Abstract
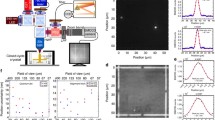
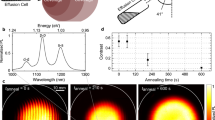
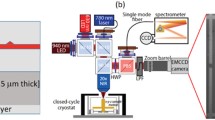
We report a study of direct laser fabrication that produces quantum dots with their density higher than the critical density without appearance of large clumps. Atomic force microscopy is used to image GaAs(001) surfaces that are irradiated by high power laser pulses interferentially. The analysis suggests that high density quantum dots be fabricated directly on semiconductor surfaces during epitaxial growth processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Luque, A. Martí, The Intermediate Band Solar Cell: Progress Toward the Realization of an Attractive Concept, Advanced Materials, 22 (2010) 160–174.
D. Bimberg, M. Grundmann, N.N. Ledentsov, Quantum Dot Heterostructures, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1999.
V. Shchukin, N.N. Ledentsov, D. Bimberg, Epitaxy of Nanostructures, Springer, Berlin, 2003.
D. Zhou, G. Sharma, S.F. Thomassen, T.W. Reenaas, B.O. Fimland, Optimization towards high density quantum dots for intermediate band solar cells grown by molecular beam epitaxy, Applied Physics Letters, 96 (2010) 061913–061913.
M. Jo, T. Mano, Y. Sakuma, K. Sakoda, Extremely high-density GaAs quantum dots grown by droplet epitaxy, Applied Physics Letters, 100 (2012) 212113.
C.M. Clegg, H. Yang, Guided assembly of quantum dots through selective laser heating, Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 108 (2013) 252–255.
B. Rezek, C.E. Nebel, M. Stutzmann, Laser beam induced currents in polycrystalline silicon thin films prepared by interference laser crystallization, Journal of Applied Physics, 91 (2002) 4220–4228.
C.V. Shank, R.V. Schmidt, Optical technique for producing 0.1-µ periodic surface structures, Applied Physics Letters, 23 (1973) 154–155.
T.A. Savas, M. Farhoud, H.I. Smith, M. Hwang, C.A. Ross, Properties of large-area nanomagnet arrays with 100 nm period made by interferometric lithography, Journal of Applied Physics, 85 (1999) 6160–6162.
A. Haghizadeh, H. Yang, Direct laser fabrication of GaAs nanostructures on GaAs(001) in MBE reactor in-situ, in: SPIE Proceedings, 2015, pp. 93520P-93520P-93528.
D.J. Kim, H. Yang, Shape control of InGaAs nanostructures on nominal GaAs(001): dashes and dots, Nanotechnology, 19 (2008) 475601.
W. Zhao, R.W. Verhoef, M. Asscher, Diffusion of potassium on Re(001) investigated by coverage grating-optical second-harmonic diffraction, J. Chem. Phys., 107 (1997) 5554–5560.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghizadeh, A., Yang, H. High density quantum dots by direct laser fabrication. MRS Advances 1, 2025–2030 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2016.270
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2016.270