Abstract
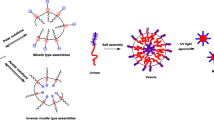
In the literature, a few biological cells have been used as templates to form microcapsules of a variety of shapes and sizes. In this study, we proved the concept that living cells like platelets can be encapsulated with polyelectrolytes using electrostatic layer-by-layer self-assembly (LBL), and, most importantly, the encapsulation process did not induce activation of the platelets. Glycol-chitosan and poly-L-glutamic acid were electrostatically deposited onto platelets, and the encapsulation was confirmed using confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Transmission electron microscopy observation further confirmed that the encapsulation process was mild and the activation of platelets was negligible. The encapsulation of living biological cells like platelets can serve as a model system in a wide range of biomedical applications including local and sustained drug delivery, immune protection of artificial tissues, and versatile artificial blood.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.P. Lanza and W.L. Chick: Transplantation of encapsulated cells and tissues. Surgery 121(1), 1 (1997).
G. Decher: Fuzzy nanoassemblies: Toward layered polymeric multicomposites. Science 277(5330), 1232 (1997).
B. Li, B. Jiang, B. Boyce, and B. Lindsey: Multilayer polypeptide nanoscale coatings for the prevention of biomedical device associated infections. Biomaterials 30, 2552 (2009).
B. Li, B. Jiang, M.J. Dietz, E.S. Smith, N.B. Clovis, and K.M.K. Rao: Evaluation of local MCP-1 and IL-12 nanocoatings for infection prevention in open fractures. J. Orthop. Res. 28, 48 (2010).
H. Li, H. Ogle, B. Jiang, M. Hagar, and B. Li: Cefazolin embedded biodegradable polypeptide nanofilms promising for infection prevention: A preliminary study on cell responses. J. Orthop. Res. 28, 992 (2010).
B. Jiang and B. Li: Tunable drug incorporation and release from polypeptide multilayer nanofilms. Int. J. Nanomed. 4, 37 (2009).
B. Jiang and B. Li: Polypeptide nanotechnology coatings for preventing dental and orthopaedic device-associated infection. J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part B 88(2), 332 (2009).
C. Cortez, E. Tomaskovic-Crook, A.P.R. Johnston, B. Radt, S.H. Cody, A.M. Scott, E.C. Nice, J.K. Heath, and F. Caruso: Targeting and uptake of multilayered particles to colorectal cancer cells. Adv. Mater. 18, 1998 (2006).
R. Heuberger, G.B. Sukhorukov, J. Vörös, M. Textor, and H. Möhwald: Biofunctional polyeletrolyte multilayers and microcapsules: Control of non-specific and bio-specific protein adsorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 15, 357 (2005).
A. Diaspro, D. Silvano, S. Krol, O. Cavalleri, and A. Gliozzi: Single living cell encapsulation in nano-organized polyelectrolyte shells. Langmuir 18, 5047 (2002).
S. Krol, S. Guerra, M. Grupillo, A. Diaspro, A. Gliozzi, and P. Marchetti: Multilayer nanoencapsulation. New approach for immune protection of human pancreatic islets. Nano Lett. 6, 1933 (2006).
B. Neu, A. Voigt, R. Mitlöhner, S. Leporatti, C.Y. Gao, E. Donath, H. Kiesewetter, H. Möhwald, H.J. Meiselman, and H. Bäumler: Biological cells as templates for hollow microcapsules. J. Microencapsulation 18(3), 385 (2001).
H. Ai, M. Fang, S.A. Jones, and Y.M. Lvov: Electrostatic layer-by-layer nanoassembly on biological microtemplates: Platelets. Biomacromolecule 3, 560 (2002).
E. Donath, S. Moya, B. Neu, G.B. Sukhorukov, R. Georgieva, A. Voigt, H. Bäumler, H. Kiesewetter, and H. Möhwald: Hollow polymer shells from biological templates: Fabrication and potential applications. Chemistry 8(23), 5481 (2002).
H. Onishi and Y. Machida: Biodegradation and distribution of water-soluble chitosan in mice. Biomaterials 20, 175 (1999).
H.S. Li and B. Li: Platelet-rich plasma: Its biological properties and applications, in Biocompatibility of materials, devices and drug release systems, edited by Frank Columbus (Nova Science Publishers, Inc: New York, NY, In press, 2010)
H. Uludag, P. De Vos, and P.A. Tresco: Technology of mammalian cell encapsulation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 42, 29 (2000).
Cell Encapsulation Technology and Therapeutics, edited by W.M. Kühtreiber, R.P. Lanza, and W.L. Chick (Boston, MA: Birkhäuser, 1999).
T. Visted, R. Bjerkvig, and P.O. Enger: Cell encapsulation technology as a therapeutic strategy for CNS malignancies. Neuro-oncol. 3, 201 (2001).
Y. Zhong, B. Li, and D.T. Haynie: Fine tuning of physical properties of designed polypeptide multilayer films by control of pH. Biotechnol. Progr. 22(1), 126 (2006).
S. Mehta and J.T. Watson: Platelet rich concentrate: Basic science and current clinical applications. J. Orthop. Trauma 22(6), 432 (2008).
J.G. White: Platelet ultrastructure, in Hemostasis and Thrombosis, 3rd ed., edited by A.L. Bloom, C.D. Forbes, D.P. Thomas, and E.G.D. Tuddenham (Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1994).
L.V. Parise, S.S. Smyth, A.S. Shet, and B.S. Coller: Platelet morphology, biochemistry, and function, in Williams Hematology, 7th ed., edited by M.A. Lichtman, E. Beutler, T.J. Kipps, U. Seligsohn, K. Kaushansky, and J.T. Prchal (McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.: Columbus, OH, 2006).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Financial support from the NSF (OISE-0737735), NSF EPSCoR RII, AO Foundation, Osteosynthesis and Trauma Care Foundation, and WV NASA EPSCoR is acknowledged. Project S-07-43L was supported by the AO Research Fund of the AO Foundation. Any opinions, findings, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the funding agencies. Microscope experiments and image analysis were performed in part in the West Virginia University Imaging Facility, which is supported in part by the Mary Babb Randolph Cancer Center and NIH grant P20 RR016440. The authors also appreciate the use of the electron microscope at the Microscopic Imaging Facilities at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), Morgantown, WV. The authors thank Diane Schwegler-Berry at NIOSH and Karen Martin at WVU for imaging, Bingbing Jiang for the critical point drying treatment of platelets, and Suzanne Smith for proofreading.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Q., Li, H. & Li, B. Nanoencapsulating living biological cells using electrostatic layer-by-layer self-assembly: Platelets as a model. Journal of Materials Research 26, 347–351 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2010.23
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2010.23