Abstract
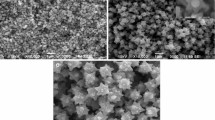
Low temperature (25 °C–80 °C) synthesis of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (,20 nm) at short synthesis periods (;30 min) was achieved by precipitation. The precipitation system was formed using zinc acetate dihydrate as zinc source, ethylene glycol (EG) as solvent and polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) as chelating agent. The size of spherical ZnO nanoparticles was manipulated by the choice of precipitation temperature (13.0 6 1.9 nm at 25 °C and 9.0 6 1.3 nm at 80 °C), which essentially changes the nature of adsorption events between ZnO crystals and organic molecules. The particle size can also be regulated by the amount of chelating agent as a result of further enhancement in adsorption between ZnO crystals and organic additives. The spherical ZnO nanoparticles were agglomerated into triangular form when different solvent was used–by substituting water for EG, which has different adsorption ability. Accordingly, formation and growth mechanisms controlling the size and morphology of ZnO nanoparticles have been proposed.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.K. Gupta: Application of zinc oxide varistors. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73, 1817 (1990).
M. Singhai, V. Chhabra, P. Kang, and D.O. Shah: Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles for varistor application using Zn-substituted aerosol of microemulsion. Mater. Res. Bull. 32, 239 (1997).
T. Gao and T.H. Wang: Synthesis and properties of multipod-shaped ZnO nanorods for gas-sensor applications. Appl. Phys. A 80, 1451 (2005).
L. Liao, H.B. Lu, J.C. Li, H. He, D.F. Wang, D.J. Fu, C. Liu, and W.F. Zhang: Size dependence of gas sensitivity of ZnO nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 1900 (2007).
Y.B. Li, Y. Bando, and D. Golberg: ZnO nanoneedles with tip surface perturbations: Excellent field emitters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 3603 (2004).
C-L. Cheng, S-H. Chao, and Y-F. Chen: Enhancement of field emission in nanotip-decorated ZnO nanobottles. J. Cryst. Growth 311, 4381 (2009).
K. Ramamoorthy, C. Sanjeeviraja, M. Jayachandran, K. Sankaranarayanan, P. Bhattacharya, and L.M. Kukreja: Preparation and characterization of ZnO thin films on InP by laser-molecular beam epitaxy technique for solar cells. J. Cryst. Growth 226, 281 (2001).
S. Choopun, A. Tubtimtae, T. Santhaveesuk, S. Nilphai, E. Wongrat, and N. Hongsith: Zinc oxide nanostructures for applications as ethanol sensors and dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256, 998 (2009).
B. Liu and H.C. Zeng: Hydrothermal synthesis of ZnO nanorods in the diameter regime of 50 nm. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 4430 (2003).
U. Pal and P. Santiago: Controlling the morphology of ZnO nanostructures in a low-temperature hydrothermal process. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 15317 (2005).
R. Ayouchi, F. Martin, D. Leinen, and J.R. Ramos-Barrado: Growth of pure ZnO thin films prepared by chemical spray pyrolysis on silicon. J. Cryst. Growth 247, 497 (2003).
M.T. Htay, Y. Hashimoto, N. Momose, and K. Ito: Position-selective growth of ZnO nanowires by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. J. Cryst. Growth 311, 4499 (2009).
M. Ristic, S. Music, M. Ivanda, and S. Popovic: Sol-gel synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline ZnO powders. J. Alloys Compd. 397, L1 (2005).
J. Li, S. Srinivasan, G.N. He, J.Y. Kang, S.T. Wu, and F.A. Ponce: Synthesis and luminescence properties of ZnO nanostructures produced by the sol-gel method. J. Cryst. Growth 310, 599 (2008).
T. Ahmad, S. Vaidya, N. Sarkar, S. Ghosh, and A.K. Ganguli: Zinc oxalate nanorods: A convenient precursor to uniform nanoparticles of ZnO. Nanotechnology 17, 1236 (2006).
O.A. Yildirim and C. Durucan: Synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles elaborated by microemulsion method. J. Alloys Compd. 506, 944 (2010).
D. Tao, W. Qian, Y. Huang, and F. Wei: A novel low-temperature method to grow single-crystal ZnO nanorods. J. Cryst. Growth 271, 353 (2004).
J. Wang and L. Gao: Wet chemical synthesis of ultra long and straight single-crystalline ZnO nanowires and their excellent UV emission properties. J. Mater. Chem. 13, 2551 (2003).
C. Wang, E. Shen, E. Wang, L. Gao, Z. Kang, C. Tian, Y. Lan, and C. Zhang: Controllable synthesis of ZnO nanocrystals via a surfactant-assisted alcohol thermal process at a low temperature. Mater. Lett. 59, 2867 (2005).
R. Xie, D. Li, H. Zhang, D. Yang, M. Jiang, T. Sekiguchi, B. Liu, and Y. Bando: Low-temperature growth of uniform ZnO particles with controllable ellipsoidal morphologies and characteristic luminescence patterns. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 19147 (2006).
X. Sui, Y. Liu, C. Shao, Y. Liu, and C. Xu: Structural and photoluminescent properties of ZnO hexagonal nanoprisms synthesized by microemulsion with polyvinyl pyrrolidone served as surfactant and passivant. Chem. Phys. Lett. 424, 340 (2006).
