Abstract
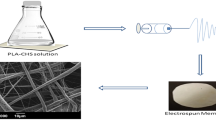
Poly(lactide) (PLA) composites filled with electrospun nylon 6 fibers were prepared. This allowed us to simultaneously improve the mechanical properties and tune the degradation of the PLA matrix. The interfacial adhesion between the PLA matrix and the nylon fibers was good. The major effect of electrospun fibers on the matrix was that of modifying the semicrystalline framework, thickening the polymer lamellae. This allowed an increase in the mechanical properties of the material, and on the other hand to modify its degradation behavior. The modulus of the composites was increased up to 3-fold with respect to neat PLA. The peculiar morphology of matrix–filler interaction moreover slowed down the degradation rate of the material and improved the dimensional stability of the specimens during the degradation process. This shows the potential of electrospun fibers as a way to tune the durability of PLA-based products, widening the range of application of this promising material.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Sinha Ray and M. Okamoto: Biodegradable polylactide and its nanocomposites: Opening a new dimension for plastics and composites. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 24, 815 (2003).
S. Sinha Ray and J. Ramontjia: Polylactide-based nanocomposites, in Biodegradable Polymers Blends and Composites from Renewable Resources, edited by L. Yu (Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2009), pp. 389–414.
K. Oksman, M. Skrifvars, and J.F. Selin: Natural fibres as reinforcement in polylactic acid (PLA) composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 63, 1317 (2003).
N. Graupner, A.S. Herrmann, and J. Müssig: Natural and man-made cellulose fibre-reinforced poly(lactic acid) (PLA) composites: An overview about mechanical characteristics and application areas. Composites Part A 40, 810 (2009).
M.S. Huda, L.T. Drzal, M. Misra, and A.K. Mohanty: Wood-fiber-reinforced poly(lactic acid) composites: Evaluation of the physicomechanical and morphological properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 102, 4856 (2006).
Q.K. Meng, M. Hetzer, and D. De Kee: PLA/clay/wood nanocomposites: Nanoclay effects on mechanical and thermal properties. J. Compos. Mater. 45, 1145 (2010).
L.S. Wang, H.C. Chen, Z.C. Xiong, X.B. Pang, and C.D. Xiong: A completely biodegradable poly[(l-lactide)-co-(e-caprolactone)] elastomer reinforced by in situ poly(glycolic acid) fibrillation: Manufacturing and shape-memory effects. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 295, 381 (2010).
L. Suryanegara, A.N. Nakagaito, and H. Yano: The effect of crystallization of PLA on the thermal and mechanical properties of microfibrillated cellulose-reinforced PLA composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 69, 1187 (2009).
R. Rizvi, O. Khan, and H.E. Naguib: Development and characterization of solid and porous polylactide-multiwall carbon nanotube composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 51, 43 (2011).
D. Wu, L. Wu, W. Zhou, M. Zhang, and T. Yang: Crystallization and biodegradation of polylactide/carbon nanotube composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 50, 1721 (2010).
W.M. Chiu, Y.A. Chang, H.Y. Kuo, M.H. Lin, and H.C. Wen: A study of carbon nanotubes/biodegradable plastic polylactic acid composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 108, 3024 (2008).
A. Zucchelli, M.L. Focarete, C. Gualandi, and S. Ramakrishna: Electrospun nanofibers for enhancing structural performance of composite materials. Polym. Adv. Technol. 22, 339 (2010).
R. Neppalli, C. Marega, A. Marigo, M.P. Bajgai, H.Y. Kim, and V. Causin: Poly(epsilon-caprolactone) filled with electrospun nylon fibres: A model for a facile composite fabrication. Eur. Polym. J. 46, 968 (2010).
R. Neppalli, C. Marega, A. Marigo, M.P. Bajgai, H.Y. Kim, and V. Causin: Improvement of tensile properties and tuning of the biodegradation behavior of polycaprolactone by addition of electrospun fibers. Polymer 52, 4054 (2011).
M. Swart, R.T. Olsson, M.S. Hedenqvist, and P.E. Mallon: Organic–inorganic hybrid copolymer fibers and their use in silicone laminate composites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 50, 2143 (2010).
J.S. Kim and D.H. Reneker: Mechanical properties of composites using ultrafine electrospun fibers. Polym. Compos. 20, 124 (1999).
M.M. Bergshoef and G.J. Vancso: Transparent nanocomposites with ultrathin, electrospun nylon-4,6 fiber reinforcement. Adv. Mater. 11, 1362 (1999).
