Abstract
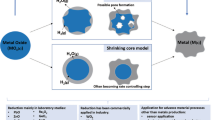
A reduction of iron (III) oxides deposited on expanded graphite (EG) matrixes of three types in hydrogen flow was studied in dynamic and static regimes. In the dynamic regime, the EG matrix was shown not to influence the temperature range of the iron (III) oxide reduction. However, the C/O atomic ratios, varying depending on the type of EG matrixes, affect the completeness of reduction of these oxides to metallic iron. The reduction kinetics of iron (III) oxides deposited on EG and of bulk oxides were found to be similar and could be described by the combination of expanded Prout–Tompkins autocatalysis and n-dimensional growth of nuclei models. The prolonged hydrogen treatment at 600 °C of the samples in the static regime results in quantitative reduction of iron (III) oxide to α-Fe independent of the type of EG matrix used. The obtained samples demonstrate the relatively high values of saturation magnetization of 35 emu/g together with a high sorption capacity for crude oil of 93 g/g.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Chen, K.F. Lam, Q. Zhang, B. Pan, M. Arruebo, and K. Yeung: Synthesis of highly selective magnetic mesoporous adsorbent. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 9804 (2009).
M. Bystrzejewski, K. Pyrzynska, A. Huczko, and H. Lange: Carbon-encapsulated magnetic nanoparticles as separable and mobile sorbents of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. Carbon 47, 1189 (2009).
G. Wang, Q. Sun, Y. Zhang, J. Fan, and L. Ma: Sorption and regeneration of magnetic exfoliated graphite as a new sorbent for oil pollution. Desalination 263, 183 (2010).
M. Toyoda and M. Inagaki: Heavy oil sorption using exfoliated graphite. New application of exfoliated graphite to protect heavy oil pollution. Carbon 38, 199 (2000).
M.A. Lutfullin, O.N. Shornikova, A.V. Vasiliev, K.V. Pokholok, V.A. Osadchaya, M.I. Saidaminov, N.E. Sorokina, and V.V. Avdeev: Petroleum products and water sorption by expanded graphite enhanced with magnetic iron phases. Carbon 66, 417 (2014).
D. Huber: Synthesis, properties, and applications of iron nanoparticles. Small 1, 482 (2005).
F. Beguin and E. Frackowiak: Electrochemical synthesis of iron supported on exfoliated graphite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 57, 841 (1996).
J. Urbaniak, J.M. Skowroński, and B. Olejnik: Preparation of Fe2O3-exfoliated graphite composite and its electrochemical properties investigated in alkaline solution. J. Solid State Electrochem. 14, 1629 (2010).
M.A. Lutfullin, O.N. Shornikova, K.V. Pokholok, N.E. Sorokina, and V.V. Avdeev: Preparation and properties of exfoliated graphite modified with iron compounds. Inorg. Mater. 48, 1175 (2012).
Z. Huan, J. Zhao-hui, H. Lu, and Q. Cheng-hu: Synthesis of nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on exfoliated graphite for removal of nitrate. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 16, 345 (2006).
O.N. Shornikova, N.E. Sorokina, and V.V. Avdeev: The effect of graphite nature on the properties of exfoliated graphite doped with nickel oxide. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 69, 1168 (2008).
V.V. Avdeev, N.E. Sorokina, and O.A. Tverezovskaya. The Synthesis of GICs with HNO3. The news of Moscow University, Vol. 40, 1999, p. 422.
Y. Volfkovich, V. Bagotzky, V. Sosenkin, and I. Blinov: The standard contact porosimetry. Colloids Surf., A 187–188, 349 (2001).
G.J. Long, ed.: Mossbauer Spectroscopy Applied to Inorganic Chemistry, Vol. 2 (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1987), p. 506.
R. Zboril: Iron(III) oxides from thermal processes—Synthesis, structural and magnetic properties, Mossbauer spectroscopy characterization and applications. Chem. Mater. 14, 969 (2002).
T.K. Kundu, M. Mukherjee, and D. Chakravorty: Growth of nano-a-Fe2O3 in a titania matrix by the sol-gel route. J. Mater. Sci. 33, 1759 (1998).
S. Pei and H-M. Cheng: The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon 50, 3210 (2012).
H-K. Jeong, Y.P. Lee, M.H. Jin, E.S. Kim, J.J. Bae, and Y.H. Lee: Thermal stability of graphite oxide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 470, 255 (2009).
Y.V. Baldokhina, I.P. Suzdaleva, V.E. Prusakova, D.A. Burnazyana, V.P. Korneevb, L.V. Kovalenkob, and G.E. Folmanisb: A study of nanostructures formed in the hydrogen reduction of Fe(OH)3. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 6, 81 (2012).
J. Phillips: Application of Mossbauer spectroscopy for the characterization of iron-containing catalysts. Hyperfine Interact. 111, 3 (1998).
H-Y. Lin, Y-W. Chen, and C. Li: The mechanism of reduction of iron oxide by hydrogen. Thermochim. Acta 400, 61 (2003).
A. Pineau, N. Kanari, and I. Gaballah: Kinetics of reduction of iron oxides by H2. Part I: Low temperature reduction of hematite. Thermochim. Acta 447, 89 (2006).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (Grant No. 12-03-00939a). Also, the authors acknowledge support from M.V. Lomonosov Moscow State University Program of Development for the use of their equipment, in particular S. Chernyak and S. Savilov.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lutfullin, M., Shornikova, O., Dunaev, A. et al. The peculiarities of reduction of iron (III) oxides deposited on expanded graphite. Journal of Materials Research 29, 252–259 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.384
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.384