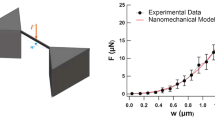
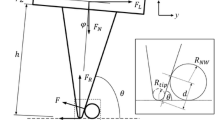
Abstract
Nanowires have attracted tremendous research interests due to their potential applications. Their mechanical properties are critical for the reliability and durability of the nanowire-based devices. Compared to many other characterization techniques, the lateral probing of a nanowire using nanoindentation has the advantage of relatively simple sample preparation. However, the data analysis is difficult due to the complex contact mechanics. In all previous studies, some questionable approximations have been made to proceed with data analysis. In this study, a quantitative physical picture of nanowire lateral probing is proposed, which we believe is the first time in the literature. Three-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA) is performed and compared to a double-contact analytical model in which the two contacts, namely contact 1 (indenter/nanowire) and contact 2 (nanowire/substrate), are considered. Both the FEA and analytical models are for a specific case: an elastic spherical indention of a GaN nanowire on a Si substrate. We find that contact 1 cannot be well approximated by a Hertzian elliptical contact as assumed in many studies. We also find a large contact deformation at contact 2, which has been ignored in almost all previous studies. Finally, the adhesion condition and nanowire-receding at contact 2 are found to have insignificant effects on the data analysis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.J. Sirbuly, A. Tao, M. Law, R. Fan, and P. Yang: Multifunctional nanowire evanescent wave optical sensors Adv. Mater. 19, 61 (2007).
Y.J. Choi, I.S. Hwang, J.G. Park, K.J. Choi, J.H. Park, and J.H. Lee: Novel fabrication of an SnO2 nanowire gas sensor with high sensitivity Nanotechnology 19, 095508 (2008).
V.V. Dobrokhotov, M.M. Yazdanpanah, S. Pabba, A. Safir, and R.W. Cohn: Visual force sensing with flexible nanowire buckling springs Nanotechnology 19, 035502 (2008).
M.W. Li, R.B. Bhiladvala, T.J. Morrow, J.A. Sioss, K.K. Lew, J.M. Redwing, C.D. Keating, and T.S. Mayer: Bottom-up assembly of large-area nanowire resonator arrays Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 88 (2008).
A.B.H. Tay and J.T.L. Thong: High-resolution nanowire atomic force microscope probe grown by a field-emission induced process Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 5207 (2004).
S.P. Bao and S.C. Tjong: Mechanical behaviors of polypropylene/carbon nanotube nanocomposites: The effects of loading rate and temperature Mater. Sci. Eng, A 485, 508 (2008).
P.M. Ajayan, L.S. Schadler, and P.V. Braun: Nanocomposite Science and Technology (Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2003).
X.D. Li, P. Nardi, C.W. Baek, J.M. Kim, and Y.K. Kim: Direct nanomechanical machining of gold nanowires using a nanoindenter and an atomic force microscope J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, 551 (2005).
G. Feng, W.D. Nix, Y. Yoon, and C.J. Lee: A study of the mechanical properties of nanowires using nanoindentation J. Appl. Phys. 99, 074304 (2006).
X.D. Li, H.S. Gao, C.J. Murphy, and K.K. Caswell: Nanoindentation of silver nanowires Nano Lett. 3, 1495 (2003).
M.F. Yu, T. Kowalewski, and R.S. Ruoff: Investigation of the radial deformability of individual carbon nanotubes under controlled indentation force Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1456 (2000).
M.-J. Minaryolandan and M.F. Yu: Reversible radial deformation up to the complete flattening of carbon nanotubes in nanoindentation J. Appl. Phys. 103, 073516 (2008).
H. Ni, X.D. Li, G.S. Cheng, and R. Klie: Elastic modulus of single-crystal GaN nanowires J. Mater. Res. 21, 2882 (2006).
T.-H. Fang and W.-J. Chang: Nanolithography and nanoindentation of tantalum-oxide nanowires and nanodots using scanning-probe microscopy Physica B 352, 190 (2004).
S.X. Mao, M. Zhao, and Z.L. Wang: Nanoscale mechanical behavior of individual semiconducting nanobelts Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 993 (2003).
E.P.S. Tan and C.T. Lim: Nanoindentation study of nanofibers Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 123106 (2005).
N. Lonnroth, C.L. Muhlstein, C. Pantano, and Y. Yue: Nanoindentation of glass wool fibers J. Non-Cryst. Solids 354, 3887 (2008).
H. Ni and X.D. Li: Young’s modulus of ZnO nanobelts measured using atomic force microscopy and nanoindentation techniques Nanotechnology 17, 3591 (2006).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic-modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
K.L. Johnson: Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, New York, 1987).
Contact Technology Guide, Vol. 12.1 (ANSYS, Inc, Canonsburg, PA, 2009).
J. Castillo and J.R. Barber: Lateral contact of slender prismatic bodies Proc. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 453, 2397 (1997).
Z.H. Xu and X.D. Li: Sample size effect on nanoindentation of micro-/nanostructures Acta Mater. 54, 1699 (2006).
G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, and F.R. Brotzen: On the generality of the relationship among contact stiffness, contact area, and elastic-modulus during indentation J. Mater. Res. 7, 613 (1992).
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the financial support from a Keystone Innovation Starter Kit (KISK) grant from the Pennsylvania Department of Community and Economic Development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Askari, D., Feng, G. Finite element analysis of nanowire indentation on a flat substrate. Journal of Materials Research 27, 586–591 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.420
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.420