Abstract
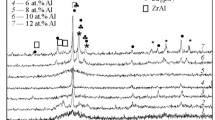
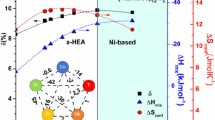
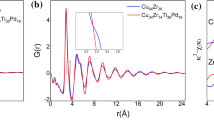
Alloying effects of iridium on the glass formability (GFA) of the Zr-Ir-Cu-Al system have been investigated, and several new bulk metallic glasses (BMGs) with high GFA have been successfully developed. Additions of Ir in the Zr-Cu-Al system can yield a beneficial distribution in atomic sizes, but the strong chemical interaction of the Zr-Ir atomic pair limits the maximum addable Ir contents and the resultant GFA. Our analyses indicate that the optimum composition for alloying elements is determined by not only topological but also chemical factors. Phase competition upon solidification, rather than effects from individual affecting factors, dictates the GFA of BMG systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Inoue: Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 48, 279 (2000).
W.L. Johnson: Bulk glass-forming metallic alloys: Science and technology. MRS Bull. 24, 42 (1999).
H. Ma, L.L. Shi, J. Xu, Y. Li, and E. Ma: Discovering inch-diameter metallic glasses in three-dimensional composition space. Appl. Phys. Lett. 87, 181915 (2005).
Z.P. Lu and C.T. Liu: A new glass-forming ability criterion for bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 50, 3501 (2002).
Y.M. Wang, X.F. Zhang, J.B. Qiang, Q. Wang, D.H. Wang, D. Li, C.H. Shek, and C. Dong: Composition optimization of the Al–Co–Zr bulk metallic glasses. Scr. Mater. 50, 829 (2004).
N. Nishiyama and A. Inoue: Glass-forming ability of Pd42.5Cu30Ni7.5P20alloy with a low critical cooling rate of 0.067 K/s. Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 568 (2002).
H. Choi-Yim, D.H. Xu, and W.L. Johnson: Ni-based bulk metallic glass formation in the Ni–Nb–Sn and Ni–Nb–Sn-X (X = B, Fe, Cu) alloy systems. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 1030 (2003).
H.W. Kui, A.L. Greer, and D. Turnbull: Formation of bulk metallic glass by fluxing. Appl. Phys. Lett. 45, 615 (1984).
W.H. Wang, J.J. Lewandowski, and A.L. Greer: Understanding the glass-forming ability of Cu50Zr50alloys in terms of a meta-stable eutectic. J. Mater. Res. 20, 2307 (2005).
Z.P. Lu, C.T. Liu, and W.D. Porter: Role of yttrium in glass formation of Fe-based bulk metallic glasses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2581 (2003).
Z.P. Lu, C.T. Liu, J.R. Thomson, and W.D. Porter: Structural amorphous steels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 92, 245503 (2004).
D. Ma, H. Tan, D. Wang, Y. Li, and E. Ma: Strategy for pinpointing the best glass-forming alloys. Appl. Phys. Lett. 86, 191906 (2005).
Z.P. Lu, J. Shen, D.W. Xing, J.F. Sun, and C.T. Liu: Binary eutectic clusters and glass formation in ideal glass-forming liquids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 071910 (2006).
Z.P. Lu and C.T. Liu: A scheme to design multi-component bulk metallic glasses in ideal glass-forming liquids. Mater. Trans. 48, 2476 (2007).
W.H. Wang, C. Dong, and C.H. Shek: Bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44, 45 (2004).
Z.P. Lu and C.T. Liu: Role of minor alloying additions in formation of bulk metallic glasses: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 3965 (2004).
F.Q. Guo, S.J. Poon, and G.J. Shiflet: Enhanced bulk metallic glass formability by combining chemical compatibility and atomic size effects. J. Appl. Phys. 97, 013512 (2004).
O.N. Senkov and D.B. Miracle: Effect of the atomic size distribution on glass forming ability of amorphous metallic alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 2183 (2001).
A. Takeuchi and A. Inoue: Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying element, Mater. Trans. 46, 2817 (2005).
Y. Liu, C.T. Liu, E.P. George, and X.Z. Wang: Thermal diffusion and compositional inhomogeneity in cast Zr50Cu50bulk metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 051919 (2006).
T.B. Massalski, J.L. Murray, L.H. Bennett, H. Baker, and L. Kacprzak: Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, OH, 1986), p. 187.
T. Egami and Y. Waseda: Atomic size effect on the formability of metallic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 64, 113 (1984).
Z.P. Lu, D. Ma, C.T. Liu, and Y.A. Chang: Competitive formation of glasses and glass-matrix composites. Intermetallics 15, 253 (2007).
Z.P. Lu, C.T. Liu, Y. Wu, H. Tan, Y. Li, and G.L. Chen: Composition effects on glass-forming ability and its indicator γ. Intermetallics 16, 410 (2008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Z.Y., Wu, Y., Li, H.X. et al. Alloying effects of iridium on glass formation and glass-forming ability of the Zr-Cu-Al system. Journal of Materials Research 24, 1619–1623 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0188
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0188