Abstract
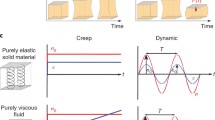
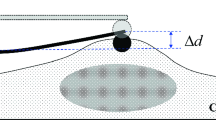
This paper presents a shear assay method for the determination of the viscoelastic properties of biological cells. The method was applied to the measurement of the viscoelastic properties of human osteosarcoma (HOS) cells. It involves a combination of shear assay experiments and digital image correlation techniques. Following in situ observations of cell deformation during shear assay experiments, a digital image correlation (DIC) technique was used to determine the local displacement and strain fields. The creep curves were also extracted from multiple digital images that were used to extract the time dependence of local strain under constant stress conditions. The measured creep curves were well described by a generalized viscoelastic Maxwell model. The extracted elastic and viscous parameters were in good agreement with results obtained from prior studies with other techniques. The results also suggested that the nucleus is stiffer than the surrounding cytoplasm of HOS cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Kapur, D.J. Baylink, K.H.W Lau: Fluid flow shear stress stimulates human osteoblast proliferation and differentiation through multiple interacting and competing signal transduction pathways. Bone 32, 241 (2003).
E.A. Nauman, R.L. Satcher, T.M. Keaveny, B.P. Halloran, D.D. Bikle: Osteoblasts respond to pulsatile fluid flow with short-term increase in PGE2 but no change in mineralization. J. Appl. Physiol. 90, 1849 (2001).
V.I. Sikavitsas, J.S. Temeno, A.G. Mikos: Biomaterials and bone mechanotransduction. Biomaterials 22, 2581 (2001).
J.G. McGarry, J. Klein-Nulend, M.G. Mullender, P.J. Prendergast: A comparison of strain and fluid shear stress in stimulating bone cell responses—A computational and experimental study. FASEB J. 18, 1 (2004).
U. Liegibel, U. Sommer, B. Bundschuh, B. Schweizer, U. Hischer, A. Lieder, P. Nawroth, C. Kasperk: Fluid shear of low magnitude increases growth and expression of TGF beta 1 and adhesion molecules in human bone cells in vitro. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 112, 356 (2004).
R. Suwanarusk, B. Cooke, A. Dondorp, K. Silamut, J. Sattabongkot, N. White, R. Udomsangpetch: The deformability of red blood cells parasitized by Plasmodium falciparum and P-vivax. J. Infect. Dis. 189, 190 (2004).
T. Vankooten, J. Schakenraad, H. Vandermei, H. Busscher: Development and use of a parallel plate flow chamber for studying cellular adhesion to solid-surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 26, 725 (1992).
B. Cooke, S. Usami, I. Perry, G. Nash: A simplified method for culture of endothelial-cells and analysis of adhesion of blood-cells under conditions of flow. Microvasc. Res. 45, 33 (1993).
Y. Wan, J. Yang, J. Yang, J. Bei, S. Wang: Cell adhesion on gaseous plasma modified poly-(L-lactide) surface under shear stress field. Biomaterials 24, 3757 (2003).
G. Bao, S. Suresh: Cell and molecular mechanics of biological materials. Nat. Mater. 2, 715 (2003).
C. Zhu, G. Bao, N. Wang: Cell mechanics: Mechanical response, cell adhesion, and molecular deformation. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2, 189 (2000).
A. Bausch, F. Ziemann, A. Boulbitch, K. Jacobson, E. Sackmann: Local measurements of viscoelastic parameters of adherent cell surfaces by magnetic bead microrheometry. Biophys. J. 75, 2038 (1998).
F. Guilak, J. Tedrow, R. Burgkart: Viscoelastic properties of the cell nucleus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 269, 781 (2000).
H. Wu, T. Kuhn, V. Moy: Mechanical properties of l929 cells measured by atomic force microscopy: Effects of anticytoskeletal drugs and membrane crosslinking. Scanning 20, 389 (1998).
S. Yamada, D. Wirtz, S. Kuo: Mechanics of living cells measured by laser tracking microrheology. Biophys. J. 78, 1736 (2000).
A. Bausch, W. Moller, E. Sackmann: Measurement of local viscoelasticity and forces in living cells by magnetic tweezers. Biophys. J. 76, 573 (1999).
C. Lo, J. Ferrier: Electrically measuring viscoelastic parameters of adherent cell layers under controlled magnetic forces. Eur. Biophys. J. 28, 112 (1999).
K. Van-Vliet, G. Bao, S. Suresh: The biomechanics toolbox: Experimental approaches for living cells and biomolecules. Acta Mater. 51, 5881 (2003).
H. Shiga, Y. Yamane, E. Ito, K. Abe, K. Kawabata, H. Haga: Mechanical properties of membrane surface of cultured astrocyte revealed by atomic force microscopy. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 39, 3711 (2000).