G.M. Bayley, M. Hedenqvist, and P.E. Mallon: Large strain and toughness enhancement of poly(dimethyl siloxane) composite films filled with electrospun polyacrylonitrile-graft-poly(dimethyl siloxane) fibres and multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Polymer 52, 4061 (2011).
K.P. Matabola, A.R. de Vries, A.S. Luyt, and R. Kumar: Studies on single polymer composites of poly(methyl methacrylate) reinforced with electrospun nanofibers with a focus on their dynamic mechanical properties. Express Polym. Lett. 5, 636 (2011).
L.S. Chen, Z.M. Huang, G.H. Dong, C.L. He, L. Liu, Y.Y. Hu, and Y. Li: Development of a transparent PMMA composite reinforced with nanofibers. Polym. Compos. 30, 239 (2009).
H. Fong: Electrospun nylon 6 nanofiber reinforced BIS-GMA/TEGDMA dental restorative composite resins. Polymer 45, 2427 (2004).
M. Tian, Y. Gao, Y. Liu, Y. Liao, R. Xu, N.E. Hedin, and H. Fong: Bis-GMA/TEGDMA dental composites reinforced with electrospun nylon 6 nanocomposite nanofibers containing highly aligned fibrillar silicate single crystals. Polymer 48, 2720 (2007).
A.M. Hindeleh and D.J. Johnson: The resolution of multipeak data in fiber science. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 4, 259 (1971).
C.G. Vonk: Synthetic polymers in the solid state, in Small Angle X-ray Scattering, edited by O. Glatter and O. Kratky (Academic press, London, 1982), p. 433.
D. Blundell: Models for small-angle X-ray scattering from highly dispersed lamellae. Polymer (Guildf.) 19, 1258 (1978).
C. Marega, A. Marigo, G. Cingano, R. Zannetti, and G. Paganetto: Small-angle X-ray scattering from high-density polyethylene: Lamellar thickness distributions. Polymer (Guildf.) 37, 5549 (1996).
C. Marega, A. Marigo, and V. Causin: Small-angle X-ray scattering from polyethylene: Distorted lamellar structures. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 90, 2400 (2003).
C. Marega, V. Causin, and A. Marigo: A SAXS-WAXD study on the mesomorphic-α transition of isotactic polypropylene. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 109, 32 (2008).
R. Hosemann and S.N. Bagchi: Direct Analysis of Diffraction by Matter (North-Holland Pub. Co, Amsterdam, 1962).
M. Avrami: Granulation, phase change, and microstructure kinetics of phase change III. J. Chem. Phys. 9, 177 (1941).
D.M. Lincoln, R.A. Vaia, Z.G. Wang, B.S. Hsiao, and R. Krishnamoorti: Temperature dependence of polymer crystalline morphology in nylon 6/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Polymer 42, 9975 (2001).
D. Homminga, B. Goderis, I. Dolbnya, H. Reynaers, and G. Groeninckx: Crystallization behavior of polymer/montmorillonite nanocomposites. Part I. Intercalated poly(ethylene oxide). Polymer 46, 11359 (2005).
C. Marega, V. Causin, A. Marigo, G. Ferrara, and H. Tonnaer: Perkalite as an innovative filler for isotactic polypropylene-based nanocomposites. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9, 2704 (2009).
V. Causin, B.X. Yang, C. Marega, S.H. Goh, and A. Marigo: Structure-property relationship in polyethylene reinforced by polyethylene-grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Nanosci. Nanotech. 8, 1790 (2008).
V. Causin, B.X. Yang, C. Marega, S.H. Goh, and A. Marigo: Nucleation, structure and lamellar morphology of isotactic polypropylene filled with polypropylene-grafted multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Eur. Polym. J. 45, 2155 (2009).
V. Causin, C. Marega, R. Saini, A. Marigo, and G. Ferrara: Crystallization behavior of isotactic polypropylene based nanocomposites. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 90, 849 (2007).
S. Hambir, N. Bulakh, and J.P. Jog: Polypropylene/clay nanocomposites: Effect of compatibilizer on the thermal, crystallization and dynamic mechanical behavior. Polym. Eng. Sci. 42, 1800 (2002).
J. Ma, S. Zhang, Z. Qi, L. Li, and Y. Hu: Crystallization behaviors of polypropylene/montmorillonite nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 83, 1978 (2002).
P. Maiti, P.H. Nam, M. Okamoto, N. Hasegawa, and A. Usuki: Influence of crystallization on intercalation, morphology, and mechanical properties of polypropylene/clay nanocomposites. Macromolecules 35, 2042 (2002).
