Abstract
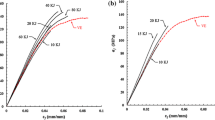
A novel dispersant “mono-2-(methacryloyloxy)ethyl succinate” was formulated for dispersing 30-nm SiC nanoparticles in vinyl ester resin. The eight carbon rule was used as the guideline to achieve a particle–particle separation of 20 to 60 nm for colloid stability. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was performed to characterize the SiC particle surfaces. Only a negligible amount of oxidized layer was observed; which illustrates that the SiC surface is basic. Thus, the Lewis base-Lewis acid reactions make the functional group–COOH an effective adsorbate to the SiC nanoparticle surface. The organofunctional group “methacrylates,” which exhibits the best wet strength with polyester copolymerizes with styrene monomers in the vinyl ester during cure. Hence, this novel dispersant also acts as an efficient coupling agent that reacts with both SiC and vinyl ester. The monolayer coverage dosage of 62 fractional wt% of the dispersant was used to attain the minimum filled resin viscosity. The multicomponent compositional imaging using atomic force microscopy confirmed the monodisperse SiC nanoparticles in vinyl ester. The 3 vol% SiC reinforced vinyl ester achieved a 75% increase in modulus, 42% increase in strength, and 75% increase in toughness as compared with the neat resin without nanofiller reinforcement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.C. Roco: Nanoparticles and nanotechnology research. J. Nano-part. Res. 1, 1 (1999).
V.M.F. Evora and A. Shukla: Fabrication, characterization, and dynamic behavior of polyester/TiO2 nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 361, 358 (2003).
V. Yong and H.T. Hahn: Processing and properties of SiC/vinyl ester nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 15, 1338 (2004).
V. Yong and H.T. Hahn: Dispersant optimization using design of experiments for SiC/vinyl ester nanocomposites. Nanotechnology 16, 354 (2005).
M.T. Ton-That, F. Perrin-Sarazin, K.C. Cole, M.N. Bureau, and J. Denault: Polyolefin nanocomposites: Formulation and development. Polym. Eng. Sci. 44, 1212 (2004).
V. Yong and H.T. Hahn: Rheology of silicon carbide/vinyl ester nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 102, 4365 (2006).
H. Preiss, L.M. Berger, and M. Braun: Formation of black glasses and silicon carbide from binary carbonaceous/silica hydrogels. Carbon 33, 1739 (1995).
R.F. Conley: Practical Dispersion (Wiley, New York, 1996).
E. Kissa: Dispersions (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1999).
Surface analysis of semiconducting nanoparticles by FTIR spectroscopy, in Nanocrystalline Metals and Oxides: Selected Properties and Applications, edited by P. Knauth and J. Schoonman (Springer, Kluwer Academic, Boston, 2002), pp. 165–187.
M. Okuyama, G.J. Garvey, T.A. Ring, and J.S. Haggerty: Dispersion of silicon-carbide powders in nonaqueous solvents. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 72, 1918 (1989).
Q.S. Yu, Y.J. Kim, and H.B. Ma: Plasma treatment of diamond nanoparticles for dispersion improvement in water. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 231503 (2006).
M.I. Baraton and L. Merhari: Surface chemistry of TiO2 nanoparticles: Influence on electrical and gas sensing properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 1399 (2004).
C. Drake, S. Deshpande, and S. Seal: Determination of free-carrier density and space charge layer variation in nanocrystalline In3+ doped tin oxides using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 143116 (2006).
F.M. Liu, B.F. Quan, L.H. Chen, L.X. Yu, and Z.Q. Liu: Investigation on SnO2 nanopowders stored for different time and BaTiO3 modification. Mater. Chem. Phys. 87, 297 (2004).
Y. Sun and T. Miyasato: Infrared absorption properties of nanocrystalline cubic SiC films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 37, 5485 (1998).
H. Kamiya, M. Mitsui, H. Takano, and S. Miyazawa: Influence of particle diameter on surface silanol structure, hydration forces, and aggregation behavior of alkoxide-derived silica particles. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 83, 287 (2000).
T. Merlemejean, E. Abdelmounim, and P. Quintard: Oxide layer on silicon-carbide powder: A FT-IR investigation. J. Mol. Struct. 349, 105 (1995).
G.L. Harris: Properties of Silicon Carbide (EMIS Datareviews Series No. 13, IEE, INSPEC, London, UK, 1995).
L.E. Nielsen and R.F. Landel: Mechanical Properties of Polymers and Composites (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1994).
R.P. Singh, M. Zhang, and D. Chan: Toughening of a brittle thermosetting polymer: Effects of reinforcement particle size and volume fraction. J. Mater. Sci. 37, 781 (2002).
S.L. Gao and E. Mader: Characterisation of interphase nanoscale property variations in glass fibre reinforced polypropylene and epoxy resin composites. Compos. Part A: Appl. Sci. Manuf. 33, 559 (2002).
S.L. Gao, E. Mader, and S.F. Zhandarov: Carbon fibers and composites with epoxy resins: Topography, fractography and interphases. Carbon 42, 515 (2004).
B. Mader, S.L. Gao, and R. Plonka: Enhancing the properties of composites by controlling their interphase parameters. Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 147 (2004).
Z.H. Guo, T. Pereira, O. Choi, Y. Wang, and H.T. Hahn: Surface functionalized alumina nanoparticle filled polymeric nanocompo-sites with enhanced mechanical properties. J. Mater. Chem. 16, 2800 (2006).
X.P. Zhang, B.Q. Sun, R.H. Friend, H.C. Guo, D. Nau, and H. Giessen: Metallic photonic crystals based on solution-processible gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 6, 651 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yong, V., Hahn, H.T. Monodisperse SiC/vinyl ester nanocomposites: Dispersant formulation, synthesis, and characterization. Journal of Materials Research 24, 1553–1558 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0176
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0176