N. Caille, O. Thoumine, Y. Tardy, J. Meister: Contribution of the nucleus to the mechanical properties of endothelial cells. J. Biomech. 35, 177 (2002).
H. Huang, R.D. Kamm, R.T. Lee: Cell mechanics and mechanotransduction: Pathways, probes, and physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 287, C1 (2004).
R. Bly, Y. Cao, W. Moore, W. Soboyejo: Investigation of the effects of alkane phosphonic acid/RGD coatings on cell spreading and the interfacial strength between human osteosarcoma cells and Ti-6Al-4V. Mater. Sci. Eng., C (2006, in press).
Y. Wang, A.M. Cuitino: Full-field measurements of heterogeneous deformation patterns on polymeric foams using digital image correlation. Int. J. of Solids Struct. 39, 3777 (2002).
C. Baker: Methylcellulose & sodium carboxymethylcellulose: Uses in paper conservation. Book Paper Group Ann. 1, 4 (1982).
T.C. Chu, W.F. Ranson, M.A. Sutton, W.H. Peters: Applications of digital-image-correlation techniques to experimental mechanics. Exp. Mech. 25, 232 (1985).
H.A. Bruck, S.R. McNeill, M.A. Sutton, W.H. Peters: Digital image correlation using newton-raphson method of partial differential correction. Exp. Mech. 29, 261 (1989).
G. Vendroux, W.G. Knauss: Submicron: Deformation field measurements: Part 2, Improved digital image correlation. Exp. Mech. 38, 86 (1998).
J. Zhou, Z. Gao, A.M. Cuitino, W.O. Soboyejo: Effects of heat treatment on the compressive deformation behavior of open cell aluminum foams. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 386, 118 (2004).
B. Matthews, D. Overby, F. Alenghat, J. Karavitis, Y. Numaguchi, P. Allen, D. Ingber: Mechanical properties of individual focal adhesions probed with a magnetic microneedle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 313, 758 (2004).
G. Forgacs, R. Foty, Y. Shafrir, M. Steinberg: Viscoelastic properties of living embryonic tissues: A quantitative study. Biophys. J. 74, 2227 (1998).
W. Soboyejo: Mechanical Properties of Engineered Materials (Marcel Dekker, New York, 2003).
G. Givelekoglu-Scholey, A.W. Orr, I. Novak, J.J. Meister, M.A. Schwartz, A. Mogilner: Model of coupled transient changes of Rac, Rho, adhesions and stress fibers alignment in endothelial cells responding to shear stress. J. Theor. Biol. 232, 569 (2005).
E. Decave, D. Rieu, J. Dalous, S. Fache, Y. Brechet, B. Fourcade, M. Satre, F. Bruckert: Shear flow-induced motility of dicytostelium discoideum cells on solid substrate. J. Cell Sci. 116, 4331 (2003).
C. Dong, R. Skalak, K. Sung: Cytoplasmic rheology of passive neutrophils. Biorheology 28, 557 (1991).
P.A. Janmey: The cytoskeleton and cell signaling: Component localization and mechanical coupling. Physiol. Rev. 78, 763 (1998).
N. Caille, Y. Tardy, J. Meister: Assessment of strain field in endothelial cells subjected to uniaxial deformation of their substrate. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 26, 409 (1998).
H. Haga, S. Sasaki, K. Kawabata, E. Ito, T. Ushiki, T. Sambongi: Elasticity mapping of living fibroblasts by AFM and immunofluorescence observation of the cytoskeleton. Ultramicroscopy 82, 253 (2000).
N. Kataoka, K. Iwaki, K. Hashimoto, S. Mochizuki, Y. Ogasawara, M. Sato, K. Tsujioka, F. Kajiya: Measurements of endothelial cell-to-cell and cell-to-substrate gaps and micromechanical properties of endothelial cells during monocyte adhesion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 15638 (2002).
D. Brands, G. Peters, P. Bovendeerd: Design and numerical implementation of a 3-D nonlinear viscoelastic constitutive model for brain tissue during impact. J. Biomech. 37, 127 (2004).
E. Bosboom, M. Hesselink, C.O.C Bouten, M. Drost, F. Baaijens: Passive transverse mechanical properties of skeletal muscle under in vivo compression. J. Biomech. 34, 1365 (2001).
AFM study shows old cells lose their elasticity. APS (American Physical Society) News, May Issue, 13, 1 (2004).
S. Suresh, J. Spatz, J. Mills, A. Micoulet, M. Dao, C. Lim, M. Beil, T. Sefferlein: Connections between single-cell biomechanics and human disease states: Gastrointestinal cancer and malaria. Acta Biomater. 1, 16 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Y., Bly, R., Moore, W. et al. Investigation of the viscoelasticity of human osteosarcoma cells using a shear assay method. Journal of Materials Research 21, 1922–1930 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0235
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2006.0235