metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 59 (16), 6433 (2011).
C.E. Packard, O. Franke, E.R. Homer, and C.A. Schuh: Nanoscale strength distribution in amorphous versus crystalline metals. J. Mater. Res. 25 (12), 2251 (2010).
C.E. Packard and C.A. Schuh: Initiation of shear bands near a stress concentration in metallic glass. Acta Mater. 55 (16), 5348 (2007).
Y.F. Shi and M.L. Falk: Stress-induced structural transformation and shear banding during simulated nanoindentation of a metallic glass. Acta Mater. 55 (13), 4317 (2007).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to thank Dr. Tao Feng (KIT) for preparing the nanoglass samples. The discussions with Dr. Chris Eberl (KIT) on the DIC and Prof. Andrea Hodge (USC) are gratefully acknowledged. We would also like to thank Dr. Ruth Schwaiger (KIT) for providing access to the MTS/Agilent nanoindenter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franke, O., Leisen, D., Gleiter, H. et al. Thermal and plastic behavior of nanoglasses. Journal of Materials Research 29, 1210–1216 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.101
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2014.101