A. Drelinkiewicz, M. Hasik, S. Quillard, and C. Paluszkiewicz: Infrared and Raman studies of palladium-nitrogen-containing polymers interactions. J. Mol. Struct. 511-512, 205 (1999).
R.F. Silva and M.E. Zaniquelli: Morphology of nanometric size particulate aluminum-doped zinc oxide films. Colloids Surf., A 198-199, 551 (2002).
R. Wahab, Y-S. Kim, K. Lee, and H-S. Shin: Fabrication and growth mechanism of hexagonal zinc oxide nanorods via solution process. J. Mater. Sci. 45, 2967 (2010).
S.A. Studenikin, N. Golego, and M. Cocivera: Fabrication of green and orange photoluminescent, undoped ZnO films using spray pyrolysis. J. Appl. Phys. 84, 2287 (1998).
C.L. Yang, J.N. Wang, W.K. Ge, L. Guo, S.H. Yang, and D.Z. Shen: Enhanced ultraviolet emission and optical properties in polyvinyl pyrrolidone surface modified ZnO quantum dots. J. Appl. Phys. 90, 4489 (2001).
P.X. Gao and Z.L. Wang: Substrate atomic-termination-induced anisotropic growth of ZnO nanowires/nanorods by the VLS process. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 7534 (2004).
Z.L. Wang: Zinc oxide nanostructures: Growth, properties and applications. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16, R829 (2004).
L. Zhang and Y.J. Zhu: ZnO micro- and nanostructures: Microwave-assisted solvothermal synthesis, morphology control and photocatalytic properties. Appl. Phys. A 97, 847 (2009).
M.H. Rashid, M. Raula, R.R. Bhattacharjee, and T.K. Mandal: Low-temperature polymer-assisted synthesis of shape-tunable zinc oxide nanostructures dispersible in both aqueous and nonaqueous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 339, 249 (2009)
T. Ghoshal, S. Kar, and S. Chaudhuri: ZnO Doughnuts: Controlled synthesis, growth mechanism and optical properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 7, 136 (2006).
S.F. Wei, J.S. Lian, and Q. Jiang: Controlling growth of ZnO rods by polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and their optical properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 6978 (2009).
J. Zhang, H. Liu, Z. Wang, and N. Ming: Low-temperature growth of ZnO with controllable shapes and band gaps. J. Cryst. Growth 310, 2848 (2008).
C. Pacholski, A. Kornowski, and H. Weller: Self-assembly of ZnO: From nanodots to nanorods. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 41, 1188 (2002).
C.W. Yao, H.P. Wu, M.Y. Ge, L. Yang, Y.W. Zeng, Y.W. Wang, and J.Z. Jiang: Triangle-shape ZnO prepared by thermal decomposition. Mater. Lett. 61, 3416 (2007).
H. Muta, K. Ishida, E. Tamaki, and M. Satoh: An IR study on ion-specific and solvent-specific swelling of poly (N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone) gel. Polymer 43, 103 (2002).
J. Bai, Y. Li, C. Zhang, X. Liang, and Q. Yang: Preparing AgBr nanoparticles in poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) (PVP) nanofibers. Colloids Surf., A 329, 165 (2008).
Z. Zhang, C. Shao, F. Gao, X. Li, and Y. Liu: Enhanced ultraviolet emission from highly dispersed ZnO quantum dots, embedded in poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) electrospun nanofibers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 347, 215 (2010).
R. Wahab, S.G. Ansari, Y.S. Kim, H.K. Seo, G.S. Kim, G. Khang, and H-S. Shin: Low temperature solution synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoflowers. Mater. Res. Bull. 42, 1640 (2007).
M. Haase, H. Weller, and A. Henglein: Photochemistry and radiation chemistry of colloidal semiconductors. 23. Electron storage on zinc oxide particles and size quantization. J. Phys. Chem. 92, 482 (1988).
M.L. Singla, M. Shafeeq, and M.M. Kumar: Optical characterization of ZnO nanoparticles capped with various surfactants J. Lumin. 129, 434 (2009).
M. Willander, O. Nur, J.R. Sadaf, M.I. Qadir, S. Zaman, A. Zainelabdin, N. Bano, and I. Hussain: Luminescence from zinc oxide nanostructures and polymers and their hybrid devices. Materials 3, 2643 (2010).
H.S. Kang, J.S. Kang, J.W. Kim, and S.Y. Lee: Annealing effect on the property of ultraviolet and green emissions of ZnO thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 95, 1246 (2004).
M. Liu, A.H. Kitai, and P. Mascher: Point defects and luminescence-centers in zinc oxide and zinc oxide doped with manganese. J. Lumin. 54, 35 (1992).
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Middle East Technical University through Grant BAP-03-08-2009-06. OAY thanks The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey, TUBITAK, for the support by the National Scholarship Program for Ph.D. students and also METU-OYP Program. The authors thank Yunus Eren Kalay for his assistance in TEM data analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yıldırım, Ö.A., Durucan, C. Effect of precipitation temperature and organic additives on size and morphology of ZnO nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Research 27, 1452–1461 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.58
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.58