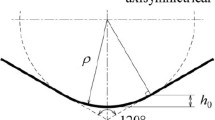
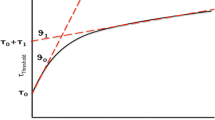
Abstract
A novel optimization approach, capable of extracting the mechanical properties of an elasto-plastic material from indentation data, is proposed. Theoretical verification is performed on two simulated configurations. The first is based on the analysis of the load–displacement data and the topography of the residual imprint of a single conical indenter. The second is based on the load–displacement data obtained from two conical indenters with different semi-angles. In both cases, a semi-analytical approach [e.g., Dao et al., Acta Mater. 49, 3899 (2001) and Bucaille et al., Acta Mater. 51, 1663 (2003)] is used to estimate Young’s modulus, yield stress, and strain hardening coefficient from the load–displacement data. An inverse finite element model, based on a commercial solver and a newly developed optimization algorithm based on a robust stochastic methodology, uses these approximate values as starting values to identify parameters with high accuracy. Both configurations use multiple data sets to extract the elastic-plastic material properties; this allows the mechanical properties of materials to be determined in a robust way.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.L. Loubet, J.M. Georges, O. Marchesini, and G. Meille: Vickers indentation curves of magnesium-oxide (MgO). J. Tribol. 106, 43 (1984).
J.B. Pethica, R. Hutchings, and W.C. Oliver: Hardness measurement at penetration depths as small as 20 nm. Philos. Mag. A 48, 593 (1983).
S. Stauss, P. Schwaller, J-L. Bucaille, R. Rabe, L. Rohr, J. Michler, and E. Blank: Determining the stress–strain behaviour of small devices by nanoindentation in combination with inverse methods. Microelectron. Eng. 67–68, 818 (2003).
M.F. Doerner and W.D. Nix: A method for interpreting the data from depth-sensing indentation. J. Mater. Res. 1, 601 (1986).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
D. Tabor: The Hardness of Metals (Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK, 1951).
Y.T. Cheng and C.M. Cheng: Scaling approach to conical indentation in elastic-plastic solids with work hardening., J. Appl. Phys. 84, 1284 (1998).
Y.T. Cheng and C.M. Cheng: Scaling, dimensional analysis, and indentation measurements. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 44, 91 (2004).
K.D. Bouzakis, N. Michailidis, and G. Erkens: Thin hard coatings stress-strain curve determination through a FEM supported evaluation of nanoindentation test results. Surf. Coat. Technol. 142, 102 (2001).
J.L. Bucaille, S. Stauss, E. Felder, and J. Michler: Determination of plastic properties of metals by instrumented indentation using different sharp indenters. Acta Mater. 51, 1663 (2003).
N. Chollacoop, M. Dao, and S. Suresh: Depth-sensing instrumented indentation with dual sharp indenters. Acta Mater. 51, 3713 (2003).
M. Dao, N. Chollacoop, K.J. Van Vliet, T.A. Venkatesh, and S. Suresh: Computational modeling of the forward and reverse problems in instrumented sharp indentation. Acta Mater. 49, 3899 (2001).
A.E. Giannakopoulos and S. Suresh: Determination of elastoplastic properties by instrumented sharp indentation. Scr. Mater. 40, 1191 (1999).
N. Huber and C. Tsakmakis: Determination of constitutive properties from spherical indentation data using neural networks. Part I: The case of pure kinematic hardening in plasticity laws. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 47, 1569 (1999).
B. Backes, K. Durst, and M. Goken: Determination of plastic properties of polycrystalline metallic materials by nanoindentation: Experiments and finite element simulations. Philos. Mag. 86, 5541 (2006).
Y.P. Cao and N. Huber: Further investigation on the definition of the representative strain in conical indentation. J. Mater. Res. 21, 1810 (2006).
I.S. Choi, M. Dao, and S. Suresh: Mechanics of indentation of plastically graded materials. I: Analysis. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 56, 157 (2008).
B. Guelorget, M. Francois, C. Liu, and J. Lu: Extracting the plastic properties of metal materials from microindentation tests: Experimental comparison of recently published methods. J. Mater. Res. 22, 1512 (2007).
X.Q. Qian, Y.P. Cao, and J. Lu: Dependence of the representative strain on the hardening functions of metallic materials in indentation. Scr. Mater. 57, 57 (2007).
S. Swaddiwudhipong, E. Harsono, J. Hua, and Z.S. Liu: Reverse analysis via efficient artificial neural networks based on simulated Berkovich indentation considering effects of friction. Eng. Comput. 24, 127 (2008).
T.W. Capehart and Y.T. Cheng: Determining constitutive models from conical indentation: Sensitivity analysis. J. Mater. Res. 18, 827 (2003).
A. Gouldstone, N. Chollacoop, M. Dao, J. Li, A.M. Minor, and Y.L. Shen: Indentation across size scales and disciplines: Recent developments in experimentation and modeling. Acta Mater. 55, 4015 (2007).
H. Lan and T.A. Venkatesh: Determination of the elastic and plastic properties of materials through instrumented indentation with reduced sensitivity. Acta Mater. 55, 2025 (2007).
H. Lan and T.A. Venkatesh: On the uniqueness and sensitivity issues in determining the elastic and plastic properties of powerlaw hardening materials through sharp and spherical indentation. Philos. Mag. 87, 4671 (2007).
J.L. Cohon: MultiObjective Programming and Planning (Academic Press, New York, 1978).
J.C. Gilbert: Differentiable Optimization: Theory and Algorithms (INRIA, Roquencourt, France, 1999).
P. Pilvin: Multiscale approach for the prediction of the materials andastic component, Ph.D. Thesis, Universite de Paris VI, France (1983).
