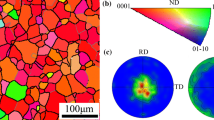
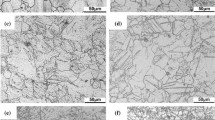
Abstract
A hot-rolled AZ31 Mg alloy sheet was subjected to dynamic plastic deformation parallel to the rolling direction with the aim of introducing {10-12} twins. Subsequent tensile tests were carried out along the predeformed direction and the initial transverse direction (TD). It was found that untwinning led to a significant drop in yield stress when tension is carried out along the predeformed direction. And {10-12} twins and strain caused by twinning were recovered by untwinning. The tensile yield stress increased slightly with prestrain was correlated with the texture hardening caused by untwinning. When tension is carried out along initial TD, {10-12} twinning activity was restrained and slip dominated plastic deformation. The tensile yield stress increased significantly with prestrain was strongly correlated with the hardening contributions of {10-12} twins. {10-12} twinning led to the obvious yield stress in-plane anisotropy but had little effect on the maximum flow stress.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.H. Avery, W.F. Hosford, and W.A. Backofen: Plastic anisotropy in magnesium alloy sheets. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 233, 71 (1965).
E.W. Kelley and W.F. Hosford: Plane-strain compression of magnesium and magnesium alloy crystals. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 242, 5 (1968).
J.A. del Valle, F. Carren, and O.A. Ruano: Influence of texture and grain size on work hardening and ductility in magnesium-based alloys processed by ECAP and rolling. Acta Mater. 54, 4247 (2006).
R. Gehrmann, M.M. Frommert, and G. Gottstein: Texture effects on plastic deformation of magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 395, 338 (2005).
J.W. Christian and S. Mahajan: Deformation twinning. Prog. Mater. Sci. 39, 1 (1995).
S.B. Yi, C.H.J. Davies, H.G. Brokmeier, R.E. Bolmaro, K.U. Kainer, and J. Homeyer: Deformation and texture evolution in AZ31 magnesium alloy during uniaxial loading. Acta Mater. 54, 549 (2006).
L. Jiang, J.J. Jonas, A.A. Luo, A.K. Sachdev, and S. Godet: Influence of {10-12} extension twinning on the flow behavior of AZ31 Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 445, 302 (2007).
L. Jiang and J.J. Jonas: Effect of twinning on the flow behavior during strain path reversals in two Mg (+Al, Zn, Mn) alloys. Scr. Mater. 58, 803 (2008).
G. Wan, B.L. Wu, Y.D. Zhang, G.Y. Sha, and C. Esling: Anisotropy of dynamic behavior of extruded AZ31 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 2915 (2010).
S.H. Choi, J.K. Kim, B.J. Kim, and Y.B. Park: The effect of grain size distribution on the shape of flow stress curves of Mg–3Al–1Zn under uniaxial compression. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 488, 458 (2008).
L.E. Murr, E. Moin, and F. Greulich: The contribution of deformation twins to yield stress: The Hall-Petch law for inter-twin spacing. Scr. Metall. 12, 1031 (1978).
M.R. Barnett, Z. Keshavarz, A.G. Beer, and D. Atwell: Influence of grain size on the compressive deformation of wrought Mg–3Al–1Zn. Acta Mater. 52, 5093 (2004).
I. Karaman, H. Sehitoglu, Y.I. Chumlyakov, I.V. Kireeva, and H.J. Maier: The effect of twinning and slip on the Bauschinger effect of Hadfield steel single crystals. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 32, 695 (2001).
X.Y. Lou, M. Li, R.K. Boger, S.R. Agnew, and R.H. Wagoner: Hardening evolution of AZ31B Mg sheet. Int. J. Plast. 23, 44 (2007).
G. Proust, C.N. Tome, A. Jain, and S.R. Agnew: Modeling the effect of twinning and detwinning during strain-path changes of magnesium alloy AZ31. Int. J. Plast. 25, 861 (2009).
Y.N. Wang and J.C. Huang: The role of twinning and untwinning in yielding behavior in hot-extruded Mg–Al–Zn alloy. Acta Mater. 55, 897 (2007).
S. Kleiner and P.J. Uggowitzer: Mechanical anisotropy of extruded Mg–6%Al–1%Zn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 379, 258 (2004).
P.G. Partridge: Cyclic twinning in fatigued close-packed hexagonal metals. Philos. Mag. 12, 1043 (1965).
N.V. Dudamell, I. Ulacia, F. Gálvez, S. Yi, J. Bohlen, D. Letzig, I. Hurtado, and M.T. Pérez-Prado: Twinning and grain subdivision during dynamic deformation of a Mg AZ31 sheet alloy at room temperature. Acta Mater. 59, 6949 (2011).
L. Jiang, J.J. Jonas, R.K. Mishra, A.A. Luo, A.K. Sachdev, and S. Godet: Twinning and texture development in two Mg alloys subjected to loading along three different strain paths. Acta Mater. 55, 3899 (2007).
S.R. Agnew and O. Duygulu: Plastic anisotropy and the role of non-basal slip in magnesium alloy AZ31B. Int. J. Plast. 21, 1161 (2005).
Z. Keshavarz and M.R. Barnett: EBSD analysis of deformation modes in Mg-3Al-1Zn. Scr. Mater. 55, 915 (2006).
C.H. Caceres and A.H. Blake: On the strain hardening behaviour of magnesium at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 462, 193 (2007).
E.A. Ball and P.B. Prangnell: Tensile-compressive yield asymmetries in high strength wrought magnesium alloys. Scr. Mater. 31, 111 (1994).
S.R. Agnew, M.H. Yoo, and C.N. Tome: Application of texture simulation to understanding mechanical behavior of Mg and solid solution alloys containing Li or Y. Acta Mater. 49, 4277 (2001).
M.R. Barnett: A Taylor model based description of the proof stress of magnesium AZ31 during hot working. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34A, 1799 (2003).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51071183, 50890170, and 51271208) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. CDJXS11132225).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lou, C., Zhang, X., Wang, R. et al. Mechanical behavior and microstructural characteristics of magnesium alloy containing {10-12} twin lamellar structure. Journal of Materials Research 28, 733–739 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.394
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.394