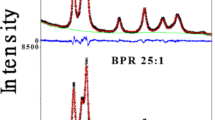
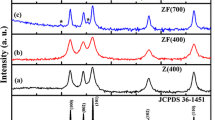
Abstract
Powder X-ray diffraction analyses of Mn-and Cu-doped ZnO powders calcined at 500˚C, show shifts in the wurtzite type semiconductor's lattice constants and unit cell volume which correspond to the nominal concentrations of transition metal dopants. Marked reductions in the a-lattice constant and unit cell volume for a small concentration of Cu dopants, which is not maintained upon increased Cu concentration, suggest a change in the copper ion hybridization state due to the dopant concentration. In all the samples, only ZnO and CuO phases were detected, aiding the ascertainment of any ferromagnetic response from the samples as arising from the formation of a true dilute magnetic semiconductor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sluiter, M. H. F. et al. “First principles based design and experimental evidence for a ZnO-based ferromagnet at room temperature.” Physical Review Letters 94(18): 187204 1–3 (2005).
Dietl T., H. O., F. Matsukura, J. Cibert, D. Ferrand “Zener Model Description of Ferromagnetism in Zinc-Blende Magnetic Semiconductors.” Science 287(5455): 1019–1022 (2000).
Fukumura, T., et al. “Magnetic Oxide Semiconductors.” Semicond. Sci. Technol. 20: S103–S111 (2005).
Chambers, S. A. and R. F. Farrow “New possibilities for ferromagnetic semiconductors.” MRS Bulletin 28(10): 729–733 (2003).
Feng X. “Electronic structures and ferromagnetism of Cu- and Mn-doped ZnO.” Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 16: 4251–4259 (2004).
Kittilstved, K. R. et al. “Chemical manipulation of High-T-C ferromagnetism in ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductors.” Physical Review Letters 94(14): 147209 1–3 (2005).
Han, S. J. et al. “A key to room-temperature ferromagnetism in Fe-doped ZnO: Cu.” Appl. Phys. Lett. 81(22): 4212–4214 (2002).
Sharma, P. et al. “Ferromagnetism above room temperature in bulk and transparent thin films of Mn-doped ZnO.” Nature Materials 2(10): 673–677 (2003).
Buchholz, D. B. and R. P. H. Chang “Room-temperature ferromagnetism n Cu-doped ZnO thin films.” Applied Physics Letters 87(8): 082504 1–3 (2005).
Jin, Z. W. et al. “High throughput fabrication of transition-metal-doped epitaxial ZnO thin films: A series of oxide-diluted magnetic semiconductors and their properties.” Applied Physics Letters 78(24): 3824–3826 (2001).
Kittilstved, K. R. and D. R. Gamelin “Activation of high-T-c ferromagnetism in Mn2+-doped ZnO using amines.” Journal of the American Chemical Society 127(15): 5292–5293 (2005).
Sharma, P. et al. “Room temperature spintronicmaterial—Mn-doped ZnO revisited.” Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials 282: 115–121(2004).
Rao, C. N. R. and F. L. Deepak “Absence of ferromagnetism in Mn- and Co-doped ZnO.” Journal of Materials Chemistry 15(5): 573–578 (2005).
International Centre for Diffraction Data, 12 Campus Boulevard, Newtown Square, PA 19073–3273
http://database.iem.ac.ru/mincryst/
Poly Software International, P.O. Box 60, Pearl River, NY 10965, www.polysoftware.com
R.B. Von Dreele, A.C. Larson, www.ncnr.nist.gov/programs/crystallography/software/gsas.html Copyright Regents of University of California, 2001
WebElementsTM Periodic table (professional edition) http://www.webelements.com/
Brumage, W. H. et al. “Temperature-dependent paramagnetic susceptibilities of Cu2+ and Co2+ as dilute impurities in ZnO.” Physical Review B 6310(10): 104411 1–4 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noice, L., Seipel, B., Grathoff, G. et al. Structural Studies of ZnO Calcined with Transition Metal Oxides. MRS Online Proceedings Library 891, 1010 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-0891-EE10-10
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-0891-EE10-10