V. Causin, C. Marega, A. Marigo, G. Ferrara, and A. Ferraro: Morphological and structural characterization of polypropylene/conductive graphite nanocomposites. Eur. Polym. J. 42, 3153 (2006).
Z. Su, W. Guo, Y. Liu, Q. Li, and C. Wu: Non-isothermal crystallization kinetics of poly(lactic acid)/modified carbon black composite. Polym. Bull. 62, 629 (2009).
S.M. Huang, J.J. Hwang, H.J. Liu, and L.H. Lin: Crystallization behavior of poly(l-lactic acid)/montmorillonite nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 117, 434 (2010).
M. Li, D. Hu, Y. Wang, and C. Shen: Nonisothermal crystallization kinetics of poly(lactic acid) formulations comprising talc with poly(ethylene glycol). Polym. Eng. Sci. 50, 2298 (2010).
T. Dobreva, J.M. Perena, E. Pérez, R. Benavente, and M. Garcìa: Crystallization behavior of poly(l-lactic acid)-based ecocomposites prepared with kenaf fiber and rice straw. Polym. Compos. 31, 974 (2010).
Y.T. Shieh, T.K. Twu, C.C. Su, R.H. Lin, and G.L. Liu: Crystallization kinetics study of poly(l-lactic acid)/carbon nanotubes nanocomposites. J. Polym. Sci. B: Polym. Phys. 48, 983 (2010).
R. Mat Taib, S. Ramarad, Z.A. Mohd Ishak, and M. Todo: Properties of kenaf fiber/polylactic acid biocomposites plasticized with polyethylene glycol. Polym. Compos. 31, 1213 (2010).
R. Neppalli, V. Causin, C. Marega, R. Saini, M. Mba, and A. Marigo: Structure, morphology and biodegradability of poly(ε-caprolactone) based nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. (2011, in press).
S. Sinha Ray, K. Yamada, M. Okamoto, and K. Ueda: New polylactide-layered silicate nanocomposites. 2. Concurrent improvements of material properties, biodegradability and melt rheology. Polymer 44, 857 (2003).
M. Jollands and R.K. Gupta: Effect of mixing conditions on mechanical properties of polylactide/montmorillonite clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 118, 1489 (2010).
Y. Di, S. Iannace, E. Di Maio, and L. Nicolais: Poly(lactic acid)/organoclay nanocomposites: Thermal, rheological properties and foam processing. J. Polym. Sci. B: Polym. Phys. 43, 689 (2005).
R.W. Truss and T.K. Yeow: Effect of exfoliation and dispersion on the yield behavior of melt-compounded polyethylene-montmorillonite nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 100, 3044 (2006).
B. Pukanszky, I. Mudra, and P. Staniek: Relation of crystalline structure and mechanical properties of nucleated polypropylene. J. Vinyl Add. Technol. 3, 53 (1997).
I. Armentano, M. Dottori, E. Fortunati, S. Mattioli, and J.M. Kenny: Biodegradable polymer matrix nanocomposites for tissue engineering: A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 95, 2126 (2010).
Q. Zhou and M. Xanthos: Nanoclay and crystallinity effects on the hydrolytic degradation of polylactides. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 93, 1450 (2008).
S. Sinha Ray, K. Yamada, M. Okamoto, and K. Ueda: Control of biodegradability of polylactide via nanocomposite technology. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 288, 203 (2003).
M.A. Paul, C. Delcourt, M. Alexandre, P. Degee, F. Monteverde, and P. Dubois: Polylactide/montmorillonite nanocomposites: Study of the hydrolytic degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 87, 535 (2005).
F. Mei, J.S. Zhong, X.P. Yang, X.Y. Ouyang, S. Zhang, X.Y. Hu, Q. Ma, J.G. Lu, S.K. Ryu, and X.L. Deng: Improved biological characteristics of poly(l-lactic acid) electrospun membrane by incorporation of multiwalled carbon nanotubes/hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 8, 3729 (2007).
Acknowledgment
Ramesh Neppalli is grateful to Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Padova e Rovigo for the support of his Ph.D. grant. This work was financed by the PRAT project of the University of Padova CPDA099194/09.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neppalli, R., Marega, C., Marigo, A. et al. Electrospun nylon fibers for the improvement of mechanical properties and for the control of degradation behavior of poly(lactide)-based composites. Journal of Materials Research 27, 1399–1409 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.70
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.70