Abstract
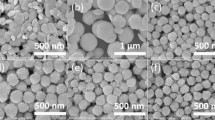
Hollow nanoparticles of hexagonal close-packed (hcp)-NaYF4:Yb,Er were synthesized by thermal decomposition of trifmoroacetate precursors at 340 °C via vacancy diffusion, likely due to the Kirkendall effect and Ostwald ripening mechanism. The average outer diameter, inner diameter, and shell thickness of these hollow particles were 14 ± 3 nm, 7 ± 2 nm, and 4 ± 1 nm, respectively. The surface effects on the fluorescence properties of these hollow particles were studied by comparing with that of solid NaYF4: Yb,Er (average size ~ 15 ± 3 nm) and solid NaYF4 core/NaYF4: Yb,Er shell (NaYF4 core ~10 ± 1 nm and NaYF4:Yb,Er shell ~3 ± 2 nm) nanoparticles containing similar composition of Yb and Er ions. The green, red, and total emission intensities decreased with increasing upconversion active volume-normalized surface area. Surface coatings of undoped NaYF4 on both inner and outer surfaces of the hollow nanoparticles enhanced the total emission intensity by ~ 19 and ~5 times compared with those of the hollow and solid NaYF4:Yb,Er nanoparticles, respectively.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Burda, X. Chen, R. Narayanan, and M.A. El-Sayed: Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem. Rev. 105, 1025 (2005).
N. Menyuk, K. Dwight, and J.W. Pierce: NaYF4:Yb, Er-An efficient upconversion phosphor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 21, 159 (1972).
Y. Wang, L. Tu, J. Zhao, Y. Sun, X. Kong, and H. Zhang: Upconversion luminescence of P-NaYF4:Yb +, Er +@ß-NaYF4 core/shell nanoparticles: Excitation power density and surface dependence. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 7164 (2009).
D. Yuan, G.S. Yi, and G.M. Chow: Effects of size and surface on luminescence properties of submicron upconversion NaYF4:Yb, Er particles. J. Mater. Res. 24, 2042 (2009).
L.P. Qian, D. Yuan, G.S. Yi, and G.M. Chow: Critical shell thickness and emission enhancement of NaYF4:Yb, Er/NaYF4/ silica core/shell/shell nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. 24, 3559 (2009).
S. Heer, K. Kompe, H.U. Giidel, and M. Haase: Highly efficient multicolour upconversion emission in transparent colloids of lanthanide-doped NaYF4 nanocrystals. Adv. Mater. 16, 2102 (2004).
J.W. Stouwdam, G.A. Hebbink, J. Huskens, and F.C.J.M. van Veggel: Lanthanide-doped nanoparticles with excellent luminescent properties in organic media. Chem. Mater. 15, 4604 (2003).
J. Shan, M. Uddi, R. Wei, N. Yao, and Y. Ju: The hidden effects of particle shape and criteria for evaluating the upconversion luminescence of the lanthanide doped nanophosphors. J. Phys. Chem. C 114, 2452 (2010).
S.F. Lim, W.S. Ryu, and R.H. Austin: Particle size dependence of the dynamic photophysical properties of NaYF4:Yb, Er nanocrystals. Opt. Express 18, 2309 (2010).
G.S. Yi and G.M. Chow: Water-soluble NaYF4:Yb, Er(Tm)/ NaYF4/polymer core/shell/shell nanoparticles with significant enhancement of upconversion fluorescence. Chem. Mater. 19, 341 (2007).
H.X. Mai, Y.W. Zhang, L.D. Sun, and C.H. Yan: Highly efficient multicolor up-conversion emissions and their mechanisms of monodisperse NaYF4:Yb, Er core and core/shell-structured nanocrystals. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 13721 (2007).
L. Li, Y. Chu, Y. Liu, and L. Dong: Template-free synthesis and photocatalytic properties of novel Fe2O3 hollow spheres. J. Phys. Chem. C 111, 2123 (2007).
E. Ghadiri, N. Taghavinia, S.M. Zakeeruddin, M. Gratzel, and J.E. Moser: Enhanced electron collection efficiency in dye-sensitized solar cells based on nanostructured TiO2 hollow fibers. Nano Lett. 10, 1632 (2010).
Z.Z. Li, L.X. Wen, L. Shao, and J.F. Chen: Fabrication of porous hollow silica nanoparticles and their applications in drug release control. J. Controlled Release 98, 245 (2004).
S. Liu, R. Xing, F. Lu, R.K. Rana, and J.J. Zhu: One-pot template-free fabrication of hollow magnetite nanospheres and their application as potential drug carriers. J. Phys. Chem. C 113, 21042 (2009).
J. Ding and G. Liu: Water-soluble hollow nanospheres as potential drug carriers. J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 6107 (1998).
K.N. Tu and U. Gosele: Hollow nanostructures based on the Kirkendall effect: Design and stability considerations. Appl. Phys. Left 86, 093111 (2005).
N. Ren, B. Wang, Y.H. Yang, Y.H. Zhang, W.L. Yang, Y.H. Yue, Z. Gao, and Y. Tang: General method for the fabrication of hollow microcapsules with adjustable shell compositions. Chem. Mater. 17, 2582 (2005).
