Abstract
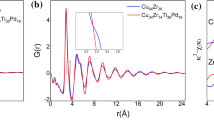
The microstructures of Zr70Cu30 and Zr70Ni30 metallic glasses (MGs) were investigated via the synchrotron radiation techniques combined with the reverse Monte-Carlo simulations. Although Cu and Ni are neighbor elements in the periodic table and their atomic radii are almost the same in length, it is found that atomic- and cluster-scale structural differences occur between these two Zr-based MGs. In particular, the relatively regular clusters caused by the narrow distributions of atomic separations and bond angles are detected in Zr70Cu30. This is the structural origin of the different glass-forming abilities in ZrCu and ZrNi alloys. This work has implications for understanding of the glass-forming mechanism in this class of glassy materials.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Finney: Modelling the structures of amorphous metals and alloys. Nature 266, 309 (1977).
J.P.K Doye and D.J. Wales: The structure and stability of atomic liquids: From clusters to bulk. Science 271, 484 (1996).
A. Inoue: Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 48, 279 (2000).
D.B. Miracle: A structural model for metallic glasses. Nat. Mater. 3, 697 (2004).
H.W. Sheng, W.K. Luo, F.M. Alamgir, J.M. Bai, and E. Ma: Atomic packing and short-to-medium-range order in metallic glasses. Nature 439, 419 (2006).
A.R. Yavari: Materials science–A new order for metallic glasses. Nature 439, 405 (2006).
Y. Li, Q. Guo, J.A. Kalb, and C.V. Thompson: Matching glass-forming ability with the density of the amorphous phase. Science 322, 1816 (2008).
K. Georgarakis, A.R. Yavari, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, J. Antonowicz, M. Stoica, Y. Li, M. Satta, A. LeMoulec, G. Vaughan, and A. Inoue: Atomic structure of Zr-Cu glassy alloys and detection of deviations from ideal solution behavior with Al addition by x-ray diffraction using synchrotron light in transmission. Appl. Phys. Lett. 94, 3 (2009).
H.L. Peng, M.Z. Li, W.H. Wang, C.Z. Wang, and K.M. Ho: Effect of local structures and atomic packing on glass forming ability in CuxZr100-x metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 3 (2010).
X.J. Liu, G.L. Chen, X. Hui, T. Liu, and Z.P. Lu: Ordered clusters and free volume in a Zr-Ni metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 3 (2008).
L. Huang, C.Z. Wang, S.G. Hao, M.J. Kramer, and K.M. Ho: Short- and medium-range order in amorphous Zr2Ni metallic alloy. Phys. Rev. B 81, 6 (2010).
K.H.J Buschow and N.M. Beekmans: Thermal stability and electronic properties of amorphous Zr-Co and Zr-Ni alloys. Phys. Rev. B 19, 3843 (1979).
D.B. Miracle, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, L.V. Louzguina-Luzgina, and A. Inoue: An assessment of binary metallic glasses: Correlations between structure, glass forming ability and stability. Int. Mater. Rev. 55, 218 (2010).
L. Yang, S. Yin, X.D. Wang, Q.P. Cao, J.Z. Jiang, K. Saksl, and H. Franz: Atomic structure in Zr70Ni30 metallic glass. J. Appl. Phys. 102, 5 (2007).
K. Georgarakis, A.R. Yavari, M. Aljerf, D.V. Louzguine-Luzgin, M. Stoica, G. Vaughan, and A. Inoue: On the atomic structure of Zr-Ni and Zr-Ni-Al metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 7 (2010).
J. Saida, M. Kasai, E. Matsubara, and A. Inoue: Stability of glassy state in Zr-based glassy alloys correlated with nano icosahedral phase formation. Ann. Chim. Sci. Mat. 27, 77 (2002).
A. Inoue, T. Zhang, and T. Masumoto: Glass-forming ability of alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 156, 473 (1993).
D.H. Xu, B. Lohwongwatana, G. Duan, W.L. Johnson, and C. Garland: Bulk metallic glass formation in binary Cu-rich alloy series–Cu100-xZrx (x=34, 36 38.2, 40 at.%) and mechanical properties of bulk Cu64Zr36 glass. Acta Mater. 52, 2621 (2004).
D. Wang, Y. Li, B.B. Sun, M.L. Sui, K. Lu, and E. Ma: Bulk metallic glass formation in the binary Cu-Zr system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 4029 (2004).
L. Yang, G.Q. Guo, L.Y. Chen, S.H. Wei, J.Z. Jiang, and X.D. Wang: Atomic structure in Al-doped multicomponent bulk metallic glass. Scr. Mater. 63, 879 (2010).
L. Yang, J.H. Xia, Q. Wang, C. Dong, L.Y. Chen, X. Ou, J.F. Liu, J.Z. Jiang, K. Klementiev, K. Saksl, H. Franz, J.R. Schneider, and L. Gerward: Design of Cu8Zr5-based bulk metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 3 (2006).
L. Yang, G.Q. Guo, G.Q. Zhang, and L.Y. Chen: Structural origin of the high glass-forming ability in Y-doped bulk metallic glasses. J. Mater. Res. 25, 1701 (2010).
Y.Q. Cheng and E. Ma: Atomic-level structure and structure-property relationship in metallic glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 56, 379 (2011).
D. Ma, A.D. Stoica, X.L. Wang, Z.P. Lu, M. Xu, and M. Kramer: Efficient local atomic packing in metallic glasses and its correlation with glass-forming ability. Phys. Rev. B 80, 014202 (2009).
L. Yang and G.Q. Guo: Preferred clusters in metallic glasses. Chin. Phys. B 19, 126101 (2010).
X.K. Xi, L.L. Li, B. Zhang, W.H. Wang, and Y. Wu: Correlation of atomic cluster symmetry and glass-forming ability of metallic glass. Phys. Rev. Lett. 99, 4 (2007).
X.K. Xi, M.T. Sandor, Y.H. Liu, W.H. Wang, and Y. Wu: Structural changes induced by microalloying in Cu46Zr47-xAl7Gdx metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 61, 967 (2009).
Z.D. Sha, Y.P. Feng, and Y. Li: Statistical composition-structure-property correlation and glass-forming ability based on the full icosahedra in Cu-Zr metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 96, 3 (2010).
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to thank HASYLAB in Germany and SSRF in China for the use of the advanced synchrotron radiation facilities. Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 10805027), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK2008397), and the NUAA Research Funding (Grant No. NS2010168) are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, GQ., Yang, L., Huang, CL. et al. Structural origin of the different glass-forming abilities in ZrCu and ZrNi metallic glasses. Journal of Materials Research 26, 2098–2102 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.216
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.216