Abstract
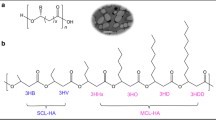
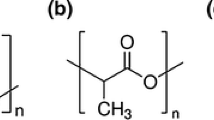
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) are degradable (co)polyesters synthesized by microorganisms with a variety of side-chains and co-monomer ratios. PHAs can be efficiently hydrolyzed under alkaline conditions and by PHA depolymerase enzymes, altering their physicochemical properties. Using 2D Langmuir monolayers as model system to study the degradation behavior of macromolecules, we aim to describe the the interdependency between the degradation of two PHAs and the surface potential, which influences material-proteins interaction and cell response. We hypothesize that the mechanism of hydrolysis of the labile ester bonds in (co)polyesters defines the evolution of the surface potential, owing to the rate of accumulation of charged insoluble degradation products. The alkaline hydrolysis and the enzymatically catalyzed hydrolysis of PHAs were previously defined as chain-end scission and random-scission mechanisms, respectively. In this study, these two distinct scenarios are used to validate our model. The surface potential change during the chain-end scission of poly(3-R-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) under alkaline conditions was compared to that of the enzymatically catalyzed hydrolysis (random-scission) of poly[(3-R-hydroxyoctanoate)-co-(3-R-hydroxyhexanoate)] (PHOHHx), using the Langmuir monolayer technique. In the random-scission mechanism the dissolution of degradation products, measured as a decrease in the area per molecule, was preceded by a substantial change of the surface potential, provoked by the negative charge of the broken ester bonds accumulated in the air-water interface. In contrast, when chains degraded via the chain-ends, the surface potential changed in line with the dissolution of the material, presenting a kinetic dependent on the surface area of the monolayers. These results provide a basis for understanding PHAs degradation mechanism. Future research on (co)polymers with different main-chain lengths might extend the elucidation of the surface potential development of (co)polyesters as Langmuir monolayer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Metwally and U. Stachewicz, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 104, 109883 (2019).
O. Nedela, P. Slepicka and V. Svorcik, Materials (Basel) 10 (10), 1115 (2017).
E. Sambha’a, A. Lallam and A. Jada, J. Polym. Environ. 18 (4), 532–538 (2010).
T. Ivanova, A. Svendsen, R. Verger and I. Panaiotov, Colloid Polym. Sci. 278 (8), 719–727 (2000).
N. Grozev, A. Svendsen, R. Verger and I. Panaiotov, Colloid Polym. Sci. 280 (1), 7–17 (2002).
T. Ivanova, A. Malzert, F. Boury, J. E. Proust, R. Verger and I. Panaiotov, Colloids Surf., B 32 (4), 307–320 (2003).
K. Balashev, T. Ivanova, K. Mircheva and I. Panaiotov, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 360 (2), 654–661 (2011).
R. Machatschek, B. Schulz and A. Lendlein, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 40 (1), 1800611 (2019).
R. Machatschek, B. Schulz and A. Lendlein, MRS Adv. 3 (63), 3883–3889 (2018).
M. Koller, Molecules 23 (2), 362 (2018).
F. Fan, L. Wang, Z. Ouyang, Y. Wen and X. Lu, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 102 (7), 3229–3241 (2018).
N. A. Tarazona, R. Machatschek and A. Lendlein (submitted).
M. Scandola, M. Pizzoli, G. Ceccorulli, A. Cesaro, S. Paolletti and L. Navarini, Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 10 (6), 373–377 (1988).
L. J. R. Foster and B. J. Tighe, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 87 (1), 1–10 (2005).
J. Yu, D. Plackett and L. X. L. Chen, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 89 (2), 289–299 (2005).
V. Martinez, P. G. de Santos, J. Garcia-Hidalgo, D. Hormigo, M. A. Prieto, M. Arroyo and I. de la Mata, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 99 (22), 9605–9615 (2015).
N. A. Tarazona, R. Machatschek, B. Schulz, M. A. Prieto and A. Lendlein, Biomacromolecules 20 (9), 3242–3252 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarazona, N.A., Machatschek, R. & Lendlein, A. Relation between Surface Area and Surface Potential Change during (co)Polyesters Degradation as Langmuir Monolayer. MRS Advances 5, 667–677 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2019.458
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2019.458