Abstract
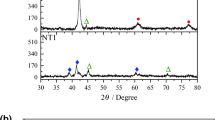
Despite many investigations on the corrosion behavior of NiTi shape memory alloys (SMAs) in various simulated physiological solutions by electrochemical measurements, few have reported detailed information on the corrosion products. In the present study, the structure and composition of the corrosion products on NiTi SMAs immersed in a 0.9% NaCl physiological solution are systematically investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), x-ray energy dispersion spectroscopy (EDS), and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). It is found that attack by Cl- results in nickel being released into the solution and decrease in the local nickel concentration at the pitting sites. The remaining Ti reacts with dissolved oxygen from the solution to form titanium oxides. After long-term immersion, the corrosion product layer expands over the entire surface and XPS reveals that the layer is composed of TiO2, Ti2O3, and TiO with relatively depleted Ni. The growth rate of the corrosion product layer decreases with immersion time, and the corrosion product layer is believed to impede further corrosion and improve the biocompatibility of NiTi alloy in a physiological environment. It is found that the release rate of nickel is related to the surface structure of the corrosion product layer and immersion time. A corrosion mechanism is proposed to explain the observed results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.A. Shabalovskaya Surface, corrosion and biocompatibility aspects of nitinol as an implant material. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 12, 69 (2002)
K.W.K. Yeung, W.W. Lu, K.D.K. Luk, K.M.C. Cheung Mechanical testing of a smart spinal implant locking mechanism based on nickel-titanium alloy. Spine 31, 2296 (2006)
T. Duerig, A. Pelton, D. Stockel An overview of nitinol medical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 273–275, 149 (1999)
F. Widu, D. Drescher, R. Junker, C. Bourauel Corrosion and biocompatibility of orthodontic wires. J. Mater. Sci.- Mater. M ed. 10, 275 (1999)
F.X. Gil, J.M. Manero, J.A. Planell Relevant aspects in the clinical applications of NiTi shape memory alloys. J. Mater. Sci.- Mater. M ed. 7, 403 (1996)
S.A. Shabalovskaya On the nature of the biocompatibility and on medical applications of NiTi shape memory and superelastic alloys. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 6, 267 (1996)
S.W. Robertson, R.O. Ritchie In vitro fatigue–crack growth and fracture toughness behavior of thin-walled superelastic nitinol tube for endovascular stents: A basis for defining the effect of crack-like defects. Biomaterials 28, 700 (2007)
S.A. Shabalovskaya, H. Tian, J.W. Anderegg, D.U. Schryvers, W.U. Carroll, J.V. Humbeeck The influence of surface oxides on the distribution and release of nickel from Nitinol wires. Biomaterials 30, 468 (2009)
N. Shevchenko, M.T. Pham, M.F. Maitz Studies of surface modified NiTi alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 235, 126 (2004)
W. Jia, M.W. Beatty, R.A. Reinhardt, T.M. Petro, D.M. Cohen, C.R. Maze, E.A. Strom, M. Hoffman Nickel release from orthodontic arch wires and cellular immune response to various nickel concentrations. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 48, 488 (1999)
W.M. Carroll, M.J. Kelly Corrosion behavior of nitinol wires in body fluid environments. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 67, 1123 (2003)
G. Rondelli Corrosion resistance tests on NiTi shape memory alloy. Biomaterials 17, 2003 (1996)
J.Q. Wang, N.X. Li, E.H. Han, W. Ke Effect of pH, temperature and Cl- concentration on electrochemical behavior of NiTi shape memory alloy in artificial saliva. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. M ed. 17, 885 (2006)
D.J. Wever, A.G. Veldhuizen, de J. Vries, H.J. Busscher, D.R.A. Uges, van J.R. Horn Electrochemical and surface characterization of a nickel–titanium alloy. Biomaterials 19, 761 (1998)
G. Rondelli, P. Torricelli, M. Fini, L. Rimondini, R. Giardino In vitro corrosion study by EIS of an equiatomic NiTi alloy and an implant quality AISI 316 stainless steel. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 79, 320 (2006)
X.J. Li, J.Q. Wang, E.H. Han, W. Ke Influence of fluoride and chloride on corrosion behavior of NiTi orthodontic wires. Acta Biomater. 3, 807 (2007)
B. Clarke, W. Carroll, Y. Rochev, M. Hynes, D. Bradley, D. Plumley Influence of nitinol wire surface treatment on oxide thickness and composition and its subsequent effect on corrosion resistance and nickel ion release. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 76, 61 (2006)
H.H. Huang, Y.H. Chiu, T.H. Lee, S.C. Wu, H.W. Yang, K.H. Su, C.C. Hsu Ion release from NiTi orthodontic wires in artificial saliva with various acidities. Biomaterials 24, 3585 (2003)
G. Rondelli, B. Vicentini Localized corrosion behavior in simulated human body fluids of commercial Ni–Ti orthodontic wires. Biomaterials 20, 785 (1999)
Y.C. Xin, K.F. Huo, T. Hu, G.Y. Tang, Paul K. Chu Corrosion products on biomedical magnesium alloy soaked in simulated body fluids. J. Mater. Res. 24, 2711 (2009)
M. Pourbaix Electrochemical corrosion of metallic biomaterials. Biomaterials 5, 122 (1984)
S.A. Shabalovskaya, J.W. Anderegg Surface spectroscopic characterization of TiNi nearly equiatomic shape memory alloys for implants. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 13, 2624 (1995)
M.H. Wong, F.T. Cheng, G.K.H. Pang, H.C. Man Characterization of oxide film formed on NiTi by laser oxidation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 448, 97 (2007)
C.L. Chu, T. Hu, S.L. Wu, Y.S. Dong, L.H. Yin, Y.P. Pu, P.H. Lin, C.Y. Chung, K.W.K. Yeung, Paul K. Chu Surface structure and properties of biomedical NiTi shape memory alloy after Fenton’s oxidation. Acta Biomater. 3, 795 (2007)
M.H. Wong, F.T. Cheng, H.C. Man In situ hydrothermal synthesis of oxide film on NiTi for improving corrosion resistance in Hank’s solution. Scr. Mater. 56, 205 (2007)
M.P. Seah Quantification of AES and XPS Practical Surface Analysis, Auger and X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Vol. 1, 2nd ed. edited by D. Briggs and M.P. Seah (John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, UK 1990)
R.C. Weast, M.J. Astle CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL 1982)
C.L. Chu, C.Y. Chung, P.K. Chu Surface oxidation of NiTi shape memory alloy in a boiling aqueous solution containing hydrogen peroxide. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 417, 104 (2006)
C.L. Chu, C.Y. Chung, Y.P. Pu, P.H. Lin Graded surface structure in chemically polished NiTi shape memory alloy after NaOH treatment. Scr. Mater. 52, 1117 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, T., Chu, C., Xin, Y. et al. Corrosion products and mechanism on NiTi shape memory alloy in physiological environment. Journal of Materials Research 25, 350–358 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2010.0051
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2010.0051