Abstract
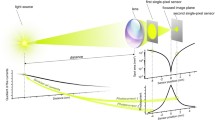
The human visual system perceives much smaller spatial steps in edges between high contrast regions than equivalents fine, periodic features. This characteristic is known as hyperacuity. We have designed, simulated, fabricated and characterized amorphous silicon sensors which provide hyperacuity information. The individual pixels are position sensitive detectors, the outputs of which provide the x and y first moments of the cell illumination pattern as well as the average gray level. In the simplest case the top electrode of a standard p-i-n diode sensor is replaced by four edge strip electrodes. Both quadrilateral cells (having all four lateral electrodes on the same side of the p-i-n diode) and duolateral cells (having x-electrodes on top and y-electrodes on bottom) have been tested. Results of probing the cells with rastered spots show that both types provide usable linearity and sensitivity. The duolateral structure provides greater orthogonality of the x and y information. One μm spatial resolution can be achieved with devices compatible with standard amorphous silicon sensor processing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. N. Curry, J. Electronic Imaging 2, (1993).
G. Westheimer, “Visual hyperacuity”, in Progress in Sensor Physiology / (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1981).
H. J. Woltring, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices ED-22, 581 (1975).
W. Schottky, Phys. Zeitschrift 31, 913 (1930).
J. T. Wallmark, Proc. IRE 45, 474 (1957).
G. Lucovsky, J. Applied Physics 31, 1088(1960).
S. Arimoto, H. Yamamoto, H. Ohno and H. Hasegawa, J. Applied Physics 57, 4778(1985).
M. Yamaguchi, S. Murakami, S. Todo, and Y. Tawada, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 149, 631 (1989).
E. Fortunato, M. Vieira, L. Ferreira, C. N. Carvalho, G. Lavareda and R. Martins, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 297, 981 (1993).
W. P. Connors, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices ED-18, 591 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biegelsen, D.K., Jackson, W.B., Lujan, R. et al. Hyperacuity Image Sensors. MRS Online Proceedings Library 377, 833–838 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-377-833
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-377-833