Abstract
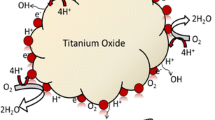
Titanium-based ceramic supports designed for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells were synthesized, and catalytic activity was explored using electrochemical analysis. Synthesis of high surface area TiO2 and TiO supports was accomplished by rapidly heating a gel of polyethyleneimine-bound titanium in a tube furnace under a forming gas atmosphere. X-ray diffraction analysis revealed anatase phase formation for the TiO2 materials and crystallite sizes of less than 10 nm in both cases. Subsequent disposition of platinum through an incipient wetness approach leads to highly dispersed crystallites of platinum, less than 6 nm each, on the conductive supports. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)/energy dispersive x-ray analysis results showed a highly uniform Ti and Pt distribution on the surface of both materials. The supports without platinum are highly stable to acidic aqueous conditions and show no signs of oxygen reduction reactivity (ORR). However, once the 20 wt% platinum is added to the material, ORR activity comparable to XC-72-based materials is observed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.L. Borup, J.R. Davey, F.H. Garzon, D.L. Wood, and M.A. Inbody: PEM fuel cell electrocatalyst durability measurements. J. Power Sources 163(1), 76 (2006).
R.L. Borup, F.H. Garzon, D.L. Wood, J.R. Davey, and E.L. Brosha: PEM electrode durability measurements. Presented at Electrochemical Society, Second International Conference on Polymer Batteries and Fuel Cells June 12-17, 2005, Las Vegas, NV (2005).
T.A. Bekkedahl, L.J. Bregoli, R.D. Breault, E.A. Dykeman, J.P. Meyers, T.W. Patterson, T. Skiba, C. Vargas, D.Y. Yang, and S. Jung: Reducing fuel cell cathode potential during startup and shutdown. U.S. Patent No. 20040081866. (2004).
F.H. Garzon, J.R. Davey, and R.L. Borup: Fuel cell catalyst particle size growth characterized by x-ray scattering methods. ECS Trans. 8(1), 153 (2005).
R.L. Borup, J.R. Davey, D. Wood, F. Garzon, M. Inbody, and D. Guidry: PEM Fuel Cell Durability. 2005 DOE Hydrogen Program Review, (Department of Energy, Washington, DC, 2005).
M.S. Wilson, F.H. Garzon, K.E. Sickafus, and S. Gottesfeld: Modeling and experimental diagnostics in polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 140(10), 2872 (1993).
K.L. More: Microstructural Characterization of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell Membrane Electrode Assemblies. DOE Annual Report (Department of Energy, Washington, DC, 2005).
F.H. Garzon, J.R. Davey, and R.L. Borup: Fuel cell catalyst particle size growth characterized by x-ray scattering methods. ECS Meeting Abstracts, Vol. MA 2005-02, 2223 (2005).
D. Raistrick: Modified gas diffusion electrode for proton exchange membrane fuel cells, in Proceedings of the Symposium on Diaphragms, Separators, and Ion Exchange Membranes, the Electrochemical Society, edited by J.W. Van Zee, R.E. White, K. Kinoshita, and H.S. Burney (The Electrochemical Society, Inc., Pennington, NJ, 1986); p. 172.
D. Raistrick: Electrode assembly for use in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. U.S. Patent No. 4,876,115, (1989).
E.A. Ticianelli, C.R. Derouin, and S. Srinivasan: Localization of platinum in low catalyst loading electrodes to attain high-power densities in SPE fuel cells. J. Electroanal. Chem. 251, 275 (1988).
E.A. Ticianelli, C.R. Derouin, A. Redondo, and S. Srinivasan: Methods to attain high-power densities in solid-polymer electrolyte fuel-cells using low platinum loading electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 135, 2209 (1988).
M.S. Wilson: Membrane catalyst layer for fuel cells. U.S. Patent No. 5,234,777, (1993).
M.S. Wilson and S. Gottesfeld: High-performance catalyzed membranes of ultra-low pt loadings for polymer electrolyte fuel-cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 139, L28–L30 (1992).
M.S. Wilson and S. Gottesfeld: Thin-film catalyst layers for polymer electrolyte fuel-cell electrodes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 22, 1 (1992).
D.A. Stevens, M.T. Hicks, G.M. Haugen, and J.R. Dahn: Ex situ and in situ stability studies of PEMFC catalysts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 152(12), A2309 (2005).
F. Coloma, A. Sepulveda-Escribano, and F. Rodriguez-Reinoso: Heat-treated carbon-blacks as supports for platinum catalysts. J. Catal. 154(2), 299 (1995).
E. Antolini and E.R. Gonzalez: Ceramic materials as supports for low-temperature fuel cell catalysts. Solid State Ionics 180, 746 (2009).
Y. Shao, J. Liu, Y. Wang, and Y. Lin: Novel catalyst support materials or PEM fuel cells: Current status and future prospects. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 46 (2009).
T. Maiyalagan, B. Viswanathan, and U.V. Varadaraju: Nitrogen containing carbon nanotubes as supports for Pt—alternate anodes for fuel cell applications. Electrochem. Commun. 7(9), 905 (2005).
A. Kongkanand, S. Kuwubata, G. Girishkumar, and P. Kamat: Single-wall carbon nanotubes supported platinum nanoparticles with improved electrocatalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction. Langmuir 22(5), 2392 (2006).
X. Wang, W. Li, Z. Chen, M. Waje, and Y. Yan: Durability investigation of carbon nanotube as catalyst support for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sources 158(1), 154 (2006).
J. Shim, C. Lee, H. Lee, J. Lee, and E. Cairns: Electrochemical characteristics of Pt–WO3/C and Pt–TiO2/C electrocatalysts in a polymer electrolyte fuel cell. J. Power Sources 102(1–2), 172 (2001).
L. Xiong and A. Manthiram: Synthesis and characterization of methanol tolerant Pt/TiOx/C nanocomposites for oxygen reduction in direct methanol fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 49(24), 4163 (2004).
G. Wu, M.A. Nelson, N.H. Mack, S. Ma, P. Sekhar, F.H. Garzon, and P. Zelenay: Titanium dioxide-supported non-precious metal oxygen reduction electrocatalyst. Chem. Commun. 46(40), 7489 (2010).
K.J. Blackmore, L. Elbaz, E. Bauer, E.L. Brosha, K. More, T.M. McCleskey, and A.K. Burrell: High surface area Molybdenum nitride support for fuel cell electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 158(10), B1255 (2011).
N.M. Markovic, T.J. Schmidt, V. Stamenkovic, and P.N. Ross: Oxygen reduction reaction on Pt and Pt bimetallic surfaces: A selective review. Fuel Cells 1(2), 105 (2001).
Y. Cai and R.R. Adzic: Platinum monolayer electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction: Improvements induced by surface and subsurface modifications of cores. Adv. Phys. Chem. 2011, 530397, 1–16 (2011).
Acknowledgment
We wish to thank the U.S. Department of Energy Hydrogen Program for providing funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armstrong, K.J., Elbaz, L., Bauer, E. et al. Nanoscale titania ceramic composite supports for PEM fuel cells. Journal of Materials Research 27, 2046–2054 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.169
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2012.169