Abstract
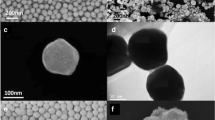
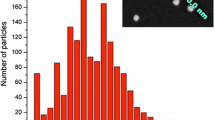
We used miniemulsion to synthesize novel water-soluble dispersion of nanocapsules with a polyaniline (PANI) shell and luminescent ultrasmall Si nanoparticle core with diameters of 50–300 nm. The capsules are functionalized with aromatic sulfonic acid. The capsules may be reconstituted in thin films or structured surfaces. The stability of the luminescence and dispersion of the capsules is studied under a wide range of pH conditions. The multiplicity of nanoparticles in the core provides highly amplified and reproducible signal for luminescence-based imaging using standard fluorescence microscopy, while the PANI shell allows a variety of routes for functionalization as well as electrical interrogation, which enables a wide range of biosensing/imaging applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. He, C. Fan, and S.T. Lee: Silicon nanostructures for bioapplications. Nanotoday 5, 282 (2010).
F. Erogbogbo, K.T. Yong, I. Roy, G. Xu, P.N. Prasad, and M.T. Swihart: Biocompatible luminescent silicon quantum dots for imaging of cancer cells. ACS Nano 2, 873 (2008).
M.H. Nayfeh and L. Mitas: Silicon nanoparticles: New photonic and electronic material at the transition between solid and molecule, in Nanosilicon, edited by V. Kumar (Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008); pp. 1–78.
D.S. English, L.E. Pell, Z. Yu, P.F. Barbara, and B.A. Korgel: Size tunable visible luminescence from individual organic monolayer stabilized silicon nanocrystal quantum dots. Nano Lett. 2, 681 (2002).
M. Nayfeh, E. Rogozhina, and L. Mitas: Silicon nanoparticles: Next generation of ultrasensitive fluorescent markers, in Synthesis, Functionalization, and Surface Treatment of Nanoparticles, edited by M.-I. Baratron (American Scientific Publishers, Stevenson Ranch, CA, 2002); pp. 1–59.
G. Belomoin, J. Therrien, A. Smith, S. Rao, S. Chaieb, and M.H. Nayfeh: Observation of a magic discrete family of ultrabright Si nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 841 (2002).
D. Nielsen, L. Abuhassan, M. Alchihabi, A. Al-Muhanna, J. Host, and M.H. Nayfeh: Current-less anodization of intrinsic silicon powder grains: Formation of fluorescent Si nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 114302 (2007).
O. Ackakir, J. Therrien, G. Belomoin, N. Barry, J. Muller, E. Gratton, and M.H. Nayfeh: Detection of luminescent single ultrasmall silicon nanoparticle using fluctuation spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1857 (2000).
M.H. Nayfeh, J. Therrien, G. Belomoin, O. Akcakir, N. Barry, and E. Gratton: Stimulated blue emission and second harmonic generation from films of ultrasmall Si nanoparticles, in Microcrystalline and Nanocrystalline Semiconductors—2000, edited by P.M. Fauchet, J.M. Buriak, L.T. Canham, N. Koshida, and B.E. White Jr. (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 638, Warrendale, PA, 2001); p. F9.5.
M. Nayfeh, O. Akcakir, G. Belomoin, N. Barry, J. Therrien, and E. Gratton: Second harmonic generation in microcrystallite films of ultrasmall Si nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77, 4086 (2000).
G. Wang, K. Mantey, M.H. Nayfeh, and S.T. Yau: Enhanced amperometric detection of glucose using Si-29 particles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 243901 (2006).
G. Wang, S.T. Yau, K. Mantey, and M.H. Nayfeh: Fluorescent Si nanoparticle-based electrode for sensing biomedical substances. Opt. Commun. 281, 1765 (2008).
Q. Liu, M.H. Nayfeh, and S.T. Yau: A silicon nanoparticle-based polymeric nano-composite material for glucose sensing. J. Electroanal. Chem. 657, 172 (2011).
K. Mantey, M. Kwit, M.H. Nayfeh, A. Kumar, L.D. Stephenson, and A.J. Nelson: Measurement of the photostability of silicon nanoparticles under UVA and near infrared irradiation. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 064316 (2010).
K. Mantey, M.H. Nayfeh, B. Al-Hreish, J. Boparai, A. Kumar, L.D. Stephenson, A.J. Nelson, S.A. Alrokayan, and K.M. Abu-Salah: Silicon nanoparticle-functionalized fiberglass pads for sampling. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 064321 (2011).
E. Rogozhina, G. Belomoin, A. Smith, L. Abuhassan, N. Barry, O. Akcakir, P.V. Braun, and M.H. Nayfeh: Si-N linkage in ultrabright, ultrasmall Si nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 3711 (2001).
G. Belomoin, E. Rogozhina, J. Therrien, P.V. Braun, L. Abuhassan, M.H. Nayfeh, L. Wagner, and L. Mitas: Effect of surface termination on the band gap of ultrabright Si29 nanoparticles: Experiments and computational models. Phys. Rev. B 65, 193406 (2002).
A.J. Heeger: Semiconducting metallic polymers: Fourth generation polymeric materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 40, 2591 (2001).
A.G. Green and A.E. Woodhead: Aniline black and allied compounds. J. Chem. Soc. 97, 2388 (1910).
A.A. Syed and M.K. Dinesan: Polyaniline-A novel polymeric material. Talanta 38, 815 (1991).
P. Banerjee: Carboxymethylcellulose stabilized polyaniline dispersions and conducting copolymer latex composites. Eur. Polym. J. 34, 841 (1998).
D. Chattopadhyay and B.M. Mandal: Methyl cellulose stabilized polyaniline dispersions. Langmuir 12, 1585 (1996).
J. Stejskal and P. Kratochvil: Polyaniline dispersions. 5. Poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) as steric stabilizers. Langmuir 12, 3389 (1996).
P. Banerjee, S.N. Bhattacharyya, and B.M. Mandal: Poly(vinyl methyl-ether) stabilized colloidal polyaniline dispersions. Langmuir 11, 2414 (1995).
E.C. Cooper and B. Vincent: Electrically conducting organic films and beads based on conducting latex particles. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 22, 1580 (1989).
S.P. Armes, M. Aldissi, S. Agnew, and S. Gottesfeld: Aqueous colloidal dispersions of polyaniline formed by using poly(vinylpyridine)-based steric stabilizers. Langmuir 6, 1745 (1990).
S.H. Lee, D.H. Lee, K. Lee, and C.W. Lee: High-performance polyaniline prepared via polymerization in a self-stabilized dispersion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 15, 1495 (2005).
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge NSF Grant OISE 11-03-398.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elhalawany, N., Maximenko, Y., Yamani, Z. et al. Soluble silicon nanoparticles–polyaniline capsules for biosensing and imaging. Journal of Materials Research 28, 210–215 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.325
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.325