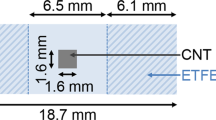
Abstract
We report the mechanical behavior of vertically aligned carbon nanotube films, grown on Si substrates using atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition, subjected to in situ large displacement (up to 70 μm) flat-punch indentations. We observed three distinct regimes in their indentation stress–strain curves: (i) a short elastic regime, followed by (ii) a sudden instability, which resulted in a substantial rapid displacement burst manifested by an instantaneous vertical shearing of the material directly underneath the indenter tip by as much as 30 μm, and (iii) a positively sloped plateau for displacements between 10 and 70 μm. In situ nanomechanical indentation experiments revealed that the shear strain was accommodated by an array of coiled carbon nanotube “microrollers,” providing a low-friction path for the vertical displacement. Mechanical response and concurrent deformation morphologies are discussed in the foam-like deformation framework with a particular emphasis on boundary conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.M. McCarter, R.F. Richards, S.D. Mesarovic, C.D. Richards, D.F. Bahr, D. McClain, and J. Jiao: Mechanical compliance of photolithographically defined vertically aligned carbon nanotube turf. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 7872 (2006).
A.A. Zbib, S.D. Mesarovic, E.T. Lilleodden, D. McClain, J. Jiao, and D.F. Bahr: The coordinated buckling of carbon nanotube turfs under uniform compression. Nanotechnology 19, 175704 (2008).
B.A. Cola, J. Xu, and T.S. Fisher: Contact mechanics and thermal conductance of carbon nanotube array interfaces. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 52, 3490 (2009).
A. Misra, J.R. Greer, and C. Daraio: Strain rate effects in the mechanical response of polymer-anchored carbon nanotube foams. Adv. Mater. 20, 1 (2008).
A.Y. Cao, P.L. Dickrell, W.G. Sawyer, M.N. Ghasemi-Nejhad, and P.M. Ajayan: Super-compressible foamlike carbon nanotube films. Science 310, 1307 (2005).
J. Cho, C. Richards, D. Bahr, J. Jiao, and R. Richards: Evaluation of contacts for a MEMS thermal switch. J. Micromech. Microeng. 18(105012), 1–6 (2008).
J.F. Waters, P.R. Guduru, M. Jouzi, J.M. Xu, T. Hanlon, and S. Suresh: Shell buckling of individual multiwalled carbon nanotubes using nanoindentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 103109 (2005).
S. Pathak, Z.G. Cambaz, S.R. Kalidindi, J.G. Swadener, and Y. Gogotsi: Viscoelasticity and high buckling stress of dense carbon nanotube brushes. Carbon 47, 1969 (2009).
S. Pathak, E.J. Lim, P. Pour Shahid Saeed Abadi, S. Graham, B.A. Cola, and J.R. Greer: Higher recovery and better energy dissipation at faster strain rates in carbon nanotube bundles: An in situ study. ACS Nano 6(3), 2189–2197 (2012).
M. Kumar and Y. Ando: Chemical vapor deposition of carbon nanotubes: A review on growth mechanism and mass production. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 10, 3739 (2010).
S.B. Hutchens, L.J. Hall, and J.R. Greer: In situ mechanical testing reveals periodic buckle nucleation and propagation in carbon nanotube bundles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 2338 (2010).
S.B. Hutchens, A. Needleman, and J.R. Greer: Analysis of uniaxial compression of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 59, 2227 (2011).
J. Suhr, P. Victor, L.C.S. Sreekala, X. Zhang, O. Nalamasu, and P.M. Ajayan: Fatigue resistance of aligned carbon nanotube arrays under cyclic compression. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 417 (2007).
T. Tong, Y. Zhao, L. Delzeit, A. Kashani, M. Meyyappan, and A. Majumdar: Height independent compressive modulus of vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays. Nano Lett. 8, 511 (2008).
S.D. Mesarovic, C.M. McCarter, D.F. Bahr, H. Radhakrishnan, R.F. Richards, C.D. Richards, D. McClain, and J. Jiao: Mechanical behavior of a carbon nanotube turf. Scr. Mater. 56, 157 (2007).
A. Qiu, D.F. Bahr, A.A. Zbib, A. Bellou, S.D. Mesarovic, D. McClain, W. Hudson, J. Jiao, D. Kiener, and M.J. Cordill: Local and non-local behavior and coordinated buckling of CNT turfs. Carbon 49, 1430 (2011).
Q. Zhang, Y.C. Lu, F. Du, L. Dai, J. Baur, and D.C. Foster: Viscoelastic creep of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 43, 315401 (2010).
C.P. Deck, J. Flowers, G.S.B. McKee, and K. Vecchio: Mechanical behavior of ultralong multiwalled carbon nanotube mats. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 23512 (2007).
M. Xu, D.N. Futaba, T. Yamada, M. Yumura, and K. Hata: Carbon nanotubes with temperature-invariant viscoelasticity from-196 degrees to 1000 degrees C. Science 330, 1364 (2010).
M. Xu, D.N. Futaba, M. Yumura, and K. Hata: Carbon nanotubes with temperature-invariant creep and creep-recovery from −190 to 970 °C. Adv. Mater. 23, 3686 (2011).
C. Cao, A. Reiner, C. Chung, S-H. Chang, I. Kao, R.V. Kukta, and C.S. Korach: Buckling initiation and displacement dependence in compression of vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays. Carbon 49, 3190 (2011).
