Abstract
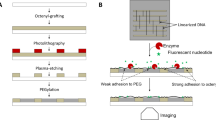
One of the challenges in the development of molecular scale devices is the integration of nano-objects or molecules onto desired locations on a surface. This integration comprises their accurate positioning, their alignment, and the preservation of their functionality. Here, we proved how capillary assembly in combination with soft lithography can be used to perform DNA molecular combing to generate chips of isolated DNA strands for genetic analysis and diagnosis. The assembly of DNA molecules is achieved on a topologically micropatterned polydimethylsiloxane stamp inducing almost simultaneously the trapping and stretching of single molecules. The DNA molecules are then transferred onto aminopropyltriethoxysilane-coated surfaces. In fact, this technique offers the possibility to tightly control the experimental parameters to direct the assembly process. This technique does not induce a selection in size of the objects, therefore it can handle complex solutions of long (tens of kbp) but also shorter (a few thousands of bp) molecules directly in solution to allow the construction of future one-dimensional nanoscale building templates.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.J. Kricka: Microchips, microarrays, biochips and nanochips: Personal laboratories for the 21st century. Clin. Chim. Acta 307, 219 (2001).
N.C. Seeman: DNA in a material world. Nature 421, 427 (2003).
C.M. Niemeyer: Progress in “engineering up” nanotechnology devices utilizing DNA as a construction material. Appl. Phys., A: Mater. Sci. Process. 68, 119 (1999).
K. Lund, A.J. Manzo, N. Dabby, N. Michelotti, A. Johnson-Buck, J. Nangreave, S. Taylor, R. Pei, M.N. Stojanovic, N.G. Walter, E. Winfree, and H. Yan: Molecular robots guided by prescriptive landscapes. Nature 465, 206 (2010).
D. Gerhold, T. Rushmore, and C.T. Caskey: DNA chips: Promising toys have become powerful tools. Trends Biochem. Sci. 24, 168 (1999).
M. Cuzin: DNA chips: A new tool for genetic analysis and diagnostics. Transfus. Clin. Biol. 8, 291 (2001).
E. Braun, Y. Eichen, U. Sivan, and G. Ben-Yoseph: DNA templated self-assembly of a conductive wire connecting two electrodes. Nature 391, 775 (1998).
K. Keren, M. Krueger, R. Gilad, G. Ben-Yoseph, U. Sivan, and E. Braun: Sequence-specific molecular lithography on single DNA molecules. Science 297, 72 (2002).
Z.X. Deng and C.D. Mao: DNA-templated fabrication of 1D parallel and 2D crossed metallic nanowire arrays. Nano Lett. 3, 1545 (2003).
C.F. Monson and A.T. Woolley: DNA-templated construction of copper nanowires. Nano Lett. 3, 359 (2003).
K. Nguyen, M. Monteverde, A. Filoramo, L. Goux-Capes, S. Lyonnais, P. Jegou, P. Viel, M. Goffman, and J-P. Bourgoin: Synthesis of thin and highly conductive DNA-based palladium nanowires. Adv. Mater. 20, 1099 (2008).
J.M. Köhler, A. Csáki, J. Reichert, R. Möller, W. Straube, and W. Fritzsche: Selective labeling of oligonucleotide monolayers by metallic nanobeads for fast optical readout of DNA-chips. Sens. Actuators B 76, 166 (2001).
D. Bensimon, A. Bensimon, and F. Heslot: Process for aligning, adhering and stretching nucleic acid strands on a support surface by passage through a meniscus. U.S. Patent No. 5 840 862 (1998).
D. Bensimon, A.J. Simon, V. Croquette, and A. Bensimon: Stretching DNA with a receding meniscus: Experiments and models. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 4754 (1995).
A. Bensimon, A. Simon, A. Chiffaudel, V. Croquette, F. Heslot, and D. Bensimon: Alignment and sensitive detection of DNA by a moving interface. Science 265, 2096 (1994).
Y.L. Lyubchenko, A.A. Gall, L.S. Shlyakhtenko, R.E. Harrington, B.L. Jacobs, S.M. Oden, and P.I. Lindsay: Atomic force microscopy imaging of double stranded DNA and RNA. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 10(3), 589 (1992).
J. Vesenka, M. Guthold, C.L. Tang, D. Keller, E. Delaine, and C. Bustamante: Substrate preparation for reliable imaging of DNA molecules with scanning force microscope. Ultramicroscopy 42 (2), 1243 (1992).
C. Bustamante, J. Vesenka, C.L. Tang, W. Rees, M. Gothold, and R. Keller: Circular DNA molecules imaged in air by scanning force microscopy. Biochemistry 31(1), 22 (1992).
T. Thundat, D.P. Allison, R.J. Warmack, G.M. Brown, K.B. Jacobson, J.J. Schrick, and T.L. Ferrell: Atomic force microscopy of DNA on mica and chemically modified mica. Scanning Microsc. 6(4), 911 (1992).
N. Kaji, Y. Tezuka, Y. Takamura, M. Ueda, T. Nishimoto, H. Nakanishi, Y. Horiike, and Y. Baba: Separation of long DNA molecules by quartz nanopillar chips under a direct current electric field. Anal. Chem. 76(1), 15 (2004).
