Abstract
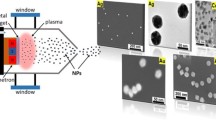
The mechanisms involved in the formation of titanium (Ti) nanoclusters produced by sputtering and inert gas condensation were investigated experimentally and numerically. Ti nanoclusters were generated inside an ultrahigh vacuum compatible system under different source parameters, i.e., inert gas flow rate (fAr), length of the aggregation region (L), and sputtering discharge power (P). Nanocluster size and yield were measured using a quadrupole mass filter (QMF). The variation of the above source parameters enabled fine-tuning of the nanocluster size and yield. Herein, Ti nanoclusters were produced within the size range 3.0-10.0 nm. The combination between the nanocluster size and yield as a function of source parameters enabled understanding Ti nanocluster formation mechanisms, i.e., three-body and two-body collisions. The results show that two-body collisions dominate nanocluster production at low fAr while the three-body collisions dominate at high fAr. In addition, nanocluster size increases as L increases due to the increase in nanocluster nucleation and growth times. The maximum nanocluster yield was obtained at fAr that maximize the probability of three-body and two-body collisions. Nanoclusters could be produced within an optimum range of the sputtering discharge power wherein the nanocluster size and yield increase with increasing the discharge power as a result of increasing the amount of sputtered material. The experimental results were compared with a theoretical model of nanocluster formation via three-body collision. Detailed understanding of the evolution of size and yield of Ti (and Ti-oxide) nanoclusters is essential for producing nanoclusters that can be utilized for environmental applications such as conversion of carbon dioxide and water vapor into hydrocarbons.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Yamamuro, K. Sumiyama, W. Sakurai, and K. Suzuki: Cr cluster deposition by plasma-gas-condensation method. Supramol. Sci. 5, 239 (1998).
A.I. Ayesh, N. Qamhieh, H. Ghamlouche, S. Thaker, and M. EL-Shaer: Fabrication of size-selected Pd nanoclusters using a magnetron plasma sputtering source, J. Appl. Phys. 107, 034317 (2010).
A.I. Ayesh: Electronic transport in Pd nanocluster devices, Appl. Phys. Lett. 98, 133108 (2011).
H. Haberland, M. Karrais, M. Mall, and Y. Thurner: Thin films from energetic cluster impact: A feasibility study, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 10, 3266 (1992).
J.C. Sánchez-López and A. Fernández: The gas-phase condensation method for the preparation of quantum-sized ZnS nanoparticles, Thin Solid Films 317, 497–499 (1998).
K.E.J. Lehtinen and M. Kulmala: A model for particle formation and growth in the atmosphere with molecular resolution in size, Atmos. Chem. Phys. 3, 251–257 (2003).
A. Simchi, R. Ahmadi, S.M. Seyed Reihani, and A. Mahdavi: Kinetics and mechanisms of nanoparticle formation and growth in vapor phase condensation process, Mater. Des. 28, 850–856 (2007).
S. Ikezawa, H. Homyara, T. Kubota, R. Suzuki, S. Koh, F. Mutuga, T. Yoshioka, A. Nishiwaki, Y. Ninomiya, M. Takahashi, K. Baba, K. Kida, T. Hara, and T. Famakinwa: Applications of TiO2 film for environmental purification deposited by controlled electron beam-excited plasma, Thin Solid Films 386, 173–176 (2001).
J. Liqiang, S. Xiaojun, C. Weimin, X. Zili, D. Yaoguo, and F. Honggang: The preparation and characterization of nanoparticle TiO2/Ti films and their photocatalytic activity, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 64, 615–623 (2003).
A.I. Ayesh, S. Thaker, N. Qamhieh, and H. Ghamlouche: Size-controlled Pd nanocluster grown by plasma gas-condensation method, J. Nanopart. Res. 13, 1125 (2011).
A.I. Ayesh, N. Qamhieh, S.T. Mahmoud, and H. Alawadhi: Fabrication of size-selected bimetallic nanoclusters using magnetron sputtering, J. Mater. Res. 27(18), 2441–2446 (2012).
A.N. Banerjee, R. Krishna, and B. Das: Size controlled deposition of Cu and Si nano-clusters by an ultra-high vacuum sputtering gas aggregation technique. Appl. Phys. A 90, 299 (2008).
H. Haberland: Nanoclusters of Atoms and Molecules (Springer, Berlin, 1995).
T. Hihara and K. Sumiyama: Formation and size control of a Ni cluster by plasma gas condensation. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 5270 (1998).
S. Pratontep, S.J. Carroll, C. Xirouchaki, M. Streun, and R.E. Palmer: Size-selected cluster beam source based on radio frequency magnetron plasma sputtering and gas condensation, Rev. Sci. Instrum. 76, 045103 (2005).
A.A. Lushnikov and M. Kulmala: Dimers in nucleating vapors, Phys. Rev. E 58, 3157 (1998).
K.E.J. Lehtinen, U. Backman, J.K. Jokiniemi, and M. Kulmala: Three-body collisions as a particle formation mechanism in silver nanoparticle synthesis, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 274, 526–530 (2004).
N.A. Fuchs and A.G. Sutugin: High dispersed aerosols, in Topics in Current Aerosol Research, Part 2, edited by G.M. Hidy and J.R. Brock (Pergamon, New York, 1971).
J.K. Jokiniemi, M. Lazaridis, K.E.J. Lehtinen, and E.I. Kauppinen: Numerical simulation of vapour-aerosol dynamics in combustion processes, J. Aerosol Sci. 25, 429 (1994).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Emirates Foundation (United Arab Emirates) under Grant Ref. No. 2011/177 and United Arab Emirates University under grant code G00000840. The authors would like to thank Mr. S. Tariq at FMHS (United Arab Emirates University) for the TEM images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayesh, A.I., Ahmed, H.A., Awwad, F. et al. Mechanisms of Ti nanocluster formation by inert gas condensation. Journal of Materials Research 28, 2622–2628 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.246
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2013.246