Y. Wang, A.S. Angelatos, and F. Caruso: Template synthesis of nanostructured materials via layer-by-layer assembly. Chem. Mater. 20, 848 (2008).
D.H.M. Buchold and C. Feldmann: Nanoscale y-AlO(OH) hollow spheres: Synthesis and container-type functionality. Nano Lett. 7, 3489 (2007).
Y.S. Lin, S.H. Wu, C.T. Tseng, Y. Hung, C. Chang, and C.Y. Mou: Synthesis of hollow silica nanospheres with a microemulsion as the template. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 3542 (2009).
F. Zhang, Y. Shi, X. Sun, D. Zhao, and G.D. Stucky: Formation of hollow upconversion rare-earth fluoride nanospheres: Nanoscale Kirkendall effect during ion exchange. Chem. Mater. 21, 5237 (2009).
J. Shan, N. Yao, and Y. Ju: Phase transition induced formation of hollow structures in colloidal lanthanide-doped NaYF4 nanocrystals. J. Nanopart. Res. 12, 1429 (2010).
Y. Yin, R.M. Rioux, C.K. Erdonmez, S. Hughes, G.A. Somorjai, and A.P. Alivisatos: Formation of hollow nanocrystals through the nanoscale Kirkendall effect. Science 304, 711 (2004).
Y. Yin, C.K. Erdonmez, A. Cabot, S. Hughes, and A.P. Alivisatos: Colloidal synthesis of hollow cobalt sulfide nanocrystals. Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 1389 (2006).
H.J. Fan, U. Gosele, and M. Zacharias: Formation of nanotubes and hollow nanoparticles based on Kirkendall and diffusion processes: A review. Small 3, 1660 (2007).
A. Cabot, M. Ibaiiez, P. Guardia, and A.P. Alivisatos: Reaction regimes on the synthesis of hollow particles by the Kirkendall effect. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 11326 (2009).
Y. Wang, L. Cai, and Y. Xia: Monodisperse spherical colloids of Pb and their use as chemical templates to produce hollow particles. Adv. Mater. 17, 473 (2005).
E.O. Kirkendall: Diffusion of zinc in alpha brass. Trans. AIME 147, 104 (1942).
A.D. Smigelskas and E.O. Kirkendall: Zinc diffusion in alpha brass. Trans. AIME 171, 130 (1947).
H.G. Yang and H.C. Zeng: Preparation of hollow anatase TiO2 nanospheres via Ostwald ripening. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 3492 (2004).
J. Li and H.C. Zeng: Hollowing Sn-doped TiO2 nanospheres via Ostwald ripening. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 15839 (2007).
G. Lin, J. Zheng, and R. Xu: Template-free synthesis of uniform CdS hollow nanospheres and their photocatalytic activities. J. Phys. Chem. C 112, 7363 (2008).
G.S. Yi and G.M. Chow: Synthesis of hexagonal-phase NaYF4:Yb, Er and NaYF4:Yb, Tm nanocrystals with efficient up-conversion fluorescence. Adv. Funct. Mater. 16, 2324 (2006).
H.X. Mai, Y.W. Zhang, R. Si, Z.G. Yan, L.D. Sun, L.P. You, and C.H. Yan: High-quality sodium rare-Earth fluoride nanocrystals: Controlled synthesis and optical properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 6426 (2006).
L. Wang and Y. Li: Controlled synthesis and luminescence of lanthanide doped NaYF4 nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 19, 727 (2007).
C. Liu, H. Wang, X. Li, and D. Chen: Monodisperse, size-tunable and highly efficient P-NaYF4:Yb, Er(Tm) up-conversion luminescent nanospheres: Controllable synthesis and their surface modifications. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 3546 (2009).
W. Feng, L.D. Sun, Y.W. Zhang, and C.H. Yan: Solid-to-hollow single-particle manipulation of a self-assembled luminescent NaYF4:Yb, Er nanocrystal monolayer by electron-beam lithography. Small 5, 2057 (2009).
Y.W. Zhang, X. Sun, R. Si, L.P. You, and C.H. Yan: Single-crystalline and monodisperse LaF3 triangular nanoplates from a single-source precursor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 3260 (2005).
J.E. Roberts: Lanthanum and neodymium salts of trifluoroacetic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 83, 1087 (1961).
Y. Yoshimura and K. Ohara: Thermochemical studies on the lanthanoid complexes of trifluoroacetic acid. J. Alloys Compd. 408–412, 573 (2006).
Acknowledgments
Karvianto acknowledges the support of the NUS research scholarship. We thank D. Yuan, L.P. Qian, and Dr. Daniel Chua for helpful technical discussions. G.M. Chow thanks the support of this work by FoE (FB) NUS research fund and the grant from the Office of Naval Research, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karvianto, Chow, G.M. The effects of surface and surface coatings on fluorescence properties of hollow NaYF4:Yb,Er upconversion nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Research 26, 70–81 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2010.30
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2010.30