Abstract
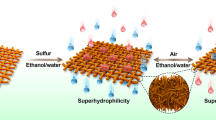
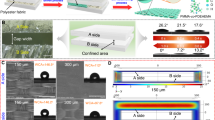
Stimuli-responsive materials with controlled reversible wettability find diverse application as self-cleaning surfaces, tunable optical lenses and microfluidic devices. We report on an electrochemical approach for dynamic control over the wetting properties of additive-free Cu/CuxO core-shell dendritic structures. By varying the oxidation state of the oxide shell phase, the entire wettability range spanning superhydrophobicity (contact angle > 150°) to superhydrophilicity (contact angle < 10°) can be precisely adjusted in-situ. During the wetting transitions, the surface transforms from a low adhesive rolling state (lotus effect) to high adhesive pinning state (petal effect), and eventually to superhydrophilic state with a water-absorbing ability (fish scale wetting). The wetting alteration is reversible via air-drying at room temperature or mild heat drying at 100°C. The reversibly redox-driven wettability switching is demonstrated for controllable oil-water separation with efficiency higher than 98 percent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. Xin and J. Hao, Chem. Soc. Rev. 39, 769 (2010).
Y. Liu, W. Yao, G. Wang, Y. Wang, A.S. Moita, Z. Han, and L. Ren, Chem. Eng. J. 303, 565 (2016).
F. Guo and Z. Guo, RSC Adv. 6, 36623 (2016).
S. Wang, K. Liu, X. Yao, and L. Jiang, Chem. Rev. 115, 8230 (2015).
B. Zahiri, P.K. Sow, C.H. Kung, and W. Mérida, Adv. Mater. Interfaces 4, (2017).
S.H. Tu, H.C. Wu, C.J. Wu, S.L. Cheng, Y.J. Sheng, and H.K. Tsao, Appl. Surf. Sci. 316, 88 (2014).
B. Su, L. Jiang, X. Jiang, and A. Yu, Powder Technol. 312, 103 (2017).
M.K. Dawood, H. Zheng, T.H. Liew, K.C. Leong, Y.L. Foo, R. Rajagopalan, S.A. Khan, and W.K. Choi, Langmuir 27, 4126 (2011).
Z.S. Iro, C. Subramani, and S.S. Dash, Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 11, 10628 (2016).
C. Haow Kung, B. Zahiri, P. Kumar Sow, and W. Mérida, Appl. Surf. Sci. 444, 15 (2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kung, C.H., Zahiri, B., Sow, P.K. et al. Electrochemical Wettability Control on Cu/CuxO Core-Shell Dendrites: In-Situ Droplet Modulation and On-Demand Oil-Water Separation. MRS Advances 3, 3163–3169 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.335
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018.335