M.R. Maschmann, Z. Qiuhong, D. Feng, D. Liming, and J. Baur: Length dependent foam-like mechanical response of axially indented vertically oriented carbon nanotube arrays. Carbon 49, 386 (2011).
P. Pour Shahid Saeed Abadi, S. Hutchens, J.H. Taphouse, J.R. Greer, B.A. Cola, and S. Graham: The effect of morphology on the micro-compression response of carbon nanotube forests. Nanoscale 4(11), 3373–3380 (2012).
M.R. Maschmann, Q. Zhang, R. Wheeler, F. Du, L. Dai, and J. Baur: In situ SEM observation of column-like and foam-like CNT array nanoindentation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 3, 648 (2011).
P.D. Bradford, X. Wang, H. Zhao, and Y.T. Zhu: Tuning the compressive mechanical properties of carbon nanotube foam. Carbon 49, 2834 (2011).
J-Y. Kim and J.R. Greer: Tensile and compressive behavior of gold and molybdenum single crystals at the nano-scale. Acta Mater. 57, 5245 (2009).
J.P. Tu, C.X. Jiang, S.Y. Guo, and M.F. Fu: Micro-friction characteristics of aligned carbon nanotube film on an anodic aluminum oxide template. Mater. Lett. 58, 1646 (2004).
J.P. Tu, L.P. Zhu, K. Hou, and S.Y. Guo: Synthesis and frictional properties of array film of amorphous carbon nanofibers on anodic aluminum oxide. Carbon 41, 1257 (2003).
K.L. Johnson: Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1987).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
V.S. Deshpande and N.A. Fleck: Isotropic constitutive models for metallic foams. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48, 1253 (2000).
M.F. Ashby: Materials Selection in Mechanical Design, 3rd ed. (Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2005).
R. Hill: The Mathematical Theory of Plasticity (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1950).
E.G. Herbert, W.C. Oliver, and G.M. Pharr: Nanoindentation and the dynamic characterization of viscoelastic solids. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 074021 (2008).
E.G. Herbert, W.C. Oliver, A. Lumsdaine, and G.M. Pharr: Measuring the constitutive behavior of viscoelastic solids in the time and frequency domain using flat punch nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 24, 626 (2009).
W.J. Wright, A.R. Maloney, and W.D. Nix: An improved analysis for viscoelastic damping in dynamic nanoindentation. Int. J. Surf. Sci. Eng. 1, 274 (2007).
W.J. Wright and W.D. Nix: Storage and loss stiffnesses and moduli as determined by dynamic nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 24(3), 863 (2009).
S. Pathak, J. Gregory Swadener, S.R. Kalidindi, H-W. Courtland, K.J. Jepsen, and H.M. Goldman: Measuring the dynamic mechanical response of hydrated mouse bone by nanoindentation. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 4, 34 (2011).
N.A. Fleck, H. Otoyo, and A. Needleman: Indentation of porous solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 29, 1613 (1992).
P. Sudheer Kumar, S. Ramchandra, and U. Ramamurty: Effect of displacement-rate on the indentation behavior of an aluminum foam. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 347, 330 (2003).
E.A. Flores-Johnson and Q.M. Li: Indentation into polymeric foams. Int. J. Solids Struct. 47, 1987 (2010).
A. Pantano, D.M. Parks, and M.C. Boyce: Mechanics of deformation of single- and multi-wall carbon nanotubes. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 52, 789 (2004).
R.S. Lakes: Viscoelastic Solids (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1998).
M.F. Doerner and W.D. Nix: A method for interpreting the data from depth-sensing indentation instruments. J. Mater. Res. 1, 601 (1986).
I.M. Ward and J. Sweeney: An Introduction to the Mechanical Properties of Solid Polymers, 2nd ed. (Wiley, West Sussex, UK, 2004).
L.J. Gibson and M.F. Ashby: Cellular Solids: Structure and Properties (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1999).
E.W. Andrews, L.J. Gibson, and M.F. Ashby: The creep of cellular solids. Acta Mater. 47, 2853 (1999).
E.W. Andrews, G. Gioux, P. Onck, and L.J. Gibson: Size effects in ductile cellular solids. Part II: Experimental results. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 43, 701 (2001).
S. Pathak, N. Mohan, E. Decolvenaere, A. Needleman, M. Bedewy, A.J. Hart, and J.R. Greer: Effect of density gradients on the deformation of carbon nanotube pillars: An in-situ study. (2012, submitted).
Y. Gogotsi: High-temperature rubber made from carbon nanotubes. Science 330, 1332 (2010).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge S. Hutchens and A. Needleman for helpful insights and guidance, E. Lim for data analysis, financial support from the Georgia Institute of Technology Foundation through the Joseph Anderer Faculty Fellowship, and the Institute for Collaborative Biotechnologies (ICB) for financial support through Grant No. W911NF-09-0001 from the U.S. Army Research Office. The content of the information does not necessarily reflect the position or the policy of the Government, and no official endorsement should be inferred. S.P. gratefully acknowledges support from the W.M. Keck Institute for Space Studies Postdoctoral Fellowship program for this work. We gratefully acknowledge critical support and infrastructure provided for this work by the Kavli Nanoscience Institute at Caltech.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material
Supplementary material can be viewed in this issue of the Journal of Materials Research by visiting http://journals.cambridge.org/jmr.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pathak, S., Mohan, N., Abadi, P.P.S.S. et al. Compressive response of vertically aligned carbon nanotube films gleaned from in situ flat-punch indentations. Journal of Materials Research 28, 984–997 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.366
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.366