M. Bocciarelli and G. Maier: Indentation and imprint mapping method for indentation of residual stresses. Comp. Mater. Sci. 39, 381 (2007).
S.N. Stauss-Ueno: Assessment of mechanical properties using instrumented indentation and inverse methods, Ph.D. Thesis, EPF Lausanne, Switzerland, (2006).
D.E. Goldberg: Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization and Machine Learning (Addison-Wesley, Reading, MA, 1989).
Z. Michalewicz: Genetic Algorithms + Data Structures = Evolution Programs (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, 1992).
I. Rechenberg: Evolutionsstrategie: Technical System Optimization from Biological Evolution Principle (Frommann-Holzboog, Stuttgart, Germany, 1973).
K. Zeng and C.H. Chiu: An analysis of laod-penetration curves from instrumented indentation. Acta Mater. 49, 3539 (2001).
M. Emmerich, A. Giotis, M. Özdemir, T. Bäck, and K. Giannakoglou: Metamodel-assisted evolution strategies, in Parallel Problem Solving from Nature VII, edited by J.J. Merelo Guervss, P. Adamidis, H.G. Bever, J-L. Fernández-Villacañas, and H-P. Schwefel (Springer, Secaucus, NJ, 2002).
ABAQUS—Standard User’s manual version 6.4 (Hibbit, Karlsson and Sorensen Inc., 2002).
J.L. Bucaille, A. Rossoll, B. Moser, S. Stauss, and J. Michler: Determination of the matrix in situ flow stress of a continuous fibre reinforced metal matrix composite using instrumented indentation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 369, 82 (2004).
Z. Gronostajski: The constitutive equations for FEM analysis. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 106, 40 (2000).
J.H. Hollomon: Tensile deformation. Trans. Am. Inst. Mining Metall. Eng. 162, 268 (1945).
G. Dieter: Mechanical Metallurgy, 2nd ed. (Mc Graw-Hill, New York, 1976).
J. Lubliner: Plasticity Theory (Macmillan, New York, 1990).
H.W. Swift: Plastic instability under plane stress. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1, 1 (1952).
W. Ramberg and W.R. Osgood: Description of stress-strain curves by three parameters. National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics, Technical Note 902 (1943).
Python Software Foundation (www.python.org, 2005).
J.H. Holland: Outline for a logical theory of adaptive systems. J. Assoc. Computing Machinery 9, 297 (1962).
H-P. Schwefel: Numerical Optimization of Computer Models, 2nd ed. (JohnWiley and Sons, New York, 1995).
L.J. Fogel: On the organization of intellect, Ph.D. Dissertation, UCLA, CA, (1964).
N. Cramer: A representation for the adaptive generation of simple sequential programs, in Genetic Algorithms and the Applications, edited by J. Grefenstette (Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah, NJ, 1985), p. 183.
T. Bäck, D. Fogel, and Z. Michalewicz: Handbook of Evolutionary Computation (Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1997).
S. Sakata, F. Ashida, and M. Zako: Structural optimization using Kriging approximation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 192, 923 (2003).
O. Ghouati and J.C. Gelin: Gradient based methods, genetic algorithms and the finite element method for the identification of material parameters, in Simulation of Materials Processing: Theory, Methods and Applications, edited by J. Huétink and F.P.T. Baaijens (A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1998), p. 157.
J. Alcalá, A.C. Barone, and M. Anglada: The influence of plastic hardening on surface deformation modes around Vickers and spherical indents. Acta Mater. 48, 3451 (2000).
M.M. Chaudhri and M. Winter: The load-bearing area of a hardness indentation. J. Phys. D 21, 370 (1988).
R. Hill, B. Storakers, and A. Zdunek: A theoretical study of the Brinell hardness test. Proc. R. Soc. London A 423, 301 (1989).
X.Y. Feng and T.C. Wang: Scaling functions in conical indentation of elastic-plastic solids. Acta Mech. 196, 245 (2008).
X-L. Gao, X.N. Jing, and G. Subhash: Two new expanding cavity models for indentation deformations of elastic strain-hardening materials. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 2193 (2006).
W. Zielinski, H. Huang, and W.W. Gerberich: Microscopy and microindentation mechanics of single crystal Fe–3 wt.% Si: Part II. TEM of the indentation plastic zone. J. Mater. Res. 8, 1300 (1993).
J.W. Harding and I.N. Sneddon: The elastic stresses produced by the indentation of the plane surface of a semi-infinite elastic solid by a rigid punch. Proc. Camb. Philol. Soc. 41, 16 (1945).
A.E.H. Love: Boussinesq’s problem for a rigid cone. Q. J. Math. 10, 161 (1939).
I.N. Sneddon: The relation between load and penetration in the axisymmetric Bossinesq problem for a punch of arbitrary profile. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
K.K. Tho, S. Swaddiwudhipong, Z.S. Liu, K. Zheng, and J. Hua: Uniqueness of reverse analysis from conical indentation tests. J. Mater. Res. 19, 2498 (2004).
J.L. Bucaille, S. Stauss, P. Schwaller, and J. Michler: A new technique to determine the elastic properties of thin metallic films using sharp indenters. Thin Solid Films 447–448, 239 (2004).
S. Swaddiwudhipong, K.K. Tho, Z.S. Liu, and K. Zeng: Material characterization based on dual indenters. Int. J. Solids Struct. 42, 69 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peyrot, I., Bouchard, P.O., Ghisleni, R. et al. Determination of plastic properties of metals by instrumented indentation using a stochastic optimization algorithm. Journal of Materials Research 24, 936–947 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0118
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0118