G. Maubach, A. Csaki, R. Seidel, M. Mertig, W. Pompe, D. Born, and W. Fritzsche: Controlled positioning of one individual DNA molecule in an electrode setup based on self-assembly and microstructuring. Nanotechnology 14, 546 (2003).
M. Washizu and O. Kurosawa: Electrostatic manipulation of DNA in microfabricated structures. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 26(6), 1165 (1990).
A. Wolff, C. Leiterer, A. Csaki, and W. Fritzsche: Dielectrophoretic manipulation of DNA in microelectrode gaps for single-molecule constructs. Front. Biosci. 13, 6834 (2008).
C.A.P. Petit and J.D. Carbeck: Combing of molecules in microchannels (COMMIC): A method for micropatterning and orienting molecules of DNA on a surface. Nano Lett. 3, 1141 (2003).
J. Opitz, F. Braun, R. Seidel, W. Pompe, B. Voit, and M. Mertig: Site-specific binding and stretching of DNA molecules at UV-light patterned aminoterpolymer films. Nanotechnology 15, 717 (2004).
M. Gad, S. Sugiyama, and T. Ohtani: Method for patterning stretched DNA molecules on mica surfaces by soft lithography. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2, 387 (2003).
P. Björk, S. Holmström, and O. Inganäs: Soft lithographic printing of patterns of stretched DNA and DNA/electronic polymer wires by surface-energy modification and transfer. Small 8, 1068 (2006).
H. Nakao, H. Shiigi, Y. Yamamoto, S. Tokonami, T. Nagaoka, S. Sugiyama, and T. Ohtani: Highly ordered assemblies of Au nanoparticles organized on DNA. Nano Lett. 3, 1391 (2003).
H. Nakao, M. Gad, S. Sugiyama, K. Otobe, and T. Ohtani: Transfer-printing of highly aligned DNA nanowires. JACS 125, 7162 (2003).
J. Guan and L.J. Lee: Generating highly ordered DNA nanostrand arrays. PNAS. 102, 18321 (2005).
L. Malaquin, T. Kraus, H. Schmid, E. Delamarche, and H. Wolf: Controlled particle placement through convective and capillary assembly. Langmuir 23, 11513 (2007).
Y. Xia and G.M. Whitesides: Soft lithography. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 37, 550 (1998).
T. Kraus, L. Malaquin, H. Schmid, W. Riess, N.D. Spencer, and H. Wolf: Nanoparticle printing with single particle resolution. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 570 (2007).
D.E. Smith, T.T. Perkins, and S. Chu: Dynamical scaling of DNA diffusion coefficients. Macromolecules 29, 1372 (1996).
T. Perkins, D. Smith, R. Larson, and S. Chu: Stretching of a single tethered polymer in a uniform flow. Science 268, 83 (1995).
J.O. Tegenfeldt, C. Prinz, H. Cao, S. Chou, W.W. Reisner, R. Riehn, Y.M. Wang, E.C. Cox, J.C. Sturm, P. Silberzan, and R.H. Austin: The dynamics of genomic-length DNA molecules in 100 nm channels. PNAS. 101, 10979 (2004).
E.V. Armbrust, J.A. Berges, C. Bowler, B.R. Green, D. Martinez, N.H. Putnam, S. Zhou, A.E. Allen, K.E. Apt, M. Bechner, M.A. Brzezinski, B.K. Chaal, A. Chiovitti, A.K. Davis, M.S. Demarest, J.C. Detter, T. Glavina, G. Goodstein, M.Z. Hadi, U. Hellsten, M. Hildebrand, B.D. Jenkins, J. Jurka, V.V. Kapitonov, N. Kroger, W.W.Y. Lau, T.W. Lane, F.W. Larimer, J.C. Lippmeier, S. Lucas, M. Medina, A. Montsant, M. Obornik, M.S. Parker, B. Palenik, G.J. Pazour, P.M. Richardson, T.A. Rynearson, M.A. Saito, D.C. Schwartz, K. Thamatrakoln, K. Valentin, A. Vardi, F.P. Wilkerson, and D.S. Rokhsar: The genome of the diatom Thalassiosira Pseudonana: Ecology, evolution, and metabolism. Science 306, 79 (2004).
E.T. Dimalanta, A. Lim, R. Runnheim, C. Lamers, C. Churas, D.K. Forrest, J.J. de Pablo, M.D. Graham, S.N. Coppersmith, S. Goldstein, and D.C. Schwartz: A microfluidic system for large DNA molecule arrays. Anal. Chem. 76, 5293 (2004).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the EC-funded project NaPa (Contract No. NMP4-CT-2003-500120). We thank the “Région Midi-Pyrénées” council, and the “Institut des Technologies Avancées en sciences du Vivant (ITAV)” for their financial support. We also thank Jean-Marie François and his research group, especially Marie-Ange Teste from the “Engineering of Biological Systems and Process Laboratory”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cerf, A., Dollat, X., Chalmeau, J. et al. A versatile method for generating single DNA molecule patterns: Through the combination of directed capillary assembly and (micro/nano) contact printing. Journal of Materials Research 26, 336–346 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2010.12
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2010.12