Abstract
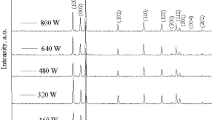
A microwave-hydrothermal process for the synthesis of crystalline zinc oxide powders has been developed in this study. Well-crystallized zinc oxide powders exhibiting different morphology, crystallinity, and particle size have been successfully prepared by controlling the process temperature and molarity of NH4OH in the starting solution. With increasing process temperature and NH4OH molarity during synthesis, the morphology of ZnO powders changes from flowerlike agglomeration to a well-developed rodlike shape. The band gap of ZnO powders increases with a decrease in the molarity of NH4OH during synthesis. Vacuum ultraviolet radiation (VUV) excited luminescence studies for ZnO powders reveal an excitation band at 161 nm possibly due to the absorption of O2- 2p electrons in the valence band. The VUV excitation band of ZnO powders observed at 161 nm will be useful for excitation of gas-discharged plasma display devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Natsume and H. Sakata: Electrical conductivity and optical properties of ZnO films annealed in hydrogen atmosphere after chemical vapor deposition, J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 12, 87 (2001).
K.B. Sundaram and A. Khan: Characterization and optimization of zinc oxide films by rf magnetron sputtering, Thin Solid Films 295, 87 (1997).
H. Ohta, M. Orita, M. Hirano and H. Hosono: Fabrication and characterization of ultraviolet-emitting diodes composed of transparent p-n heterojunction, p-SrCu2O2 and n-ZnO, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 5720 (2001).
M. Iwasaki, Y. Inubushi and S. Ito: New route to prepare ultrafine ZnO particles and its reaction mechanism, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 16, 1503 (1997).
H. Eilers and B.M. Tissue: Synthesis of nanophase ZnO, Eu2O3, and ZrO2 by gas-phase condensation with CW-CO2 laser-heating, Mater. Lett. 24, 261 (1995).
L. Znaidi, G.J.A. IlliaA. Soler, S. Benyahia, C. Sanchez and A.V. Kanaev: Oriented ZnO thin films synthesis by sol-gel process for laser application, Thin Solid Films 428, 257 (2003).
D. Jezequel, J. Guenot, N. Jouini and F. Fievet: Submicrometer zinc-oxide particles-elaboration in polyol medium and morphological-characteristics, J. Mater. Res. 10, 77 (1995).
D. Andeen, L. Loeffler, N. Padture and F.F. Lange: Crystal chemistry of epitaxial ZnO on (111) MgAl2O4 produced by hydrothermal synthesis, J. Cryst. Growth 259, 103 (2003).
C.H. Lu and C.H. Yeh: Influence of hydrothermal conditions on the morphology and particle size of zinc oxide powder, Ceram. Int. 26, 351 (2000).
S. Komarneni, R. Roy and Q.H. Li: Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of ceramic powder, Mater. Res. Bull. 27, 1393 (1992).
F. Bondioli, A.M. Ferrari, C. Leonelli, C. Siligardi and G.C. Pellacani: Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of nanocrystalline zirconia powders, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 2728 (2001).
H. Katsuki and S. Komarneni: Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of monodispersed nanophase alpha-Fe2O3, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 2313 (2001).
B.L. Newalkar, S. Komarneni and H. Katsuki: Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of barium titanate powders, Mater. Res. Bull. 36, 2347 (2001).
S. Komarneni, J.S. Komarneni, B.L. Newalkar and S. Stout: Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis of Al-substituted tobermorite from zeolites, Mater. Res. Bull. 37, 1025 (2002).
N. Kumada, N. Kinomura and S. Komarneni: Microwave hydrothermal synthesis of ABi2O6 (A = Mg, Zn), Mater. Res. Bull. 33, 1411 (1998).
T. Strachowski, E. Grzanka, B. Palosz, B. Presz, L. Slusarski and W. Lojkowski: Microwave driven hydrothermal synthesis of zinc oxide nanopowders, Solid State Phenomena 94, 187 (2003).
J. Zhong, A.H. Kitai, P. Mascher and W. Puff: The influence of processing conditions on point-defects and luminescence-centers in ZnO, J. Electrochem. Soc. 140, 3644 (1993).
H.J. Egelhaaf and D. Oelkrug: Luminescence and nonradiative deactivation of excited states involving oxygen defect centers in polycrystalline ZnO, J. Cryst. Growth 161, 190 (1996).
D.C. Look, C. Coskun, B. Claflin and G.C. Farlow: Electrical and optical properties of defects and impurities in ZnO, Physica B 340–342, 32 (2003).
L.X. Yi, Z. Xu, Y.B. Hou, X.Q. Zhang, Y.S. Wang and X.R. Xu: The ultraviolet and blue luminescence properties of ZnO: Zn thin film, Chin. Sci. Bull. 46, 1223 (2001).
Z. Fu, B. Yang, L. Li, C. Jia and W. Wu: An intense ultraviolet photoluminescence in sol-gel ZnO-SiO2 nanocomposites, J. Phys. Conden. Mater. 15, 2867 (2003).
Powder Diffraction File, Card No. 36–1451. International Center for Diffraction Data, Newtown Square, PA.
D. Chen, X. Jiao and G. Cheng: Hydrothermal synthesis of zinc oxide powders with different morphologies, Solid State Commun. 113, 363 (2000).
H.Y. Xu, H. Wang, Y.C. Zhang, W.L. He, M.K. Zhu, B. Wang and H. Yan: Hydrothermal synthesis of zinc oxide powders with controllable morphology, Ceram. Int. 30, 93 (2004).
U. Koch, A. Fojtik, H. Weller and A. Henglein: Photochemistry of semiconductor colloids preparation of extremely small ZnO particles, fluorescence phenomena and size quantization effects, Chem. Phys. Lett. 122, 507 (1985).
L. Spanhel and M.A. Anderson: Semiconductor clusters in the sol-gel process-quantized aggregation, gelation, and crystal-growth in concentrated ZnO colloids, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 113, 2826 (1991).
P. Hoyer and H. Weller: Size-dependent redox potentials of quantized zinc-oxide measured with an optically transparent thin-layer electrode, Chem. Phys. Lett. 221, 379 (1994).
G. Redmond, A. Okeeffe, C. Burgess, C. Machale and D. Fitzmaurice: Spectroscopic determination of the flat-band potential of transparent nanocrystalline ZnO films, J. Phys. Chem. 97, 11081 (1993).
V. Noack and A. Eychmuller: Annealing of nanometer-sized zinc oxide particles, Chem. Mater. 14, 1411 (2002).
H.C. Ong, A.S.K. Li and G.T. Du: Depth profiling of ZnO thin films by cathodoluminescence, Appl. Phys. Lett. 78, 2667 (2001).
C.S. Shi, Z.X. Fu, C.X. Guo, X.L. Ye, Y.G. Wei, J. Deng, J.Y. Shi and G.B. Zhang: UV luminescence and spectral properties of ZnO films deposited on Si substrates, J. Elec. Spect. Rel. Phen. 103, 629 (1999).
A.F. Kohan, G. Ceder, D. Morgan and Van C.G. Walle de: First-principles study of native point defects in ZnO, Phys. Rev. B 61, 15019 (2000).
S.A.M. Lima, F.A. Sigoli, M. Jafelicci Jr. and M.R. Davolos: Luminescent properties and lattice defects correlation on zinc oxide, Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 3, 749 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, CH., Hwang, WJ. & Godbole, S.V. Microwave-hydrothermal synthesis and photoluminescence characteristics of zinc oxide powders. Journal of Materials Research 20, 464–471 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0067
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0067