Abstract
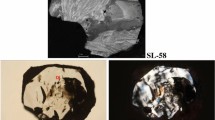
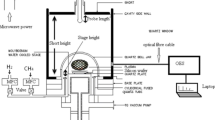
Nanocrystalline diamonds with several hundred nm in diameter have been prepared in a 13.56 MHz low pressure inductively coupled CH4/H2 or CH4/CO/H2 plasma. The bonding structures were investigated by Raman spectroscopy and electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). Visible (514 nm) and UV (325, 244 nm) excited Raman spectra with CO additive exhibit peaks at ∼1150 cm-1 assigned to sp3 bonding and at 1332 cm-1 due to zone center optical phonon mode of diamond, respectively. It indicates that the UV excitations are possibly sufficient to excite the σ state of both sp2- and sp3-bonded carbon. The high resolution EELS (HREELS) spectra with CO additive show peaks at ∼1100 cm-1 assigned to C-C stretching vibration of sp3 bonding and at ∼700 cm corresponding to the bending vibration of sp3 bonding. It is qualitatively agreement with the Raman spectra. Furthermore the EELS spectrum without CO additive exhibits two peaks at 284 eV and at 292 eV corresponding to π* states and σ* states, respectively, and is similar to that of graphite rather than that of sp2-rich amorphous carbon. The EELS spectrum with CO additive, on the other hand, shows a peak at 292 eV due to σ * states and is similar to that of diamond. A slight peak appears at ∼285 eV corresponding to π* states. It consequently implies that the particles almost consist of sp3 bondings and that the small amount of sp2 bondings are considered to exist in grain boundaries. The EESL spectra are consistent with the results of Raman scattering and HREELS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.W.R. Gilkes, D.N. Batchelder, J. Robertson, and W.I. Milne, Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 1980(1997).
V.I. Merkulov, J.S. Lannin, U.S. Veerasamy, and W.I. Milne, Phys. Rev. Lett. 78, 4869(1997).
J. Bruley, D.B. Williams, J.J. Cuomo, and D.P. Pappas, J. Microscopy 180, 22(1995).
D.M. Gruen, Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 29, 211(1999).
A.A. Talin, L.S. Pan, H.J. Doerr, and R.F. Bunshah, Appl. Phys. Lett. 69, 3842(1996).
K. Okada, S. Komatsu, and S. Matsumoto, J. Mater. Res. 14, 578(1999).
K. Okada, H. Kanda, S. Komatsu, and S. Matsumoto, J. Appl. Phys. 88, 1674(2000).
K. Okada, T. Aizawa, R. Souda, S. Komatsu, and S. Matsumoto, Diamond Relat. Mater.(in press).
R.F. Egerton and M.J. Whelan, J. Elect. Spect. Relat. Phenom. 3, 232(1974).
R.J. Nemanich, J.T. Glass, and R.E. Shroder, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A6, 1783(1988).
A.C. Ferrari and J. Robertson, Phys. Rev. B (in press).
J. Wagner, M. Ramsteiner, Ch. Wild, and P. Koidl, Phys. Rev. B40, 1817(1989).
H. Ibach and D.L. Mills, Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy, Academic Press, London, 1982.
C. Oshima, T. Aizawa, R. Souda, and Y. Ishizawa, Solid State Commun. 65, 1601(1988).
N.D. Browning, J. Yuan, and L.M. Brown, Ultramicroscopy 38, 291(1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okada, K., Kimoto, K., Komatsu, S. et al. Raman and Eels Studies on Nanocrystalline Diamond Prepared in a Low Pressure Inductively Coupled Plasma. MRS Online Proceedings Library 675, 1271 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-675-W12.7.1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-675-W12.7.1