Abstract
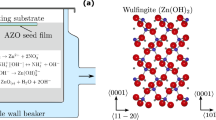
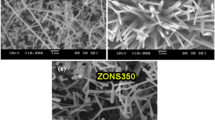
In this study, we synthesized ZnO nanowires using Au catalytic particles formed on a ZnO seed layer. We modulated the microstructure of the ZnO seed layer by changing the sputtering power to investigate how the underlying ZnO film microstructure affects the distribution of ZnO nanowires. Examining the samples after each of the three key steps of the growth process (ZnO seed layer deposition, Au catalytic particle formation, and nanowire growth) using various characterization methods such as scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and x-ray diffraction helped us illuminate the profound impacts of the grain size of the seed layer on the nanowire density.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ü. Özgür, Y.I. Alivov, C. Liu, A. Teke, M.A. Reshchikov, S. Doğan, V. Avrutin, S.-J. Cho, and H. Morkoc: A comprehensive review of ZnO materials and devices. J. Appl. Phys. 98, 041301 (2005).
M.H. Huang, S. Mao, H. Feick, H. Yan, Y. Wu, H. Kind, E. Weber, R. Russo, and P. Yang: Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers. Science 292, 1897 (2001).
P.D. Yang, H.Q. Yan, S. Mao, R. Russo, J. Johnson, R. Saykally, N. Morris, J. Pham, R.R. He, and H.J. Choi: Controlled growth of ZnO nanowires and their optical properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 12, 323 (2002).
H.E. Unalan, Y. Zhang, P. Hiralal, S. Dalal, D. Chu, G. Eda, K.B.K. Teo, M. Chhowalla, W.I. Milne, and G.A.J. Amaratunga: Zinc oxide nanowire networks for macroelectronic devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 163501 (2009).
S. Noor Mohammad: Analysis of the vapor–liquid–solid mechanism for nanowire growth and a model for this mechanism. Nano Lett. 8, 1532 (2008).
Y. Wu and P. Yang: Direct observation of vapor−liquid−solid nanowire growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 3165 (2001).
T. Ma, M. Guo, M. Zhang, Y. Zhang, and X. Wang: Density-controlled hydrothermal growth of well-aligned ZnO nanorod. Nanotechnology 18, 035605 (2007).
S.-Y. Pung, K.-L. Choy, X. Hou, and C. Shan: Preferential growth of ZnO thin films by the atomic layer deposition. Nanotechnology 19, 435609 (2008).
X. Wang, J. Song, C.J. Summers, J.H. Ryou, P. Li, R.D. Dupuis, and Z.L. Wang: Density-controlled growth of aligned ZnO nanowires sharing a common contact: A simple, low-cost, and mask-free technique for large-scale applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 7720 (2006).
H.S. Shin, J.I. Sohn, D.C. Kim, W.T.S. Huck, M.E. Welland, H.C. Choi, and D.J. Kang: Density control of ZnO nanowires grown using Au-PMMA nanoparticles and their growth behavior. Nanotechnology 20, 085601 (2009).
E.W. Petersen, E.M. Likovich, K.J. Russell, and V. Narayanamurti: Growth of ZnO nanowires catalyzed by size-dependent melting of Au nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 20, 405603 (2009).
S.H. Dalal, D.L. Baptista, K.B.D. Teo, R.G. Lacerda, D.A. Jefferson, and W.I. Milne: Controllable growth of vertically aligned zinc oxide nanowires using vapour deposition. Nanotechnology 17, 4811 (2006).
H.K. Park, M.H. Oh, S.-W. Kim, G.-H. Kim, D.-H. Youn, S. Lee, S.-H. Kim, K.-C. Kim, and S.-L. Maeng: Vertically well-aligned ZnO nanowires on c-Al2O3 and GaN substrates by Au catalyst. ETRI J. 28, 787 (2006).
B. Nikoobakht, A. Davydov, and S.J. Stranick: Controlling the growth direction of ZnO nanowires on c-plane sapphire, in Nanoparticles and Nanowire Building Blocks-Synthesis, Processing, Characterization and Theory, edited by O.J. Glembacki and C.E. Hunt (Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 818, Warrendale, PA, 2004), M8.25, p. 225.
Y.-H. Kang, C.-G. Choi, Y.-S. Kim, and J.-K. Kim: Influence of seed layers on the vertical growth of ZnO nanowires. Mater. Lett. 63, 679 (2009).
J.H. Jung, H.S. Yoon, Y.L. Kim, M.S. Song, Y. Kim, Z.G. Chen, J. Zou, D.Y. Choi, J.H. Kang, H.J. Joyce, Q. Gao, H.H. Tan, and C. Jagadish: Vertically oriented epitaxial germanium nanowires on silicon substrates using thin germanium buffer layers. Nanotechnology 21, 295602 (2010).
P.K. Sekhar, S.N. Sambandam, D.K. Sood, and S. Bhansali: Selective growth of silica nanowires in silicon catalysed by Pt thin film. Nanotechnology 17, 4606 (2006).
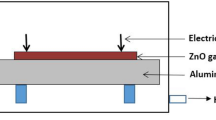
B.-I. Hwang, K. Park, H.-S. Chun, C.-H. An, H. Kim, and H.-J. Lee: The effects of the microstructure of ZnO films on the electrical performance of their thin film transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 222104 (2008).
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (2010-0558000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Lee, M.S., Park, K. et al. Effects of the microstructure of ZnO seed layer on the ZnO nanowire density. Journal of Materials Research 26, 1292–1297 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.81
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.81