Abstract
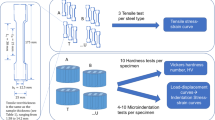
In the present work, a previously developed neural network approach for analyzing spherical indentation experiments is applied to prestressed specimens to determine the effect of residual stresses on the identified stress–strain curves. Within this scope, a comparison to other measurement errors has been made, which are caused by surface preparation and anisotropy of the material. To validate the experimental and analysis approach, the effect of compressive and tensile prestresses was also simulated using a three-dimensional finite element model. The material investigated is a rolled 2024 T351, which is widely used for manufacturing airplanes. It is shown that the existing neural network approach is able to determine the stress–strain behavior in agreement with that obtained from tensile tests. The method is robust against most error sources, such as surface roughness, coarse grain structure, and anisotropy, if a sufficient number of experiments are available. The most important influencing factor can be the residual stress causing errors up to 20% in the identified stress–strain curves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Motarjemi, M. Kocak, and V. Ventzke: Mechanical and fracture characterization of a bi-material steel plate. Int. J. Press. Vessels. Pip. 79, 181 (2002).
S.T. Amancio, S. Sheikhi, J.F. dos Santos, and C. Bolfarini: Preliminary study of the microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar friction stir welds in aircraft aluminium 2024-T351 and 6056-T4. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 206, 132 (2008).
U. Ceyhan: High Temperature Deformation and Fracture Assessment of Similar Steel Welds (Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Papierflieger, 2007). Available at: http://www.gbv.de/dms/clausthal/E_DISS/2007/db108543.pdf.
J.S. Field and M.V. Swain: Determining the mechanical properties of small volumes of material from sub micro indenter spherical indentations. J. Mater. Res. 10, 101 (1995).
B. Taljat and T. Zacharia: New analytical procedure to determine stress-strain curve from spherical indentation data. Int. J. Solids Struct. 35(33), 4411 (1998).
S. Kucharski and Z. Mroz: Identification of plastic hardening parameters of metals from spherical indentation tests. Mater. Sci. Eng. 318(1–2), 65 (2001).
S. Kucharski and Z. Mroz: Identification of hardening parameters of metals from spherical indentation test., J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 123, 245 (2004).
M. Zhao, N. Ogasawara, N. Chiba, and X. Chen: A new approach to measure—Elastic-plastic properties of bulk materials using spherical indentation. Acta Mater. 54, 23 (2006).
Y. Cao, X. Qian, and N. Huber: Spherical indentation into elasto-plastic materials: Indentation-response based definitions of representative strain. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 454–455, 1 (2007).
X. Chen, N. Ogahisa, M. Zaho, and N. Chiba: On the uniqueness of measuring elastoplastic properties from indentation: The indistinguishable mysical materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55(8), 1618 (2007).
N. Huber and Ch. Tsakmakis: A new loading history for identification of viscoplastic properties by spherical indentation. J. Mater. Res. 19(1), 101 (2004).
E. Tyulyukovskiy and N. Huber: Identification of viscoplastic material parameters from spherical indentation data: Part I. Neural networks. J. Mater. Res. 21(3), 664 (2006).
D. Klötzer, Ch. Ullner, E. Tyulyukovskiy, and N. Huber: Identification of viscoplastic material parameters from spherical indentation data: Part II. Experimental validation of the method. J. Mater. Res. 21(3), 677 (2006).
E. Tyulyukovskiy and N. Huber: Neural networks for tip correction of spherical indentation curves from bulk metals and thin films. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55, 391 (2007).
N. Huber, E. Tyulyukovskiy, H-C. Schneider, R. Rolli, and M. Weick: An indentation system for determination of viscoplastic stress-strain behaviour of small metal volumes before and after irradiation. J. Nucl. Mater. 377, 352 (2008).
G. Sines and R. Carlson: Hardness measurements for determination of residual stresses. ASTM Bull. 180, 35 (1952).
F.H. Vitovec: Stress and load dependence of microindentation hardness. ASTM Spec. Publ. 889, 175 (1985).
T.Y. Tsui, W.C. Oliver, and G.M. Pharr: Influence of stress on the measurement of mechanical properties using nanoindentation: Part I. Experimental studies in an aluminium alloy. J. Mater. Res. 11(3), 752 (1996).
C.M. Lepienski, G.M. Pharr, Y.J. Park, T.R. Watkins, A. Misra, and X. Zhang: Factors limiting the measurement of residual stresses in thin films by nanoindentation. Thin Solid Films 447–448, 251 (2004).
J.G. Swadener, B. Taljat, and G.M. Pharr: Measurement of residual stress by load and depth-sensing indentation with spherical indenters. J. Mater. Res. 16, 2091 (2001).
J.H. Underwood: Residual stress measurement using surface displacement around an indentation. Exp. Mech. 30, 373 (1973).
S. Suresh and A.E. Giannakopoulos: A new method for estimating residual stresses by instrumented sharp indentation. Acta Mater. 46(16), 5755 (1998).
S. Carlsson and P. L. Larsson: On the determination of residual stress and strain fields by sharp indentation testing. Part I: Theoretical and numerical analysis. Acta Mater. 49 (12), 2179 (2001).
S. Carlsson and P.L. Larsson: On the determination of residual stress and strain fields by sharp indentation testing. Part II: Experimental investigation. Acta Mater. 49 (12), 2193 (2001).
G. Quan, J. Heerens, and W. Brocks: Distribution of constituent particles in thick plate of Al-T351. Practical Metallogaphy 6, 304 (2004).
Testing Machines and Systems for Metals (brochure). Available at: http://www.zwick.com/frame/Control.php?action=Frame,show&mainNavId=11.
E. Tyulyukovskiy: Identification of mechanical properties of metallic materials from indentation tests. Ph.D. Thesis, FZKA-Report 7103, March (2005). Available at: http://bibliothek.fzk.de/zb/berichte/FZKA7103.pdf.
N. Huber and J. Heerens: On the effect of a general residual stress state on indentation and hardness testing. Acta Mater. 56, 6205 (2008).
E. Kreysig: Statistical Methods and Their Application (Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, Göttingen, Germany, 1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heerens, J., Mubarok, F. & Huber, N. Influence of specimen preparation, microstructure anisotropy, and residual stresses on stress–strain curves of rolled Al2024 T351 as derived from spherical indentation tests. Journal of Materials Research 24, 907–917 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0116
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0116