Abstract
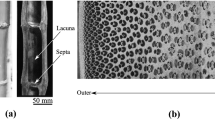
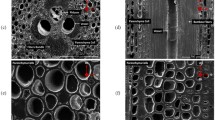
The structure, composition, and mechanical response of Australian bamboo were investigated. The graded structure, composition, and mechanical properties were confirmed by depth profiles obtained using synchrotron radiation diffraction and Vickers indentation. The mechanical performance of bamboo was strongly dependent on age. Results indicated that young bamboo has a higher strength, elastic stiffness, and fracture toughness than its older counterpart does. In addition, the hardness of bamboo is both load dependent and time dependent as a result of an expanding interfacial damage zone and indentation creep, respectively. In addition to fiber debonding, crack deflection and crack-bridging are the major energy dissipative processes for imparting a high toughness in bamboo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Liese: The structure of bamboo in relation to its properties and utilization, in Proc Int. Symp. Industrial Use of Bamboo, Beijing, China, (1992), pp. 95–100.
K. Ghavami: Bamboo as reinforcement in structural concrete elements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 27, 637 (2005).
F. Nogata, H. Takahashi: Intelligent functionally graded material: Bamboo. Compos. Eng. 5, 743 (1995).
S. Amada, Y. Ichikawa, T. Munekata, Y. Nagase, H. Shimizu: Fiber texture and mechanical graded structure of bamboo. Composites Part B 28, 13 (1997).
S. Amada, S. Untao: Fracture properties of bamboo. Composites Part B 32, 451 (2001).
S.H. Li, Q.Y. Zeng, Y.L. Xiao, S.Y. Fu, B.L. Zhou: Biomimicry of bamboo bast fiber with engineering composite materials. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 3, 125 (1995).
M.F. Ashby: Materials Selection in Mechanical Design (Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, 1992).
U.G.K Wegst, H.R. Shercliff, M.F. Ashby: The Structure and Properties of Bamboo as an Engineering Material (University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 1993).
S.C. Lakkad, J.M. Patel: Mechanical properties of bamboo, a natural composite. Fibre Sci. Technol. 14, 319 (1981).
P. van der Lugt, A.A.J.F. van den Dobbelsteen, J.J.A Janssen: An environmental, economic and practical assessment of bamboo as a building material for supporting structures. Constr. Building Mater. 20, 648 (2006).
K.F. Chung, W.K. Yu: Mechanical properties of structural bamboo for bamboo scaffoldings. Eng. Struct. 24, 429 (2002).
W.K. Yu, K.F. Chung, S.L. Chan: Axial buckling of bamboo columns in bamboo scaffolds. Eng. Struct. 27, 61 (2005).
W. Yao, Z. Li: Flexural behavior of bamboo-fiber-reinforced mortar laminates. Cem. Concr. Res. 33, 15 (2003).
R.S.P Coutts, Y. Ni: Autoclaved bamboo pulp fibre reinforced cement. Cem. Concr. Compos. 17, 99 (1995).
K. Ghavami: Bamboo as reinforcement in structural concrete elements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 27, 637 (2005).
K. Ghavami: Ultimate load behaviour of bamboo reinforced lightweight concrete beams. Cem. Concr. Compos. 17, 281 (1995).
H. Ismail, S. Shuhelmy, M.R. Edyham: The effects of a silane coupling agent on curing characteristics and mechanical properties of bamboo fibre filled natural rubber composites. Eur. Polym. J. 38, 39 (2002).
H. Ismail, M.R. Edyham, B. Rirjosentono: Bamboo fiber filled natural rubber composites: The effects of filler loading and bonding agent. Polym. Test. 21, 139 (2002).
X. Chen, Q. Guo, Y. Mi: Bamboo fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites: A study of the mechanical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 69, 1891 (1998).
M.M. Thwe, K. Liao: Environmental effects on bamboo–glass/polypropylene hybrid composites. J. Mater. Sci. 38, 363 (2003).
M.M. Thwe, K. Liao: Effects of environmental aging on the mechanical properties of bamboo–glass fiber reinforced polymer matrix hybrid composites. Composites A 33, 43 (2002).
F.G. Shin, M.W. Yipp: Analysis of the mechanical properties and microstructure of bamboo-epoxy composites. J. Mater. Sci. 3483, 24 (1989).
S. Jain, R. Kumar, U.C. Jindal: Development and fracture mechanism of the bamboo/polyester resin composite. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 12, 558 (1993).
S.H. Li, S.Y. Fu, B.L. Zhou, Q.Y. Zeng, X.R. Bao: Reformed bamboo and reformed bamboo/aluminium composite. J. Mater. Sci. 29, 5990 (1994).
T.Y. Lo, H.Z. Cui, H.C. Leung: The effect of fiber density on strength capacity of bamboo. Mater. Lett. 58, 2595 (2004).
A.C. Sekhar, R.K. Bhartari: Studies of strength of bamboo. A note on its mechanical behaviour. Ind. For. 86, 296 (1960).
A.C. Sekhar, B.S. Rawat, R.K. Bhartari: Strength of bamboos. Bambusa nutans. Ind. For. 88, 67 (1962).
G. Lim, W. Parrish, C. Ortish, M. Belletto, M. Hart: Grazing incidence synchrotron diffraction method for analyzing thin films. J. Mater. Res. 2, 471 (1987).
I.M. Low: Depth-profiling of crystal structure, texture and microhardness in a functionally-graded tooth enamel. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 87, 2125 (2004).
J. Barry: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 58, 333 (1936).
I.M. Low: Effects of load and time on the hardness of a viscoelastic polymer. Mater. Res. Bull. 33, 1753 (1998).
A.G. Atkins, Y.W. Mai: Elastic and Plastic Fracture (Ellis Horwood/John Wiley, Chichester, UK, 1988).
B.A. Latella, K.T. Short: Tension-driven cracking of an expanded austenite layer. J. Mater. Sci. 39, 4321 (2004).
I.M. Low: Vickers contact damage in micro-layered Ti3SiC2. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 18, 709 (1998).
M. Rowles, D. Lawrence, I.M. Low, P. Schmidt, and J. Lane: Indentation responses and failure micromechanisms of cellulose-fibre-mylar/reinforced epoxy laminates, in Proc. Int. Workshop on Fracture Mechanics & Advanced Engineering Materials, edited by L. Ye and Y.W. Mai (Sydney University Press, Sydney, Australia), pp. 343–350.
D. Lawrence, G. Paglia, and I.M. Low: Indentation responses and damage of polymeric composites, in Proc. Structural Integrity and Fracture 2000, edited by G. Heness (University of Technology, Syndey, Australia) pp. 119–127 (2000).
I.M. Low, M. McGrath, D. Lawrence, P. Schmidt, J. Lane, B.A. Latella: Mechanical and fracture properties of cellulose fibre reinforced epoxy laminates (in press).
B. Ji, H. Gao: Mechanical properties of nanostructure of biological materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 52, 1963 (2004).
Z. Tang, N.A. Kotov, S. Magonov, B. Ozturk: Nanostructured artificial nacre. Nat. Mater. 2, 413 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Low, I.M., Che, Z.Y. & Latella, B.A. Mapping the structure, composition and mechanical properties of bamboo. Journal of Materials Research 21, 1969–1976 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0238
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0238