Abstract
The aim of this work is the investigation of the metal-hydride transformation in magnesium (Mg) nanoparticles both as a function of particle size and in response to surface functionalization by clusters of transition metals (TM): Pd, Ni, Ti.
Mg nanoparticles were synthesized by the inert-gas condensation technique, which yields single crystals with six-fold symmetry whose average size can be controlled by tuning the inert gas pressure. After the synthesis the nanoparticles were passivated by slow exposure to oxygen, obtaining a core-shell morphology where a metallic core is coated by a MgO shell of about 5 nm thickness.
The material structure was investigated by Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), also in High Resolution (HRTEM) mode, and by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD). The sorption kinetics were analysed by a volumetric Sievert apparatus, which also allowed for a determination of the activation energies.
Small nanoparticles (≈35 nm) display interesting kinetics with gravimetric capacity of 4.5 wt.% at saturation, limited by the oxide fraction. Hydride formation proceeds by one-dimensional growth controlled by diffusion through the hydride, while the reverse transformation to metal involves interface-controlled three-dimensional growth of nuclei formed at constant rate.
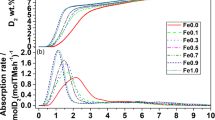
On the contrary, large nanoparticles (≈450 nm) exhibit very low reactivity due to reduced probability of hydrogen dissociation/recombination and nucleation at the particle surface. For this reason, large nanoparticles were surface-decorated by TM through in situ evaporation in the inert-gas condensation chamber. This procedure results in clusters of 3-4 nm located over a portion of the MgO shell, as shown by XRD and HRTEM on Pd-decorated sample. This treatment results in dramatically improved hydrogen sorption behavior. In fact, previously inert nanoparticles now exhibit of up to 5.6 wt.%.
Real-time diffraction studies using Synchrotron Radiation were carried out during hydrogen desorption on the Pd-decorated nanoparticles. We clearly show that a Mg-Pd intermetallic phase is formed after the first heating treatment and takes active part in the transformation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Durgun S. Ciraci T. Yildirim Phys. Rev. B77 085405 (2008).
Y. Zhao Y.H. Kim A.C. Dillon M.J. Heben S.B. Zhang Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 155504 (2005).
M. Yoon S. Yang C. Hicke E. Wang D. Geohegan Z. Zhang Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 206806 (2008).
N.L. Rosi J. Eckert M. Eddaoudi D.T. Vodak J. Kim M. O’Keeffe, O.M. Yaghi Science 300 1127 (2003).
R. Gremaud A. Baldi M. Gonzalez-Silveira, B. Dam R. Griessen Phys. Rev. B77 144204 (2008).
G. Barkhordarian T. Klassen R. Bormann J. Phys. Chem. B110 11020 (2006).
R.W.P. Wagemans J.H. van Lenthe, P.E. de Jongh, A.J. van Dillen, K.P. de Jongh, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 16675 (2005).
A.F. Gross C.C. Ahn S. L. Van Atta, P. Liu J.J. Vajo Nanotechnology 20 204005 (2009).
T.K. Nielsen K. Manickam M. Hirscher F. Besenbacher T.R. Jensen ACS NANO, in the press, DOI: 10.1021/nn901072w.
L. Pasquini E. Callini E. Piscopiello A. Montone M. Vittori Antisari, E. Bonetti Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 221905 (2009).
E. Callini L. Pasquini E. Piscopiello A. Montone M. Vittori Antisari, E. Bonetti Appl. Phys. Lett. 94 041918 (2009).
J. Huot A. Yonkeu J. Dufour J. Alloys Comp. 475 168 (2009).
A. Montone J. Grbovic M. Vittori Antisari, A. Bassetti E. Bonetti A.L. Fiorini L. Pasquini L. Mirenghi P. Rotolo Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 32 2926 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pasquini, L., Callini, E., Piscopiello, E. et al. Hydrogen Sorption in Magnesium Nanoparticles: Size- and Surface-related Phenomena. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1216, 504 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1216-W05-04
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1216-W05-04